The dual aspect concept in accounting is a core principle that states every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation remains in balance. This concept forms the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping, which records each transaction twice: once as a debit in one account and again as a credit in another. By balancing assets, liabilities, and equity, the dual aspect concept not only keeps accounts accurate but also allows businesses to represent their financial position transparently. This principle, illustrated in the equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity, maintains that every asset owned by a company has an equivalent claim by creditors or owners. The dual aspect concept plays an essential role in financial reporting by ensuring that transactions are recorded comprehensively and accurately, allowing users of financial statements—such as managers, investors, and regulators—to evaluate the business’s financial health. Each transaction’s impact on multiple accounts provides a clear, comprehensive view of a business’s finances, strengthening both internal management and external trust.
Dual Aspect Concept in Accounting
The dual aspect of accounting is very important since it ensures that all of the transactions are tracked properly and portrayed. This concept ensures the entry affects both sides of the accounting equation, showing that every company’s resources referred to are always balanced against the claims put on those resources by creditors for liabilities and owners for equity.
Key Features of the Dual Aspect Concept
- Maintains Accuracy: The dual aspect approach ensures that every transaction is recorded with corresponding entries, reducing errors.
- Enables Complete Financial Analysis: By showing how each transaction impacts both assets and liabilities or equity, the dual aspect concept provides a balanced view of finances.
- Supports Global Standards: Double-entry bookkeeping based on the dual aspect concept is universally accepted, enabling standardized accounting practices.
Example of Dual Aspect Concept
For instance, if a business purchases office equipment worth $5,000 using cash, the entry will affect both the equipment account (increasing assets) and the cash account (decreasing assets). The entry would look like this:
- Debit: Equipment $5,000 (increase in assets)
- Credit: Cash $5,000 (decrease in assets)
Each transaction is recorded twice, once as a debit and once as a credit, ensuring the accounts remain balanced and accurate.
Dual Aspect Accounting Equation
The dual aspect concept directly relates to the fundamental accounting equation, which keeps the financial statements balanced and meaningful:
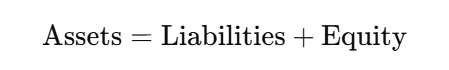
In this equation:
- Assets represent everything the company owns, such as cash, equipment, and inventory.
- Liabilities include the company’s obligations, like loans or accounts payable.
- Equity reflects the owner’s claim on the assets after all liabilities are settled.
How Dual Aspects of Accounting Work?
In the dual aspect accounting system, every transaction is recorded in at least two accounts to maintain the balance within financial statements. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Identify the Accounts Involved: Every transaction involves two or more accounts. For example, selling goods for cash involves the sales account and the cash account.
- Determine Debit and Credit Entries: Depending on the type of accounts, one will be a debit, which means it is an increase in assets or expenses, while the other will be a credit, meaning an increase in liabilities, equity, or revenue.
- Record the transaction: This entry will ensure the accounting equation is kept balanced, thereby keeping the financial health picture clear.
Example Entry for Dual Aspects of Accounting
Imagine a business pays $1,500 in rent:
- Debit: Rent Expense $1,500 (increase in expenses)
- Credit: Cash $1,500 (decrease in assets)
By debiting and crediting these accounts, the business accurately reflects the impact of the rent payment, adhering to the dual aspect concept and preserving accuracy.
Single vs. Dual Aspect of Accounting
To understand the importance of the dual aspect concept, it’s helpful to compare it with the single-entry system, which records only one side of each transaction. Here is a detailed comparison of the two:
| Feature | Single Entry | Dual Entry (Dual Aspect Concept) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Records one side of a transaction | Records both debit and credit sides |
| Completeness | Incomplete and limited | Comprehensive, shows full transaction impact |
| Error Detection | Hard to detect errors | Easier to trace and fix errors |
| Use | Simple, for small businesses | Standard for larger businesses |
| Financial Reporting | Minimal analysis capability | Allows complete financial analysis |
| Accuracy | Prone to inaccuracy | Enhances accuracy and reliability |
The dual aspect approach ensures financial statements are balanced and accurate, which is essential for stakeholders like investors, managers, and auditors.
Importance of Dual Aspect Concept in Accounting
The importance of the dual aspect concept in accounting is immense, as it strengthens the accuracy, transparency, and completeness of financial records.
- Promotes Accuracy and Reliability: The recording of both sides of a transaction under the double-entry principle minimizes the chances of making errors, hence increasing the reliability of financial data.
- Ensures Financial Decision Making: Recording each and every transaction at length will ensure informed managers’ and stakeholders’ decisions based on the correct data.
- Improves Financial Transparency: Double-entry bookkeeping creates transparency as it keeps financial records visible and traceable.
- Facilitates Financial Audits: In this method, it becomes easy for auditors to cross-check accounts and track the errors since every transaction has dual entries.
Implications on Financial Statements
The dual aspect concept significantly impacts the preparation and presentation of financial statements:
- Balance Sheet: Every transaction impacts the balance sheet either by changing assets, liabilities, or equity, thereby maintaining the accounting equation. Therefore, the balance sheet is always balanced, providing a perfect picture of the business’s financial standing.
- Income Statement: Revenues and expenses are recorded as part of double-entry accounting, directly affecting the income statement. Therefore, enabling the accurate calculation of profits or losses.
- Cash Flow Statement: It captures cash inflows and outflows according to the concept of dual aspect and, henceforth impacts cash balance along with its related accounts like revenue, expenses, etc.
The dual aspect concept ensures these statements accurately reflect a company’s financial performance and position, allowing stakeholders to assess the business’s profitability, solvency, and liquidity.
Dual Aspect Concept in Accounting FAQs
What is the dual aspect concept in accounting?
The dual aspect concept in accounting asserts that every transaction has equal and opposite effects in at least two accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation “Assets = Liabilities + Equity” stays balanced.
How does the dual aspect concept enhance financial accuracy?
By recording every transaction twice, the dual aspect concept minimizes errors, provides a clear financial picture, and enables accurate financial reporting through balanced accounts.
What is the difference between single and dual aspect accounting?
Single-entry accounting records only one side of a transaction, whereas dual-entry (dual aspect) records both debit and credit sides, ensuring balanced, comprehensive records.
How does the dual aspect concept impact financial statements?
The dual aspect concept maintains the accounting equation, which affects the balance sheet, income statement, and cashflow statement.