Consumer rights and responsibilities in India are becoming crucial to have a fair and transparent environment in today’s dynamic marketplace. With the rising tide of consumerism, it is important to know the rights attached to being a consumer so that one knows how to avoid exploitation and, more importantly, make informed decisions. The consumer protection laws in India, like the Consumer Protection Act 1986 and the new 2019 Act, put an individual on a pedestal while also holding a corporate responsibility. The consideration goes to constitutional consumer awareness; merely knowing one’s rights doesn’t suffice; one should be alert for unethical business practices, know how to file consumer complaints in India, and understand one’s responsibilities as a consumer in a growing economy.
What are Consumer Rights?
Consumer rights refer to the legal entitlements that protect buyers from unfair trade practices. These rights ensure that every Indian citizen can make purchases safely, confidently, and with full information. Consumer rights matured over the years such that all persons can consume products and services of superior quality, have full information available, and be presented with a resolution to resolve any dispute that may ensue.
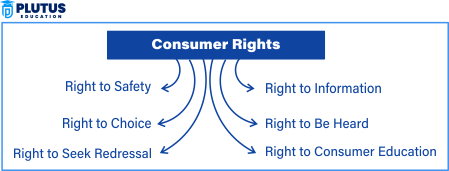
Right to Safety
The right to safety safeguards consumers against hazardous products. This right protects your health and well-being, especially concerning food products, electronics, or medicines. Goods and services mainly protect consumers from danger and harm. It guarantees that the products meet the safety standards laid down by the government, especially concerning health impacts with respect to food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. Consumers have the right to know of any hazards posed to them and to stop using any product that poses a risk to life or health.
Right to Information
Under this right, consumers must be informed about product price, quality, usage, and safety standards. Hidden clauses or misleading advertisements violate this crucial consumer right. The consumer should get all the important details related to the product or service available for purchase. Information available should be relevant to price, quality, content, safety aspects, or proper use of a commodity/service. The label and any form of advertising also provide an essential aspect of that right. Failure to deliver correct information or risk, which may go unrevealed, would fall as a breach of the consumer’s rights.
Right to Choose
From many options, consumers can freely choose without being subjected to monopoly pressure. The Consumer Protection Act prohibits any trade practices that restrict choices. The right to choose emphasizes that consumers should be given alternatives between products and services to satisfy their needs and preferences. Monopolies and any manner of unscrupulous conduct aimed at depriving consumers of choice are outlawed. The consumer is given alternatives without undue pressure from any ardent or aggressive marketing scheme aiming to coerce the consumer into a purchase.
Right to Be Heard
This consumer grievance redressal mechanism ensures your voice matters. Platforms like consumer courts in India allow you to raise complaints and seek justice. This right allows consumers to be heard in respect of grievances and complaints they have with regard to any product or service. Consumer grievances are not neglected, and the government in India has established consumer courts and forums to which consumers can present their complaints and get redress for any wrongdoings done by businesses.
Right to Seek Redressal
When there is a defective product or poor service, one can ask for a refund or compensation; the right even gives legally available avenues for redress to be made by customers in the event that the defect causes injuries or damage. Consumers have the entitlement to replacement, refund, or compensation in the event that a product is defective or if a service is rendered poorly. Additionally, the right ensures that businesses account for the substandard goods offered to consumers.
Right to Consumer Education
This right is publicized through campaigns and added to the teachings at school. That tends to say a well-informed person cannot be easily scammed by any misleading advertisement. Consumer education is one of the rights that provides an individual with knowledge of rights and responsibilities. It really empowers him to make the right choices and not to fall prey to the exploitation of others or to consume unethically. It will also assist them in learning how to use products properly and effectively and where and how they may report complaints.
What are Consumers’ Responsibilities?
Consumer responsibilities have been defined as the responsibilities consumers must perform to make ethical, informed, and reasonable purchasing decisions. Just as businesses are responsible for providing safe products and truthful information to the consumer, consumers, too, should act responsibly and protect the fairness of the marketplace.
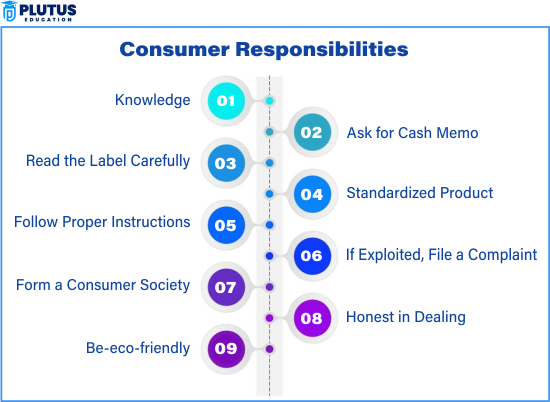
Responsibility to Be Informed
Consumers must research products, read labels, and compare prices. An informed consumer is less likely to make poor or emotional decisions. It includes the responsibility to be informed that consumers have a role and duty to educate them about the product being bought. This incorporates all the research on that particular product, reading through all the labels and instructions regarding how to use the correct approach. An informed consumer means being free from misunderstandings or wrong assumptions and results of deciding out of correct knowledge. Thereby, this responsibility seems pertinent in areas such as health and safety since the wrong usage of a particular item can cause serious negative repercussions.
Correct Usage Responsibility
Appropriate usage instructions and safety guidelines should be respected. Any misuse of a product puts the consumer at risk for his or her damages but may also constitute cause for rejection of a legitimate complaint. The consumer should read the instructions provided by the manufacturer and apply the product per the intended application. For instance, if one does not follow safety precautions while using a product in a manner that is not recommended, that will result in accidents or mishaps, for which the customer would be fully liable. Proper use also encompasses handling, storage, and disposal of products in such a way as to minimize any substantial harm being done to the environment.
Reporting Faults
Notify the seller or manufacturer when you find defects. Filing consumer complaints in India helps maintain product quality and benefits other buyers. The onus of reporting the fault of a product to the manufacturer or seller lies on the consumer. This upgrades the quality of products and spares other consumers from problems similar to that faced. Filing a formal complaint or seeking redressal ensures that businesses are liable and their product and service offerings are constantly upgraded.
Responsibility to Avoid Wastage
It is discouraged to consume goods and services in excess. Practising an ethical consumption behaviour is choosing, if possible, environmentally friendly products. Consumers are to make decisions that should be sustainable and environmentally friendly. It includes avoiding overconsumption, not buying anything when not necessary, and using resources like water, electricity, and fuel since this responsible consumption saves the environment for future generations and helps businesses that adopt the practices of sustainability.
Responsibility to Seek Redressal
Don’t hesitate to approach consumer forums or district consumer courts if your rights are violated. The consumer has a responsibility to seek redressal if they have problems with defective products or unsatisfactory services. This means that complaints should be filed with the consumer courts or consumer protection agencies. The consumer redresses his problem and, at the same time, contributes to maintaining standards in the marketplace.
Consumer Awareness
Consumer awareness refers to the consumer’s understanding and awareness of their rights and responsibilities and how the market operates. It prevents exploitation in a changing market; thus, it impacts a choice.
Importance of Consumer Awareness
Consumer awareness is important to protect people against unfair trade practices and fraudulent activities. It empowers consumers to make decisions based on factual product knowledge and price. An aware consumer contributes to a marketplace which is fair, ethical, and transparent.
Protection from Exploitation
Awareness is a shield against fraud, unreal discounts, and misleading advertisements. Consumer awareness equips them to resist fraud, misleading advertisements and other detrimental business practices. They will also know their rights, can contest such practices and not be exploited.
Informed decision-making
Knowing your rights enables smarter, value-for-money purchases, especially in sectors like e-commerce or online marketplaces. The right knowledge will enable consumers to make better purchasing decisions on product quality, price, and safety standards. Consumer awareness will ensure no individual is misled by marketing gimmicks or misinformation, hence wiser choices that suit needs.
Promoting Ethical and Responsible Consumption Awareness
Awareness encourages buying from ethical companies and supports businesses with sustainable practices. It not only serves the interests of the individual consumer but also encourages consumption on a larger scale that is responsible and ethical. The informed consumer is more likely to opt for products that are ethically produced and environmentally friendly. This is sure to ensure the health of the market and the environment at large.
Consumer Protection in India
The Consumer Protection Act 1986, along with the amendment in 2019, provides the backbone of consumer rights for all consumers in India. Strong enough to safeguard interests relating to consumers, these comprise:
- Consumer courts at district, state, and national levels.
- It establishes their rights and seller responsibilities.
- Impose penalties upon unfair practices of trade.
These areas are new and include e-commerce, deceptive advertising, and product liability. The recovery of money or goods can take place after legal procedures regarding the discrediting practices of some businesses. This calls for the idea that firms are required to respond on time to such complaints and consumer grievances openly.
Consumer Protection Laws in India: CPA 1986 & CPA 2019
The Consumer Protection Act of 1986 was India’s first formal attempt to protect buyers. In 2019, it was amended to include:
- Consumer Dispute Redressal Commissions (CDRCs) at district, state, and national levels
- Inclusion of e-commerce, misleading ads, and product liability
- Time-bound resolutions and e-filing options
Consumer Rights and Responsibilities FAQs
1. What are the six consumer rights in India?
Consumer Rights are The Right to Safety, to Information, to Choose, to Be Heard, to Redressal, and to Consumer Education. Consumerism refers to a system implemented under the Consumer Protection Act for receiving consumers’ rights.
2. What is the retail legislative act of 2019?
It is a law that protects a person’s interest as a consumer. There is coverage on e-commerce and liability regarding products, and there will be established consumer courts to address grievances.
3. Where is consumer complaint registered in India?
Consumers can register their complaints online at edaakhil.nic.in or visit consumer courts in their locality. They should carry their proof of purchase and document of the product with them.
4. What are the key responsibilities of consumers?
With being a consumer, one is entrusted to be informed, to follow the instructions regarding usage, and to report any complications, avoid wastage, and claim whenever required.
5. Why must consumers be informed?
An advantage in preventing exploitation, buying better products, and enforcing fair and ethical consumer market practices.


