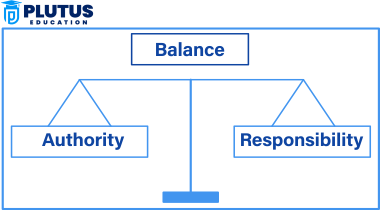
The authority and responsibility principle forms one of the major elements of classical management theory, driven by a balance between having the power to decide and the duty to accomplish assigned tasks. Authority and responsibility must go hand in hand. That is, the level at which a manager is authorized should be commensurate to the responsibility being placed upon that manager. Without this balance, effectiveness would clearly suffer by reducing efficiency in the organizations.
What is Authority?
Authority in management refers to right to influence people to get things done, issue commands, and allocate scarce organizational resources. It is the right of a person to command and thus forms an integral part of enforcing policies, guiding subordinates, and ensuring the smooth running of business activities. The source of authority can be derived from a position within an organization or from the attributes of a manager.

Types of Authority
There are several types of authority in management, each serving a unique role in the organizational hierarchy:
- Line Authority: This is a direct type of authority that allows the line manager to lead and guide his or her subordinates in the chain. It is the power to decide directly how to advance the goals of the organization.
- Staff Authority: Staff authority refers to advising and assisting the line manager. Staff specialists, such as HR or finance specialists, are advisory but are not controlling operations.
- Functional Authority: The staff members are vested with such types of authority over their activities related to specialization, like the authority of the human resource department in enforcing company-wide policies on recruitment.
- Delegated Authority: If a superior grants authority to the subordinates to carry out specific tasks on behalf of them, then such authority would come into the category of delegated authority.
Pros & Cons of Authority
While authority is necessary for organizational control, it brings both advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Clear Hierarchy: It ensures stability in the organization because it will have a clear chain of command.
- Efficient Decisions: It enables managers to make decisions quickly and on sound judgment.
- Imposition: Authority ensures that policies and objectives are followed.
Cons:
- Abuse of Power: If unchecked, authority may lead to misuse of power.
- Over-centralization: Concentrating too much authority at higher levels can slow decision-making at lower levels.
- Employee Dissatisfaction: Excessive control can reduce employee morale and creativity.
What is Responsibility?
Responsibility is the duty of one person to perform assigned duties and be held responsible for the resultant outcome. In management, responsibility is more than doing the work. Rather it also requires accountability on behalf of one’s performance as well as their team’s performance. Responsibility cannot be delegated like authority because the one in charge of the task must bear accountability for whether the task was successful or unsuccessful.

Why is Responsibility Principle of Management Important?
The responsibility principle of management is crucial because it makes managers and employees responsible for their actions. Discipline is enhanced, and problems get solved more efficiently through the principle, as tasks are performed as the organization expects them to be. A lack of direct responsibility leads to confusion among people and inefficiency.
- Accountability: Since responsibility has been created, the direct relation between responsibility and the accomplishment of a task brings accountability.
- Motivation: Once people learn what is expected of them, they tend to work more efficiently to get things done.
- Organizational Control: Defining responsibilities gives organizational managers a handle on controlling organizations to facilitate an alignment toward company goals.
Relation Between Authority and Responsibility
What is known as the most significant relationship concerning the balance of power between authority and responsibility ensures that managers are highly empowered but also accountable. For there to be efficiency in an organization, these two must balance.
- Balanced Power: Managers must have enough authority to fulfill their responsibilities but not so much that they act unilaterally without accountability. A revenue target sales manager, for example, would need authority to hire sales staff as well as authority for designing sales strategies and for budgetary allocations.
- Delegation: Delegation is passing responsibility along with authority. One can delegate tasks, and along with it, there must be enough authority transferred to the subordinate so that the task is completed. However, the manager is held responsible for the task’s success.
- Chain of Command: Clarity in the chain of command would ensure that all will know their roles, the limitations of their authority, and the scope of responsibility. This alignment avoids confusion and ensures a smooth sense of working within the organization.
Differences Between Authority and Responsibility
| Aspect | Authority | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Right to command and make decisions | Obligation to perform assigned tasks |
| Delegation | Can be delegated | Cannot be delegated |
| Purpose | To enforce policies and ensure compliance | To achieve specific organizational objectives |
| Scope | Broader, impacts decision-making | Narrower, focused on task completion |
| Accountability | Limited to the extent of delegated authority | Full accountability for task outcome |
Authority and Responsibility FAQs
What happens if a manager has more responsibility than authority?
If a manager has more responsibIf a manager has more responsibility than authority, they may struggle to perform tasks effectively because they lack the power to make necessary decisions.
How can authority be misused in an organization?
Authority can be misused if managers make decisions that benefit themselves rather than the organization, or if they overstep their power without taking responsibility.
What is the difference between authority and accountability?
Authority is the right to command, while accountability is the obligation to answer for the outcomes of assigned responsibilities.
Can responsibility be delegated?
No, responsibility cannot be delegated. Even if a task is delegated, the original person remains responsible for the outcome.
What is functional authority in management?
Functional authority is a type of authority granted to a staff member over specific functions, usually related to their area of expertise, to ensure consistency across the organization.


