Differences are seen majorly between the objectives, source of funding, and management in public and private sector organizations. Such knowledge about the differences has been useful in that it enables people to appreciate how both sectors play different roles in the economy and, more so, have their respective impacts on society. The article exhaustively covers differences by considering all aspects in a structured form.
Difference Between Public and Private Sector
Public and private sector entities differ in ownership, funding sources, objectives, operational flexibility, and accountability. Here’s an in-depth comparison covering the critical differences between these two sectors.
| Aspect | Public Sector | Private Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned and operated by the government | Owned and operated by private individuals or organizations |
| Objective | Provide services for the public good | Generate profit for stakeholders |
| Funding | Primarily funded through taxpayer money | Funded through private investments and profits |
| Accountability | Accountable to the public and government | Accountable to owners, shareholders, and customers |
| Regulation | Highly regulated with strict guidelines | Less regulated, more flexibility in operations |
| Risk-taking | Limited due to public scrutiny and accountability | High, as profits depend on risk and innovation |
| Example Industries | Healthcare, education, public transportation | Technology, finance, retail, manufacturing |
What is Public Sector?
Organizations owned and run by the government are known as the public sector. It is a system that exists to provide services to the public in the most accessible and affordable way possible without giving too much importance to profits. Public sector organizations include health care, education, law enforcement, and infrastructure development. These are significant to the welfare of society. Since they are funded through tax revenue, such organizations are accountable to the government and eventually to the people.
Characteristics of Public Sector
- Government Ownership: The public sector institutions are wholly or fully owned by the government.
- Focus on Public Welfare: The services are sometimes subsidized to be made affordable.
- Non-Profit-Oriented: Not mainly focused on making a profit, unlike the private sector.
- Funding and Accountability: Funded through the government budget and taxes; audited for public accountability.
Examples of Public Sector Organizations
- Education and Healthcare: Public universities and government hospitals aim to provide affordable services.
- Public Transportation: Railways, buses, and metro systems are run for public utility, not for profit maximization.
What is Private Sector?
Private persons or corporations own the private sector. Its objective is to earn profits without the constraints of strict political control as seen in the public sector. Instead, its performance is more in line with private owners and shareholders because its financial success depends much on efficiency, innovation, and market competitiveness. It can grow the economy by encouraging jobs, developing new technology, and supplying products or services to satisfy the wants of consumers.
Characteristics of Private Sector
- Private Ownership: Owned and managed by the individual or corporation.
- Profit Motive: Motivated by maximizing profit, which is channeled towards growth and market share.
- Funding and Flexibility: Funded by private investments and revenues. Hence more flexibility in decision-making.
- Innovation and Competition: The emphasis on innovation and competition to survive in the market.
Examples of Private Sector Organizations
- Technology and Finance: Tech firms like Apple and Google innovate to capture market share.
- Retail and Manufacturing: Companies like Walmart and Toyota are driven by profit and market demand.
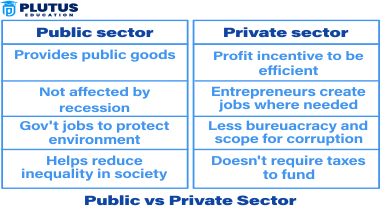
Key Differences: Public vs Private Sector
Each sector has unique characteristics that affect how they operate and serve the community. Below is a more detailed look at some specific differences:
Ownership and Control
- Public Sector: This sector is completely or largely controlled by the government. Political considerations will affect their decision, and decisions will be based on public-interest policies.
- Private Sector: Owned and controlled by a private individual or a group of individuals. It follows market forces while ensuring a customer’s needs with reasonable profit.
Funding and Financial Support
- Public Sector: Funded by taxes and, in a few instances, government bonds. Budgetary allocation relies on government priorities and political agendas.
- Private Sector: Funded by private investors, banks, or retained earnings. Funding depends on profitability and the availability of access to capital markets for the generation of funds.
Accountability and Transparency
- Public Sector: Very transparent; at times, they are compelled to publish detailed financial information in public and to the government.
- Private Sector: Mostly responsible to shareholders and other private investors; fewer compulsions for disclosure, more so among privately held companies.
Goals and Objectives
- Public Sector: The purpose is social welfare and public service, not profit. Low-cost services, stability, and resolution of social issues are the objectives.
- Private Sector: The objective is profit maximization followed by growth and market share.
Decision-Making Process
- Public Sector: Tends to be much slower due to the pace of bureaucracy and much higher oversight.
- Private Sector: Agile and often faster to react to changes in markets, etc.
Conclusion
The public and private sectors complement each other in the society. The public sector deals with essential services, while the private sector innovates and grows the economy. The unique functions, goals, and challenges that characterize each sector provide insights into their contributions to the economy.
Public and Private Sector FAQs
What is the difference between public and private sector jobs?
Public sector jobs are typically government-funded and focus on serving the public, while private sector jobs are in businesses aimed at generating profit.
Why is the public sector considered less flexible than the private sector?
The public sector follows strict regulations and oversight, limiting its flexibility compared to the private sector, which can make rapid market-driven changes.
What is the main funding source for the public sector?
The public sector is primarily funded through taxes and government budgets, whereas the private sector is funded by private investments and business profits.
How does ownership differ in the public and private sectors?
Public sector entities are government-owned, while private sector companies are owned by private individuals or shareholders.