When dealing with finance and accounting, professionals often cross paths when choosing to go for a CMA or CFA. Career goals determine the credentials between the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) and Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). CMA focuses on management accounting, where information is built for internal consumption by an organization and strategic financial management, making it a principal global qualification for graduates looking to secure high-paying jobs in corporate structures. Nevertheless, the CFA has a good reputation because it has a strong focus on investment management and financial analysis, and this can be ideal if you want to specialize in portfolio management or investment banking. Knowing the significance of comprehending these differences will allow you to make an informed decision that is appropriate for your career goal.
CMA vs CFA: Key Differences
The CMA (Certified Management Accountant) and the CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) are two top financial certifications that serve their particular career pathways. The CMA highlights management accounting and strategic financial management within companies. In contrast, the primary focus of CFA is investment analysis & portfolio management in the context with more relation to capital markets.
| Aspect | CMA (Certified Management Accountant) | CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Management accounting, strategic financial management | Investment analysis, portfolio management, financial markets |
| Target Roles | Corporate finance, management accounting, financial planning | Investment banking, portfolio management, financial analysis, advisory roles |
| Certification Body | Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) | CFA Institute |
| Number of Exams | Two parts: Part 1 (Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control) and Part 2 (Financial Decision Making) | Three levels: Level I (Knowledge and comprehension), Level II (Application and analysis), Level III (Synthesis and evaluation) |
| Work Experience Requirement | Two years in management accounting or financial management roles | Four years of relevant work experience in investment decision-making |
| Exam Duration | Each part of the CMA exam is 4 hours long | Each level of the CFA exam is 6 hours long |
| Preparation Time | Typically 1-2 years | Typically 3-4 years |
| Cost | Generally lower overall cost compared to CFA | Higher overall cost due to multiple levels and required materials |
| Global Recognition | Well-recognized for internal corporate roles globally | Highly recognized worldwide, particularly in investment and finance sectors |
| Core Competencies | Cost management, financial planning, internal controls, strategic management | Investment analysis, asset valuation, portfolio management, ethical and professional standards |
What is CMA?
US CMA, or Certified Management Accounting, is a professional certificate that provides people with the capability to handle strategic corporate and financial accounting procedures for a firm. This certification is recognized worldwide and is awarded by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) in the US.
The US CMA designation has experienced a strong increase in demand in the last few years. This growth is not specific to India alone but is noticed all over the world, thus it is a sought-after certification among finance professionals. The CMA course structure is carefully planned to address all critical areas of organizational accounting, enabling professionals to obtain critical financial information and provide recommendations to their employers, thus enabling sound financial decision-making at the organizational level. The US CMA qualification is esteemed as one of the premier management accounting credentials worldwide, acknowledged in major regions including China, India, the UK, Canada, and the Middle East.
CMA Eligibility
To start the journey of CMA certification, one should have done 12th grade. To get certified, one needs to have a Bachelor’s degree along with two years of professional work experience. Furthermore, one must obtain membership from the IMA.
US CMA Course Structure
The CMA examination is divided into two parts, each encompassing six subjects that focus on different areas of management accounting:
| Part | Subjects |
| CMA Part 1 | Financial Reporting |
| Planning, Budgeting, and Forecasting | |
| Performance Management | |
| Cost Management | |
| Internal Controls | |
| Technology and Analysis | |
| CMA Part 2 | Financial Statement Analysis |
| Corporate Finance | |
| Decision Analysis | |
| Risk Management | |
| Investment Decisions | |
| Professional Ethics |
The structured approach to both theoretical and practical aspects of management accounting in the CMA curriculum ensures that certified professionals are well-prepared to meet the challenges of the financial world and add value to their organizations.
What is CFA?
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) is a high-level certification desired by finance professionals across the globe. Targeting finance professionals who are interested in investment management, financial analysis, and portfolio management, the CFA program is famous for being demanding and versatile in its applications in the field of finance. Backed by its vast coverage of knowledge, the CFA program is an excellent option for professionals looking to take their careers to the next level in finance.
The CFA charter is internationally recognized, with charterholders employed in various financial hubs across the world including the USA, India, Hong Kong, Canada, and the UK. The charter not only opens up international career opportunities but also provides competitive edges in the employment arena. Even a partial qualification in the CFA program (e.g., clearing one or two levels) can substantially improve a candidate’s job prospects and salary potential, particularly when taken together with other qualifications such as CA, ACCA, or an MBA. This wide acceptance speaks to the CFA charter’s status as a gold standard in finance and investment analysis.
CFA Eligibility
The eligibility requirements for CFA program are simple. Prospective candidates can apply to sit for the Level 1 exam if they are graduating in their last year of undergraduate school or will do so within 23 months. Others with a minimum of four years of related professional experience may also be eligible to start the certification process, even without a bachelor’s degree. This is an open-door policy that makes the designation accessible to a broad pool of candidates.
CFA Course Structure
The CFA program is structured across three levels, each culminating in a rigorous exam that candidates must pass to advance:
- CFA Level 1: Emphasizes foundational knowledge and understanding with a high focus on investment tools.
- CFA Level 2: Has a focus on application and analysis, with more emphasis on asset valuation.
- CFA Level 3: Places emphasis on synthesis and evaluation, with a focus on portfolio management and wealth planning.
| Topics | CFA Level 1 | CFA Level 2 | CFA Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethical and Professional Standards | Basic Understanding | Higher Depth and Application | Integrated Ethics |
| Quantitative Methods | Fundamental Techniques | Advanced Analysis | Portfolio Applications |
| Economics | Basic Concepts | Detailed Application | Global Analysis |
| Financial Reporting and Analysis | Basic Analysis | Complex Valuations | Synthesis and Evaluation |
| Corporate Finance | Introductory | Advanced Decisions | Senior Management Decisions |
| Equity Investments | Basic Concepts | Detailed Valuation | Portfolio Management Focus |
| Fixed Income | Basic Instruments | Advanced Risk Analysis | Portfolio Strategies |
| Derivatives | Introductory | Complex Strategies | Risk Management Techniques |
| Alternative Investments | Overview | Specialized Sectors | Portfolio Inclusion and Risk |
| Portfolio Management & Wealth Planning | Basic Management | Detailed Strategies | Holistic Management |
CMA and CFA Salary in India
If you are reflecting on the financial repercussions of doing a CMA or CFA, consider potential earning post-delirium. Given these individuals’ skills in management accounting and financial strategic planning, many will typically find work as a corporate finance or accounting CMA enjoying competitive salaries. CFAs are, in contrast, more relevant for roles that require a deeper understanding of financial markets and investment strategies- such as investment management or financial analysis/ advisory, where they can demand higher salaries due to the edge their advanced designation gives them over less specialized professionals. CFAs usually have lower average salaries than CPAs, but certain career fields, such as investment banking or portfolio management, pay much more for the CFA. The average salary of CFA in India is around Rs. 6.84 LPA, and the salary of CMA in India is around Rs. 5.72 LPA.
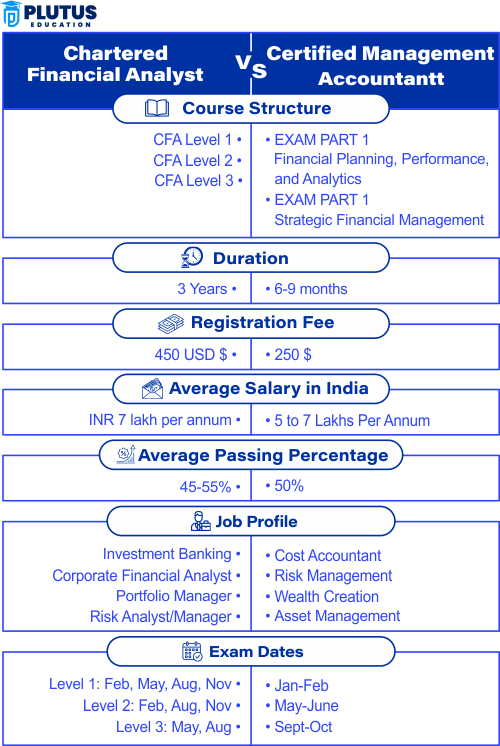
CMA and CFA in India
CFA and CMA qualifications are highly regarded in their respective fields and can lead to better career prospects for those who earn them. The CMA (Certified Management Accountant). The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) is a widely respected certification in India. CMA is the best professional certification for those who want expertise in management accounting and financial strategy, as it ensures you are proficient in cost management, internal controls & strategic planning, i.e., crucial concepts that a corporate finance firm might be seeking.
In India, where financial markets and investment are on the rise, it is also the most needed thing to have (CFA). CMAs and CFAs are designed to support different career paths—in general, the CMA is for internal corporate roles, while the CFA is more focused on investment/financial analysis. Regarding the difficulty level, CMA is often considered less challenging than the CFA due to its narrower focus and fewer levels. However, the CFA’s extensive coverage and multi-level structure generally make achieving it more difficult and time-consuming.
CFA vs CMA Which One To Choose?
Both certifications would seem useful in a financial career, but which one you want depends on where you see yourself going. The CMA is designed for those wanting to focus on the aspects of management accounting and strategic decision-making within organizations. In contrast, the CFA Program has a specific niche concerning investment analysis/financial markets. Both certifications provide a useful skill set and lead to different career opportunities, depending on where you fit in your passion or career motives.
CMA and CFA FAQs
What is the main focus of the CMA compared to the CFA?
The CMA focuses on management accounting, strategic planning, and internal controls, ideal for those working within companies. In contrast, the CFA emphasizes investment analysis, portfolio management, and financial markets, catering to careers in finance and investment.
Which certification is more suited for a career in investment banking?
The CFA is generally the preferred choice for investment banking careers due to its in-depth coverage of financial analysis, investment strategies, and market principles. It is well-regarded in roles related to portfolio management and financial advisory.
How long does it typically take to earn each designation?
The CMA can usually be completed within 1 to 2 years, depending on your study pace and exam schedule. The CFA typically takes longer, with most candidates taking about 3 to 4 years to pass all three levels of exams and meet the work experience requirements.
What are the key differences in exam content between CMA and CFA?
CMA exams concentrate on management accounting, financial planning, and decision support, focusing on practical business scenarios. The CFA exams cover a broad range of topics in financial analysis, ethics, and quantitative methods, with a strong emphasis on investment theory and practice.
Is one certification more valuable than the other in the job market?
The value of each certification depends on your career goals. The CMA is highly regarded for roles in corporate finance and management accounting. At the same time, the CFA is prestigious for investment management and financial analysis, often being more sought after in investment-related fields.