The role of expenditure in the financial management of individuals and organizations cannot be overlooked. Whether you are managing your family’s household budget or preparing the financial statement for a multinational corporation, understanding how to classify expenditures is crucial for accurate record-keeping, budgeting, and analysis. Expenditure refers to money spent or costs incurred for any particular purpose. It can include both tangible costs, for example, purchasing goods and services, and intangible costs such as depreciation or interest payments.
Expenditure Meaning
Expenditure describes the use of money spent or resources used to satisfy the need for certain goods and services. It is a reflection of how financial resources are utilized, and it can be classified into different categories based on purpose, nature, and the time of its occurrence. Generally, expenditure is an outlay of funds from an organization, government, or individual to achieve various needed requirements.
Understanding expenditure is crucial for businesses and governments since it aids cash flow management, planning for future costs, and performance tracking. It also helps with strategic decisions on the appropriate mix of capital investment and operational spending.
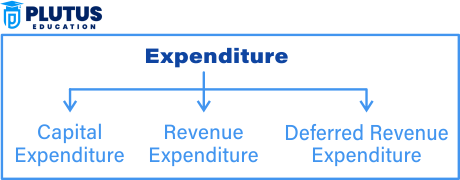
Expenditures are typically categorized into various classifications depending on the purpose and nature of the transaction. Such classifications can broadly be categorized as:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
- Revenue Expenditure (RevEx)
- Deferred Revenue Expenditure
Classification of Expenditure in Accounting
In accounting, expenditure is classified into three major categories:
- Capital Expenditure
- Revenue Expenditure
- Deferred Revenue Expenditure
Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure refers to the money an organization spends on acquiring, improving, or maintaining fixed assets, such as property, equipment, or buildings. The regular nature of such expenditures means that these are investments that will benefit the company for a long period. This can be from purchasing machinery to constructing a new office building or even the acquisition of land for future development.
Characteristics of Capital Expenditure
- Long-Term Benefit: The impact of capital expenditure is long-lasting, and it benefits the business over several years.
- Asset Creation: CapEx is often associated with the creation or acquisition of assets that have a useful life of more than one year.
- Impact on Balance Sheet: Capital expenditures are reflected in the balance sheet as fixed assets rather than on the income statement.
Capital expenditures are essentially linked to the formation of fixed assets. Therefore, they are charged as assets on the balance sheet and costs incurred are depreciated or amortized over time. This enables businesses to spread out the financial impact of large investments and to match the expense with the benefits derived from those assets.
Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expense is that expense spent on behalf of the day-to-day operations of a business. These generally possess a short-term nature and are considered as required for asset maintenance. As opposed to capital expenditure, revenue expense does not generate new long-term assets. It is incurred to maintain existing current assets and support operations in progress. Some examples include utility, wages, and raw materials.
Characteristics of Revenue Expenditure
- Short-Term Benefit: The benefits derived from revenue expenditure are typically consumed within the current financial period.
- Operational Costs: It is incurred as part of the normal operations of the business.
- Impact on Income Statement: Revenue expenditures are recorded on the income statement as expenses, which directly reduce the company’s net profit for the period.
Revenue expenditures are important in running smooth day-to-day business activities. They do not create long-term assets, meaning they are completely written off in the financial year in which they have been incurred. However, regular revenue expenditure is necessary to continue running business operations and for fixed assets to work effectively, like machinery or buildings.
Deferred Revenue Expenditure
Deferred revenue expenditure is said to be the one that has been incurred and for which benefits are not being received immediately. Instead, it spans over many years. The whole purpose of deferring the expenditure is to match the cost of the revenue that will occur in the future.
Characteristics of Deferred Revenue Expenditure
- Delayed Benefit: This type of expenditure will have a benefit in the future, but not within the current financial period.
- Long-Term Allocation: It is amortized over the years, as its benefits are realized over a longer time frame.
- Impact on Income Statement: Deferred revenue expenditures are gradually written off in the income statement over the years, usually based on the time frame that matches the benefits derived from the expense.
The expenditure of deferred revenue includes the costs of marketing associated with launching a new product or large-scale advertising programs. The business expends funds in its current period, but the benefit takes many years. The expenditure is therefore considered a deferred item and spread over several periods.
Difference Between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
The difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure is important for accounting purposes since this determines the presentation of financial statements, including their tax treatment. Both types of expenditures are essential to the business, but they differ in purpose, and their recording in the financial statements is different.
| Aspect | Capital Expenditure (CapEx) | Revenue Expenditure (RevEx) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To acquire, improve, or extend fixed assets | To meet the day-to-day operational costs |
| Benefit Duration | Long-term, benefits last more than one year | Short-term, benefits consumed within the current period |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Recorded on the balance sheet as assets, depreciated over time | Recorded on the income statement as expenses, deducted from revenue |
| Examples | Purchasing land, machinery, vehicles, or buildings | Salaries, rent, utilities, and repairs on existing assets |
Practical Example:
For instance, if a firm buys a new factory building for $2 million, then this is capital expenditure. This is because it is an investment with benefits over many years. Spending $100,000 on repairing existing equipment in a firm would fall within revenue expenditure simply because it is spent on repairing equipment to keep it working but without lengthening its life or even creating new assets.
In short, capital expenditure relates to acquisition or addition to long-term assets and revenue expenditure relates to any regular running of the business and is immediately reflected in the profit and loss account.
Adam Smith’s Classification of Public Expenditure
The famous economist Adam Smith made tremendous contributions towards the understanding of public finance and government expenditure. In his work, The Wealth of Nations, Smith identified three major types of public expenditure that a government may incur. His classification was based on the purpose and nature of the spending.
Smith’s Three Classifications of Public Expenditure
- Expenditure for Defense: The government must spend a significant portion of its revenue on the defense and security of the nation. This includes expenditures related to the army, navy, and other defense infrastructure.
- Expenditure for Justice: Smith argued that public spending should be allocated towards maintaining law and order. This includes funding for courts, police services, and legal frameworks necessary for justice.
- Expenditure for Public Infrastructure: Smith recognized the importance of public investments in infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and canals, to promote economic development and facilitate trade.
These classifications by Adam Smith highlighted that government expenditure is not arbitrary but is meant to fulfill the basic functions required for the smooth operation of society. Public expenditure, according to Smith, should align with the needs of defense, justice, and public infrastructure, ensuring societal stability and growth.
Classification of Expenditure FAQs
What is the main difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure?
The primary difference is that capital expenditure involves spending on assets that will provide long-term benefits, like machinery or buildings, while revenue expenditure involves spending on daily operational costs that are consumed within the current financial period.
What is deferred revenue expenditure?
Deferred revenue expenditure refers to expenses that have been incurred but will not provide immediate benefits. These costs are spread over a number of years. For example, large-scale advertising campaigns that benefit the company over several years.
Why is it important to classify expenditure?
Classifying expenditure helps in budgeting, financial planning, and tax reporting. It also ensures accurate financial statements and aids in making better strategic decisions for resource allocation.
How does Adam Smith classify public expenditure?
Adam Smith classified public expenditure into three categories: defense (for national security), justice (for law enforcement and legal systems), and public infrastructure (for roads, bridges, and public services).
What are examples of revenue expenditure?
Examples of revenue expenditure include rent, salaries, utility bills, and repairs on existing equipment. These costs are necessary for the business’s day-to-day operations.