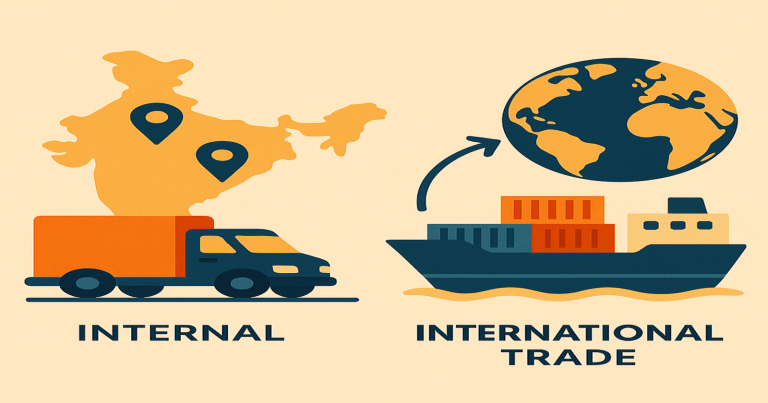
Trade means buying and selling goods or services. People trade to earn money, grow businesses, and meet needs. Trade happens every day. Some trade happens between people inside one country and some between people from different countries. These two kinds of trade are called internal trade and international trade.
The difference between internal and international trade is very important to understand. Internal trade happens only inside the borders of a country. It uses the same money and follows one government’s rules. For example, when a farmer in Punjab sells wheat to a bakery in Delhi, that is internal trade. But when India sells rice to Nepal or buys oil from Saudi Arabia, that is international trade. International trade happens between two or more countries. It uses different amounts of money and follows many rules.
What is Internal Trade?
Internal trade means trade that happens only inside the country. All buyers and sellers live in the same nation. Goods do not cross any international borders. This type of trade follows the same currency, tax rules, and government policies. It is also known as domestic trade or inland trade.
This kind of trade happens daily across cities, villages, and states. It can be small or large but always occurs within the country. For example, a milk producer in Gujarat selling milk to a sweet shop in Rajasthan is part of internal trade.
Types of Internal Trade
1. Local Trade
Local trade happens within the same town or city. For example, a vegetable seller in Bhopal sells to households nearby. This trade needs less transport and is very common in daily life. People buy groceries, clothes, and basic goods from nearby shops. This helps local sellers earn income and supports small businesses.
2. Inter-State Trade
This trade happens between different states. For example, onions grown in Maharashtra are sold in West Bengal markets. This trade uses trucks, trains, or courier services. It moves goods across long distances inside the country. Interstate trade supports farmers, industries, and transport workers.
Features of Internal Trade
- Same Currency: People only use Indian rupees. No currency exchange is needed.
- One Law: Only Indian trade rules apply.
- Low Risk: No foreign risk like war, price changes, or shipping delays.
- Fast Movement: No customs or border delays, so goods travel quickly.
- No Import Duties: The government doesn’t charge customs on internal goods.
Internal trade helps small businesses, farmers, and traders earn income. It also helps goods reach areas where they are needed, keeping the supply steady and prices fair across the country.
What is International Trade?
International trade happens when countries buy or sell goods and services. It is also called foreign trade or global trade. In this type, the buyer and the seller live in different countries. The goods cross borders. The money used is also different. The trade must follow two or more sets of laws.
For example, when India sells cotton to Bangladesh or buys computers from the USA, this is international trade. This trade is more complex than internal because of more documents, foreign exchange, customs duties, and longer delivery times.
Types of International Trade
1. Import
When a country buys goods from another country it is called import trade. Example: India imports oil from Gulf countries.
2. Export
When a country sells goods to another country it is called export trade. Example: India exports tea and spices to Europe.
3. Entrepot Trade
This happens when a country imports goods and then re-exports them after some changes. Example: Singapore imports crude oil, refines it, and exports it.
Features of International Trade
- Different Currencies: Trade may use dollars, euros, or other money.
- Two or More Governments Involved: Each country has its own rules.
- Customs Duties Apply: Taxes are paid when goods cross borders.
- Documents Needed: Shipping bills, invoices, export-import license, etc.
- Takes Time: Shipping, customs clearance, and approvals take longer.
International trade helps countries earn foreign exchange, get products they don’t make, and expand their industries. It also connects countries and makes the world more global.
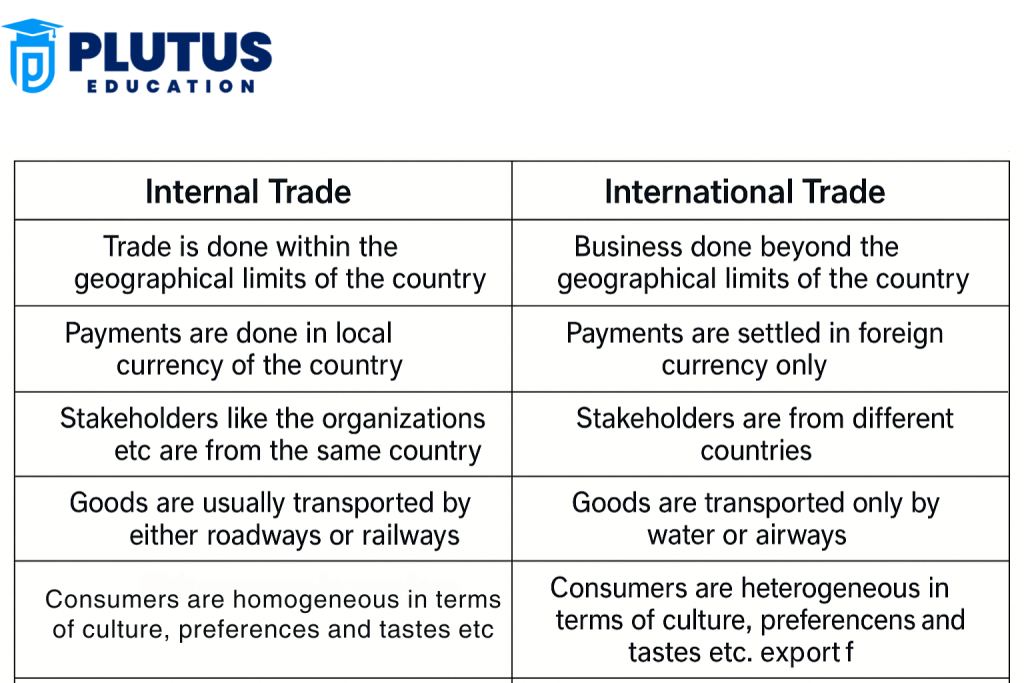
Difference Between Internal and International Trade
Internal and international trade are both important for the economy, but they work very differently. Internal trade is simple. It happens inside one country. Everyone follows the same law, uses the same money, and pays the same taxes. Goods move fast, and no customs are needed. On the other hand, international trade is more complex. It happens between countries. It involves different rules, foreign currencies, longer travel time, and extra costs like customs duties and shipping charges.
| Point of Comparison | Internal Trade | International Trade |
| Geographical Area | Happens within the same country | Happens between two or more countries |
| Currency Used | Uses the same national currency (e.g., Indian Rupee) | Uses different currencies (e.g., INR, USD, Euro) |
| Laws and Rules | Follows one set of local or national laws | Follows laws of both countries and global trade rules |
| Taxes and Duties | Includes local taxes like GST | Includes customs duties, export and import taxes |
| Transport Methods | Uses roads, railways, and local cargo services | Uses sea routes, air cargo, and international shipping |
| Time Taken | Goods are delivered quickly | Takes longer due to customs and international logistics |
| Paperwork Required | Requires simple invoices and local transport papers | Requires shipping bills, customs forms, export-import licenses |
| Cost Involved | Transport and handling cost is low | Shipping, taxes, insurance, and customs increase cost |
| Risk Level | Risk is low as it stays within one country | Risk is high due to currency change, political issues, and border delays |
| Example | Selling cotton from Gujarat to Tamil Nadu | Exporting cotton from India to Japan |
Importance of Internal Trade
Internal trade plays a big role in keeping a country’s economy strong and active. It connects producers and consumers from different states and cities. It also creates millions of jobs for drivers, sellers, shopkeepers, and factory workers.
- Keeps Economy Moving: Internal trade helps goods move from one part of the country to another. For example, vegetables grown in Punjab can be sold in markets in Assam. This movement of goods makes sure that no region runs short of basic items. It also helps the economy work smoothly every day.
- Creates Jobs: When goods move across states, many people get jobs. Truck drivers, warehouse workers, loaders, and shopkeepers earn from this process. Even small delivery boys earn through internal trade. So, this kind of trade supports many families in the country.
- Improves Income: Farmers and factory owners can sell their goods to other states, which gives them more buyers and better prices. When they earn more, they can invest in better tools, machines, or seeds, which improves their business and daily lives.
- Connects States: Internal trade helps build strong links between different regions. North India can sell wool, while South India can sell spices. This kind of connection increases friendship between states and helps people understand each other better. It also spreads culture and language.
- Reduces Wastage: Perishable items like milk, fruits, and vegetables spoil fast. Internal trade helps move them quickly to nearby cities. This reduces food waste and gives people fresh items. It also allows farmers to earn instead of throwing unsold produce.
Benefits of International Trade
International trade plays a significant role in a country’s growth. It brings in foreign money, builds global relations, and gives people access to many new things. Here are the full benefits, explained clearly.
- Earns Foreign Exchange: When a country sells goods to another country, it earns money in dollars, euros, or other foreign currencies. This foreign exchange helps the government pay for imports and repay debts. It also builds a substantial economic reserve for future needs.
- Imports Needed Items: Not every country can produce everything it needs. India imports oil, machines, and medicines that are unavailable or too costly to make here. International trade helps get these items easily from countries that produce them in large quantities.
- Improves Products: When local companies compete with foreign products, they try to improve their quality. They add new features, offer better designs, and use new technology. This makes goods better for buyers and also helps local brands grow stronger.
- Creates Jobs: Many people get jobs due to export activities. Workers in factories, employees at ports, staff in logistics companies, and customs agents all earn from international trade. As trade grows, more jobs are created in big cities and small towns.
- Builds Relations: Trade is not just about money; it also builds friendship between countries. When nations trade more, they talk, share ideas, and sign agreements. This helps in solving global problems together and keeping peace in the world.
Difference Between Internal and International Trade FAQs
1. What is the main difference between internal and international trade?
Internal trade happens within a country using the same currency and rules. International trade happens between countries and uses foreign money and extra rules.
2. Why is internal trade easier than international trade?
Internal trade uses local transport, the same money, and fewer documents. So, it is faster and cheaper than trading between countries.
3. What are some examples of international trade?
Exporting spices to Europe, importing oil from the Gulf countries, and selling tea to America are all examples of international trade.
4. How does international trade help India?
It brings foreign currency, gives jobs, improves technology, and makes Indian products famous worldwide.
5. Can a country grow without international trade?
A country may survive on internal trade, but international trade helps it grow faster, earn more, and be part of the global Economy.