A bank overdraft is a transaction in which the owner of an account withdraws more than is available in the account, leaving the account balance negative. A facility to lend the client money up to an agreed overdraft limit to bridge shortfalls is often granted to individuals and businesses to accommodate short-term needs or unexpected expenses.
Bank overdraft is perhaps one of the most used financial instruments by individuals and businesses. The bank covers the deficit that occurs when the account holder spends more than his balance in his account, up to an agreed limit. In fact, this facility can be construed as a short-term loan, enabling businesses to manage cash flow effectively, or individuals to deal with unexpected expenses. On top of these extra fees, it charges interest on this excess amount. Therefore, to care for finances wisely, one must learn about the features, types, and implications of a bank overdraft.
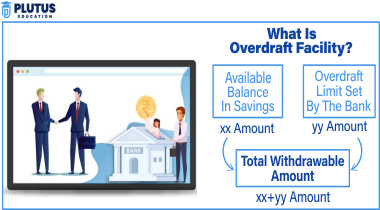
What is Bank Overdraft?
A bank overdraft refers to an overdraft facility a bank offers to the account holder, meaning when checking the account balance it would be possible to withdraw excess money that is available on the account. If such an account falls below zero, then technically means an account holder has “overdrawn” his account. Banks offer such facilities to people as well as companies. For example, to cover short-term financial gaps, cover emergency expenses, or supplement the cash flow of businesses.
- Overdrafts are normally approved by the bank in advance; however, sanctions come with a cost.
- The bank will only charge interest on the amount in excess and only for the period the overdraft extends to.
- In addition to interest, some overdrafts might have a fee or charge for each overdraft transaction.
Example
Consider a scenario where a business holds ₹10,000 in its account but needs to make a payment of ₹15,000. With an overdraft facility, the bank will allow the payment, leading to a negative balance of ₹5,000. The business would then need to repay the overdrawn amount along with applicable interest.

Features of Bank Overdraft
1. Pre-approved limit: The bank will only allow you to overdraw up to a certain amount. This is determined by the type of account, financial stability, and even the relationship with the bank.
2. Interest on Overdrawn Amount: An overdraft is the best facility for short-term loans, which is the main reason that it is used quite frequently by companies to maintain their working capital or even for individuals to face short-term expenses such as medical or marriage ceremonies.
3. Revolving Credit Facility: Unlike loans, where interest is charged on the total amount borrowed, an overdraft has interest accrual only on the amount used, and for the period it remains outstanding.
4. No Fixed Repayment Schedule: Overdraft facility with a bank A bank overdraft is considered to be a revolving credit facility. After you pay the amount withdrawn, you can draw within the limit if the facility is active.
5. No Fixed Repayment Schedule: There would be generally no fixed repayment schedule for overdrafts. The account holder can pay the amount in parts or fully as funds are available.
6. Charges: Along with interest, there may be service charges, for example, an annual charge for the maintenance of overdraft facilities, processing fees for every overdraft transaction, and penal charges for exceeding the overdraft limit.
7. Short-Term Loans: An overdraft is the best facility for short-term loans, which is the main reason that it is availed quite frequently by companies to maintain their working capital or even for individuals to face short-term expenses such as medical or marriage ceremonies.
Types of Bank Overdrafts
Understanding the types of overdrafts can help customers choose the right one according to their needs:
Secured Overdraft
In the case of a secured overdraft, an overdraft facility is granted by a bank from the borrower’s account that requires collateral such as fixed deposits or property. In case the borrower fails to repay the overdraft, the security is used from the collateral. The interest rate is generally lower in secured overdrafts because it involves less risk for the bank.
Unsecured Overdraft
An unsecured overdraft does not need collateral. This type is issued mainly due to the creditworthiness of the borrower, past banking relationship, or monthly income in the case of individuals. Unsecured overdrafts normally come with higher interest rates because they pose a higher risk to the bank.
Business Overdraft
The overdraft is frequently used by corporations to manage cash flows as well as finance everyday operations. In most cases, the banks will take into consideration how the company operates regarding its assets and, in general, its position concerning overdraft arrangements. In some cases, it can be either secured or unsecured depending on the specified overdraft type.
Personal Overdraft
A personal overdraft can usually be obtained, although, in general, this will be linked to the salary or savings account. It is mainly used to bridge shortfalls for personal expenditures, such as bills or other unforeseen emergencies.
Overdraft Protection
Some banks also offer an overdraft protection facility, wherein the money from another linked account, such as the savings account, would automatically be used if there were cases where the transactions exceeded the balance in the checking account and, thus, no overdraft fee at all.

Secured vs. Unsecured Overdraft
| Feature | Secured Overdraft | Unsecured Overdraft |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral Required | Yes | No |
| Interest Rates | Lower | Higher |
| Risk for Bank | Lower | Higher |
| Eligibility | Based on collateral value | Based on creditworthiness |
Advantages of Bank Overdraft
- Flexibility: Draw as much or as little as you need up to the approved limit, and repay when possible.
- Interest on Usage: You pay interest only on an overdraft, only on the amount by which you are overdrawn, and for such time the overdraft is outstanding.
- Quick Access to Funds: The overdraft facility is always available given that it is pre-approved, hence offering quick access to funds when needed.
- No Need for Loan Application: Overdrafts eliminate the need to apply for a new loan every time cash is required.
- Cash Management of Short-Term Business Needs: It enables the business to manage any short-term cash flow problems and not incur long-term debt.
Disadvantages of Bank Overdraft
- High Interest: While you pay interest on only the used sum, the overdraft rates are generally higher than for other kinds of loans.
- Extra Costs: Most banks charge overdraft fees for overdraft protection, transaction charges for every overdraft, or penalties for exceeding the limit.
- Temporary Solution: The overdraft has to be only a short-term solution but not a long-term financial strategy.
- Risk of Over-Dependency: Overreliance on overdraft facilities might be indicative of bad financial management and is likely to impair credit scores if not used judiciously.
Conclusion
A bank overdraft is therefore an excellent way for individuals and organizations to meet short-term cash needs. Having flexibility attached to immediate access to available funds, however the costs of overdrafts, especially in terms of interest rates and fees should be controlled. The overdrafts should be used cautiously by its user, with regard to the fact that it is to supplement some financial gap rather than a permanent loan mechanism.
Bank Overdraft FAQs
What is a bank overdraft facility?
A bank overdraft facility allows an account holder to withdraw more than their available balance, up to a pre-approved limit. This overdraft acts as a short-term loan with interest charged on the amount overdrawn.
How is interest calculated on a bank overdraft?
Interest on a bank overdraft is calculated only on the amount used and for the period it is outstanding. The rate varies depending on whether the overdraft is secured or unsecured.
What is the difference between a secured and unsecured overdraft?
A secured overdraft requires collateral such as property or fixed deposits, and generally has a lower interest rate. An unsecured overdraft, on the other hand, does not require collateral but usually carries higher interest rates.
Can I be charged a fee for using an overdraft?
Yes, apart from interest, banks may charge additional fees such as overdraft protection fees, transaction fees for each overdrawn amount, and penalties for exceeding the overdraft limit.
Is overdraft protection necessary?
Overdraft protection can be useful if you frequently run low on your account balance, as it helps avoid overdraft fees by automatically transferring money from a linked account to cover shortfalls.


