The characteristics of management help us understand what management means in day-to-day business. Management is not just about giving orders or being the boss. It is a process where people work together to achieve goals using available resources. Management brings planning, organization, leadership, and control into one smooth process. The word “management” may sound simple, but it involves many tasks like setting goals, building teams, solving problems, and making the best use of time and money. The characteristics of management show how this process works in every organization, whether it is a big company like Tata, a school, a hospital, or even a home business. Management helps achieve goals through planning and teamwork. It brings people together to work in the same direction. It focuses on results. It also includes adjusting actions when things go wrong.
Meaning of Management
Management is getting things done with and through people to achieve desired goals. It includes planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Management is not limited to business. It is used in schools, hospitals, homes, factories, and daily life.
Management ensures that people work together in an organized way. It helps avoid confusion and waste of time. It gives a clear direction to the team. Whether a company is big or small, proper management helps it grow faster and work better.
For example, they do management work when a restaurant manager plans the weekly menu, assigns staff duties, and checks the kitchen stock. The characteristics of management help us understand this role more deeply.
Nature of Management
Before understanding the characteristics, we must understand the nature of management. Nature tells us what management is like and how it behaves in real-world situations.
Management Is a Universal Activity
You will find management in every field—business, school, office, home, and government. Every place that involves work and people uses some form of management.
For example, a school principal manages teachers, students, and daily operations. A hospital administrator manages doctors, nurses, and patient services.
Management Brings Order and Discipline
When people work in groups, things can get messy. Management helps avoid chaos. It gives the work structure, properly divides tasks, and maintains discipline. It also ensures that people follow rules and timelines.
Management Is Both a Science and an Art
Like science, management uses facts, figures, and rules. It studies human behaviour, work systems, and time control. Like art, it uses creativity and personal skills. A good manager can inspire the team, solve problems, and make wise decisions.
So, the nature of management is practical, flexible, and found in all parts of life.
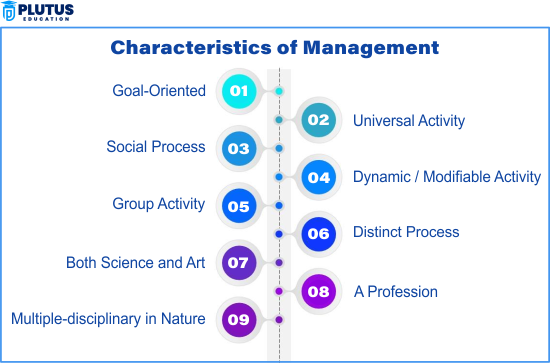
Characteristics of Management
The characteristics of management help us understand what management means in day-to-day business. Management is not just about giving orders or being the boss. It is a process where people work together to achieve goals using available resources. Management brings planning, organization, leadership, and control into one smooth process.
Management Is Goal-Oriented
The first important feature of management is that it always works towards goals. No matter the size of an organization, the aim is to reach specific results.
Goals Give Direction to Work
Every business wants to earn a profit, grow its customer base, improve quality, or become more efficient. Management helps reach these goals by planning each step and ensuring employees work in the same direction. If goals are not clear, efforts go to waste. Management sets clear targets for all departments.
For example, a company may set a goal to increase sales by 20% in the next 6 months. Managers will plan, guide, and support their teams to reach this target.
Helps in Measuring Success
Management uses goals to measure performance. When managers know the target, they can compare it with actual results. If there is a gap, they can take action to fix it. This keeps the organization on track.
So, the goal-oriented nature of management keeps everyone focused and motivated.
Management Is a Continuous Process
Management is not something you do once and forget. It is an ongoing process. Managers have to plan, act, check, and improve constantly.
Activities Never Stop
In any business, managers plan for the next day, even before the current day ends. New problems come up every day. People leave, prices rise, customers change. So, managers have to keep updating plans and actions.
For example, in a retail store, a manager must adjust inventory weekly. In a school, the principal reviews performance every month. This shows that management is always working behind the scenes.
Involves Constant Adjustment
Management adjusts according to changes. A manager changes team members if someone is not performing. They shift plans if goals are not met. This process goes on all the time.
So, management as a continuous process means it keeps moving like a cycle without stopping.
Management Is All-Pervasive
This characteristic means that management is used in every kind of organization. It is not limited to companies. You can also find it in homes, schools, hospitals, and government offices.
Present in All Fields
Whether business, education, health, or public service, every place needs proper planning, leadership, and control. A school principal, a hospital administrator, and a bank manager perform management tasks.
For example, a household budget is also a form of management. Parents plan expenses, control spending, and guide children. This shows that management is all-pervasive.
Common Principles Everywhere
Even if the setting is different, the management principles remain the same. You need to plan, organize, lead, and control everywhere. So, learning management skills can help you succeed in any job or life role.
This universal nature of management proves its value in daily life.
Management Is a Group Activity
Management is never done alone. It involves people working in teams to reach goals. One person may guide, but success needs teamwork.
Involves Coordination
Managers have to work with staff, partners, clients, and suppliers. They link the efforts of people in different roles. They create teams and keep communication clear.
For example, the manager coordinates a restaurant’s chefs, servers, and suppliers. This helps deliver the best service to customers. Without coordination, the business cannot run.
Encourages Team Spirit
Good managers build trust and help people work together. They solve conflicts and keep everyone focused on the same goal. They make every person feel important.
This proves that management is a group activity where results come from the efforts of many.
Management Is a Dynamic Function
This feature shows that management does not always work in the same way. It changes with the business world. Managers must stay alert and ready to act when new changes happen.
Adjusts to Changes in the Environment
A manager changes the marketing plan if a new competitor enters the market. If a new law affects costs, the manager changes the budget. If technology improves, the manager trains the team again.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, schools switched to online classes. Hospitals made special arrangements. Managers played a key role in all this.
Makes Organizations Flexible
When management is dynamic, the organization becomes flexible. It learns to survive in tough times. It takes advantage of new opportunities.
So, management as a dynamic function helps the organization stay strong and wise in a changing world.
Management Is Multi-Dimensional
Management is not just about people. It also deals with work, time, tools, money, and machines. It covers many areas at the same time.
Deals with Work, People, and Operations
A manager plans what work to do, how, and who will do it. They check the work’s quality and ensure everyone follows the schedule. They also manage machines, raw materials, money, and tools.
For example, a factory manager simultaneously looks after staff, production lines, safety, and customer deadlines. This shows that management is multi-dimensional.
Balances Different Resources
Management makes sure no resource is wasted. It uses everything in the best way. It balances speed with quality, cost with comfort, and risk with safety.
This skill makes management very valuable in every industry.
Management Is a Science and an Art
Management is both a science and an art. This is one of the most interesting characteristics of management. It includes rules, principles, skills, and experience.
Management as a Science
Like science, management has its theories, methods, and principles. These are tested, proven, and applied in real situations. Examples include principles of planning, motivation, or division of work.
Management follows:
- Observation (studying how companies work)
- Experiments (trying new ideas in business)
- Cause and effect (if teamwork improves, results improve)
Just like physics or chemistry, management uses facts and logic.
Management as an Art
At the same time, management involves personal skills, creativity, and experience. Every manager solves problems differently. A good manager knows how to motivate people, build strong teams, and make the right decisions at the right time.
An artist paints using colours and feelings. A manager builds success using leadership, communication, and decision-making.
So, management is a science because it uses rules and an art. After all, it needs personal skill.
Management Involves Coordination
Coordination means bringing all parts of the work together in a smooth way. It is one of the most central characteristics of management. Every manager must coordinate between people, tasks, tools, and goals.
Helps Avoid Confusion
When many people work on a project, they must know their roles. The manager assigns work and checks progress. If someone needs help, the manager supports them. This avoids delay, waste, or errors.
For example, the planner, decorator, and caterer must work as one team in an event management company. The manager links them all.
Connects All Departments
A company has many departments—marketing, sales, finance, HR, and production. If they do not share updates or data, they cannot succeed. The manager coordinates them through meetings, reports, and goals.
Coordination helps save time, reduce mistakes, and increase results.
Characteristics of Management FAQs
Q1. What are the main characteristics of management?
The main characteristics include goal orientation, continuous process, teamwork, coordination, and science and art.
Q2. Why is management called a continuous process?
Because managers must plan, monitor, and improve every day. The work never stops. It keeps changing and improving all the time.
Q3. How is management a science and an art?
Management is a science because it uses theories and principles. It is an art because it requires creativity, experience, and human skills.
Q4. What is the nature and characteristics of management?
The nature of management is to guide people and resources toward goals. Its characteristics include planning, teamwork, leadership, and coordination.
Q5. Is management needed only in big businesses?
No. It is needed in every organization. Even a small shop, school, or home needs smooth management.
Q6. What does goal-oriented mean in management?
This means that management always works to achieve the best results. There is always a target, whether it is profit, growth, or quality.
Q7. Can a person manage without a team?
No. Management is a group activity. It needs people to plan, act, and succeed together.


