ROCE and ROI are essential tools in the arsenal of financial analysis, each offering enormous insights into the efficacies and profitability of a company. They are quite similar in measuring returns but hugely different in application. ROCE is a measurement of how profitable the company as a whole is compared to the capital it employs in its business, with a greater focus on long-term financial soundness and operation. On the other hand, ROI zeroes in on the returns generated by specific investments, projects, or assets, providing a clearer picture of short-term profitability.
What is Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)?
ROCE is a financial performance indicator that measures the efficiency with which a company uses its capital to produce profit. It is very effective in determining the overall profitability of an organization, considering the total capital employed which may include both equity and debt capital. ROCE represents the ability of a firm to use its available resources effectively. Unlike other profitability measures like gross or net profit margin, ROCE assesses profitability relative to the total resource committed. This, therefore, qualifies it as the ideal tool used in analyzing capital-intensive industries, including manufacturing, real estate, and utilities.
ROCE calculates the Earnings Before Interest and Tax to exclude the impact of the structure of capital as well as tax policies so that more operative concepts are reached. It tells the investors how much profit is generated for every rupee of the capital employed, thereby providing a peek into the company’s efficiency.
Why is ROCE Important?
- Capital Efficiency: ROCE indicates the efficacious way a company uses its funds to generate returns, making it a very necessary tool for operational efficiency analysis.
- Comparative Analysis: It makes it possible to draw comparisons in cases of companies and industries that require considerable investment in capital.
- Investment Decisions: A higher ROCE value also means high profitability, thereby increasing the reliability of investors towards the investment idea.
- Strategic Planning: ROCE helps the management to identify resource-allocation inefficiencies and thereby optimize operations for enhanced performance.
Formula for ROCE
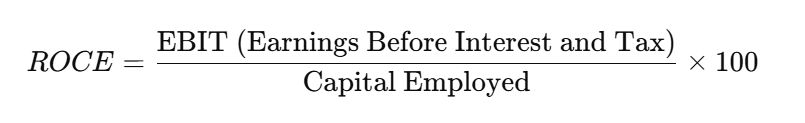
Where:
- EBIT reflects the company’s operational profitability before the influence of financing and tax decisions.
- Capital Employed is the sum of shareholder equity and debt or the difference between total assets and current liabilities.
ROCE Calculation Example
Suppose a company has the following financial details:
- EBIT: ₹10,00,000
- Total Assets: ₹50,00,000
- Current Liabilities: ₹15,00,000
To calculate ROCE:
- Determine capital employed:
Capital Employed = Total Assets – Current Liabilities = 50,00,000 – 15,00,000 = 35,00,000 - Apply the formula:
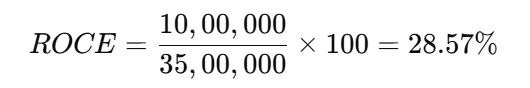
This means the company earns ₹28.57 for every ₹100 of capital employed.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
ROI is the profit generated by a particular investment compared to its cost. It is quite commonly used when managing any individual project, asset, or business initiative. ROI emphasizes the effectiveness of generating returns from a specific investment. Since it is not concerned with the entire capital structure in contrast to ROCE, ROI is focused specifically on certain expenditures. Therefore, it is a very popular metric for doing project appraisals, marketing programs, and acquiring assets.
Formula for ROI

Where:
- Net Profit is the revenue earned from the investment minus all associated costs.
- Cost of Investment includes the total capital outlay required for the project or asset.
ROI Calculation Example
Consider an investment of ₹2,00,000 in a marketing campaign that generated a revenue of ₹2,50,000:
- Calculate Net Profit:
Net Profit = Revenue – Cost = 2,50,000 – 2,00,000 = 50,000 - Apply the ROI formula:
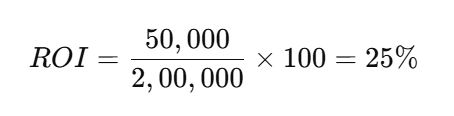
The investment generated a 25% return, indicating a profitable venture.
ROCE vs. ROI: Key Differences
ROCE and ROI offer different perspectives on financial performance, making them complementary tools. Below is a detailed comparison:
- Scope: ROCE measures overall business efficiency, whereas ROI measures the efficiency of an individual investment.
- Formula: ROCE uses EBIT and capital employed. ROI uses net profit and investment cost.
- Time Frame: ROCE tries to emphasize long-term efficiency. ROI is better for short-term evaluation.
- Debt Inclusion: ROCE takes into account the level of debt in capital employed. ROI ignores the debt feature.
| Aspect | ROCE | ROI |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Company-wide performance | Specific investments |
| Debt Consideration | Includes debt | Excludes debt |
| Applicability | Long-term efficiency | Short-term profitability |
| Best Use | Capital-intensive industries | Project and asset evaluation |
Advantages of Using Both Metrics
- Holistic View: Using ROCE for overall efficiency and ROI for specific investments offers comprehensive insights.
- Strategic Planning: Aligns operational goals with investment decisions.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Provides multiple perspectives, ensuring balanced financial analysis.
ROCE and ROI FAQs
What is the primary difference between ROCE and ROI?
ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) measures the profitability of a company relative to its total capital, including equity and debt. It provides a holistic view of operational efficiency. ROI (Return on Investment), on the other hand, assesses the profitability of specific investments or projects, focusing on returns relative to the cost of investment.
How does debt influence ROCE and ROI?
Debt is included in the calculation of ROCE as part of the total capital employed, reflecting how effectively a company uses both equity and borrowed funds. ROI, however, focuses solely on the returns generated from a specific investment and excludes considerations of debt unless it directly impacts the project cost.
Which metric is more suitable for long-term evaluation?
ROCE is better suited for long-term financial performance evaluation as it considers the overall profitability and efficiency of all employed capital over time. ROI, while useful, is typically applied to short-term or specific project evaluations.
Can ROI and ROCE both be negative?
Yes, both metrics can be negative. A negative ROI occurs when an investment incurs losses instead of profits, while a negative ROCE indicates that a company’s earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) are insufficient to cover the capital employed, signaling inefficiency.
How do ROCE and ROI help in decision-making?
ROCE helps stakeholders assess the overall efficiency of a company’s resource utilization, guiding strategic and operational improvements. ROI enables investors and managers to compare the profitability of various projects or investments, aiding in the prioritization of initiatives based on their returns.