In the fast-paced world of logistics and consumer goods, the terms packing and packaging often get intertwined, yet they refer to very different functions. While both are essential in the product life cycle, their purposes, applications, and end goals diverge sharply. A significant aspect of packing is applying protection on the products during transportation and storage. Meanwhile, packaging brings out the glorious product to attract the consumer, communicate the brand value, and make it one piece of critical information. Understanding these differences makes it very viable to streamline operations in such a way as to touch retail experience improvement and much more – it is the passion of commerce students, strategists, and ultimately all supply chain professionals.
What is Packing?
Packing involves sealing or enclosing items using protective materials such as bubble wrap, foam sheets, corrugated boxes, or pallets. These materials act as safety against external forces that may harm the product. For example, in the case of electronic goods, items are surrounded by anti-static foam and tightly packed in boxes under the condition that they prevent movement during transit. Such care will create less chance of a return case, keeping product integrity and ensuring customer satisfaction upon delivery.
Purpose of Packing in Businesses
Packing performs very fundamental logistical functions, which include the safe delivery of products. Also, packing helps companies meet particular regulatory compliance requirements, especially in industries where the safety of products is bound by law, such as pharmaceuticals or food. Apart from compliance, good packing practice also reduces breakage rates, operational losses, and the financial impacts of refunds and replacements. Brick-and-mortar retailers are able to amplify their packing efforts with the addition of tamper-evident seals as a method of e-commerce packing to add another layer of assurance to customer trust.
What is Packaging?
Packaging is the act of designing and enclosing products in an outer layer that is pleasing to the eye and informative. This may range from a box of chocolates enhanced by gold accents to a minimalist tube of toothpaste designed with a low drain on the environment. It is the packaging that introduces and almost sells the product to the customer; hence, it is directly to nurture branding, communication, and customer experience.
Role of Packaging in Marketing
Packaging gives a strategic advantage in the marketing of listed products and not only communicates attention but also provides brand recognition and expresses trust. On a shelf, a product has a few seconds to appeal to a potential buyer — in most cases, it is packaging that seals the deal. Brands use colour psychology, font choices, material texture, and innovative designs to lead a particular perception of a product. Besides, transparent and compliant labelling earns consumer trust as it brings ingredient safety and use into the open.
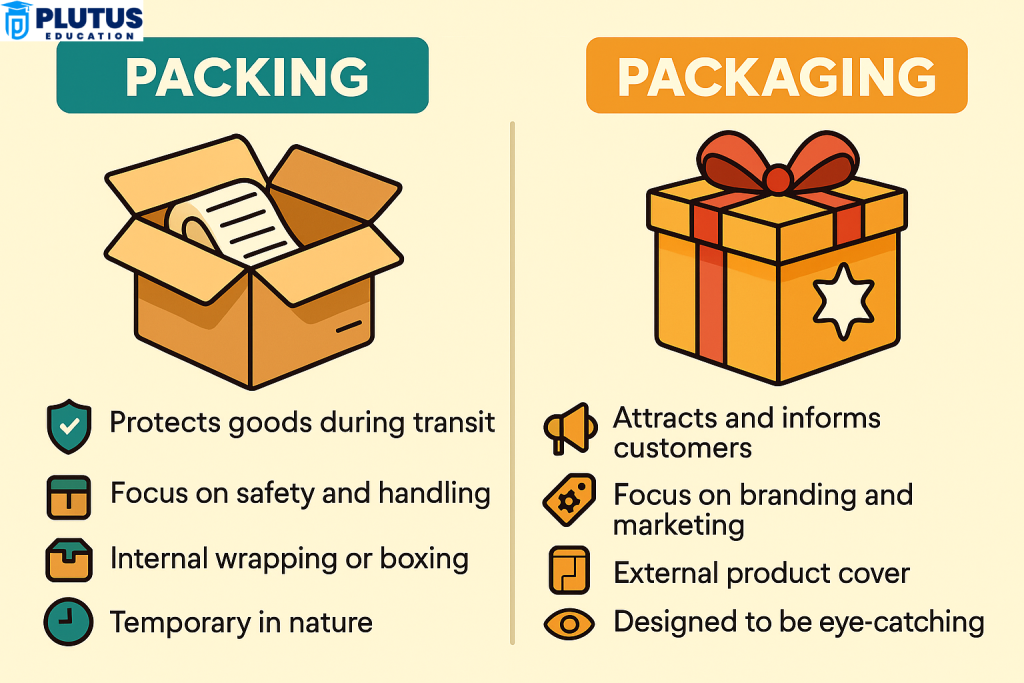
Difference Between Packaging and Packaging
Packing and packaging may have certain interlinks in their physical appearance at times; their objective and consumer interaction differ in their strongest sense. Each understanding in its sphere facilitates businesses to compartmentalize their resources better to enhance both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Functional Focus
Packing is concerned strictly with safety and logistics, particularly keeping the product intact through external stress. Products in packing first consider the perspective of warehouse handlers and delivery logistics. Packaging protects while also promoting. It is this dual role of packaging — to appeal to the customer and to provide information — that combines to give it a larger scope and a more complex form.
Consumer Interaction
Consumers do not take any note of packing as it is basically thrown away before they actually receive the product. What interacts with consumers is packaging, which is felt, seen, and therefore judged by them. Readers read nutritional information or admire the design of a product, and their experience with packaging directly influences their trust and subsequent behaviours.
Impact on Branding
By design, packing is unbranded and caters purely to the essentials. Packaging, on the other hand, has great significance as an element of the brand identity. It frequently contains visual elements like logos, taglines, the colour of the brand, and other distinctive features for easy identification of the product. Packaging consistency will aid in brand recall and loyalty-building over time.
| Aspect | Packing | Packaging |
| Definition | The process of wrapping or securing products to protect them during transit or storage. | The process of designing and enclosing a product in a consumer-facing, branded container. |
| Primary Objective | Protection from damage, breakage, leakage, or environmental exposure. | Attracting consumers, enhancing product appeal, and communicating brand information. |
| Function in Supply Chain | Supports logistics, warehousing, and safe delivery of goods. | Supports marketing, branding, legal compliance, and consumer experience. |
| Interaction Level | Minimal or no interaction with the end consumer. | High interaction; directly visible and handled by the customer. |
| Material Used | Bubble wrap, foam inserts, crates, stretch film, pallets, corrugated boxes. | Product boxes, cartons, labels, tubes, pouches, cans, glass bottles with branding elements. |
| Customization | Rarely customized beyond fit and durability. | Highly customized in color, shape, design, material, and information. |
| Visibility to Customers | Usually not seen by the customer (removed before delivery or display). | Always visible to the customer as part of the buying and unboxing experience. |
| Legal Requirements | Governed by logistics or safety regulations for transportation (esp. hazardous goods). | Must comply with labeling laws, ingredients disclosure, expiry, batch number, etc. |
| Use Case Example | Palletizing multiple units of goods for warehouse storage or shipping. | A cereal box with brand design, nutritional facts, and QR code for offers. |
| Impact on Brand Perception | None. Focused only on functionality. | Major. It influences brand identity, trust, and buying behavior. |
| Cost Factor | Focused on durability and volume efficiency — generally low cost per unit. | Higher investment due to design, printing, sustainability, and consumer targeting. |
| Role in E-commerce | Ensures safe last-mile delivery; includes tamper-proof seals and padding. | Creates the unboxing experience, influences reviews, and encourages repeat purchases. |
| Contribution to Sales | Indirect — by preventing product damage and customer dissatisfaction. | Direct — packaging can increase conversion rates and encourage impulse buying. |
| Environmental Concern | Focus on using recyclable or reusable shipping materials. | Increasing shift toward sustainable, biodegradable, or zero-waste packaging. |
| Department Responsible | Handled by logistics or warehouse teams. | Managed by branding, marketing, or product design departments. |
Types of Packing and Packaging
The methods of packing and packaging, as well as the materials used, may vary significantly from product to product, depending on the particular product itself, along with its fragility, target market, and mode of delivery. Packing and packaging are two sides of the same coin when it comes to enclosing a product, but they differ in what they aim to achieve. While packing is more concerned with the protection and efficiency of the item, packaging considers its appeal and communication. Knowing the types of packing and packaging will help determine how they can best be used together by businesses for optimum servicing.
Types of Packing Materials
Packing material would be chosen primarily for its quality of being safe at extremes. Cardboard boxes have the frame and resilience to hold their contents securely, while bubble wrap protects delicate things from getting damaged. Other packing materials, or rather accessories with regard to bulk shipping, include wooden crates, stretch film, and shrink wraps, which are usually used to stabilize and protect the cargo. The choice of materials will depend mainly on the item’s weight, shape, fragility, and shipping environment.
Types of Packaging
Packaging exists in layers: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary packaging is in direct contact with the product, like a milk carton or a toothpaste tube. Secondary packaging is used to group several units, often for retail convenience, such as a box containing multiple tubes of toothpaste. Tertiary packaging is used for transporting large quantities, such as shipping boxes or crates. Each layer plays a role in protection, presentation, and product handling.
Real-Life Examples of Packing and Packaging
The distinction between packing and packaging becomes clearer when observed in real-world scenarios across different industries. From online shopping to food delivery and retail display, both elements work together to ensure a seamless product journey.
E-commerce Deliveries
When a customer orders a laptop online, the product arrives in a sleek, branded box with model details and warranty information — that’s the packaging. However, this box is placed inside a sturdy cardboard carton, cushioned with foam or air pillows to absorb transit shocks — that’s the packing. Both are necessary to deliver a secure and satisfying unboxing experience.
Pharmaceutical Products
Medicine tablets are often packaged in blister packs with critical dosage and expiry information, meeting regulatory labeling standards. These blister packs are then packed in cardboard boxes to prevent contamination and facilitate bulk shipment to hospitals or pharmacies. Packaging serves the consumer, while packing supports distribution.
Food Products
A chocolate bar is beautifully wrapped in a colorful, branded foil — this is the packaging that attracts consumers to a store. For transport to multiple retail outlets, these bars are then packed in large cartons or boxes. The outer cartons ensure the product remains undamaged during handling and delivery.
The Business Significance
Packing and packaging have two different, yet equally important, functions in any business. While packing deals with the logistics and operational aspects of delivery, it is the job of packaging to deal with marketing, brand perception, and consumer loyalty for a product. They build the most important pillars to establish a successful product strategy.
Why Packing Matters?
Packing protects the product against damage, hence lower return rates and operational losses. In industries where the goods travel a long distance or are roughly handled, well-planned packing can satisfy the customers and meet the rules stipulated by governmental laws. In international shipping, packing is to meet specific standards to avoid penalties and ensure smooth clearance through customs.
Why Packaging Matters?
Packaging is a brand ambassador: it represents the brand to the consumer and often shapes the consumer from the beginning concerning how the product will be used. An attractive package will invoke curiosity, provide value, and create a memory. In the context of e-commerce today, where the touch and feel of products are minimal, good packaging is transformed mainly into social media content, reviews, and, ultimately, repeat purchases. Brands that are serious about the future and have customer-centred approaches invest in developing sustainable and creative packaging solutions.
Difference Between Packing and Packaging FAQs
What is the core difference between packing and packaging?
Packing is focused on protection during transit and storage, while packaging is focused on presentation, marketing, and consumer communication.
Is packaging still necessary if the product is already packed?
Yes. Packing protects the product from damage; packaging informs and attracts the customer. Both have separate functions and are equally important.
Can the same material serve as both packing and packaging?
Sometimes, yes. For example, a branded corrugated box may serve both purposes, but its design will need to balance strength with visual appeal.
Does packaging really influence customer buying behaviour?
Absolutely. Eye-catching and informative packaging can directly impact purchase decisions by instilling trust and creating a positive first impression.
Are there legal rules for packaging and packing?
Yes. Especially in pharmaceuticals, food, and hazardous goods, both packing and packaging must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure consumer safety and regulatory compliance.


