Ex ante demand is the amount of demand estimated or projected before the actual market event. It refers to forecasting or predicting consumer behavior based on various factors such as changes in price, income variations, and market conditions. Unlike ex post demand, ex ante demand predicts and determines future expectations. Ex ante demand can assist businesses, economists, and policymakers in proper planning and preparation for market conditions. Understanding ex ante demand enables organizations to prepare for market conditions, better in tune with the needs of consumers, which further aids in the optimal production and pricing decision.
What is Ex Ante Aggregate Demand?
Ex ante aggregate demand is an aggregate level of planned spending on goods and services produced in the economy at given levels of output before actual market transactions take place. It is important to economic forecasting and planning in that it encompasses not just individual consumer choices but also the expectations of businesses and governments. When economists or businesses predict future demand, they consider factors such as consumer confidence, expected income, and anticipated price changes. In this case, the word “aggregate” refers to the sum of all demand in the economy, taking into account all sectors such as households, firms, and the government.
Key Factors Influencing Ex Ante Aggregate Demand
Ex ante aggregate demand helps determine economic strategies and policies. Policymakers adjust interest rates or fiscal policies based on these projections so that the economy does not overheat or stagnate. Businesses also use these demand forecasts to determine production levels and marketing strategies. Several factors shape ex ante aggregate demand:
- Anticipated Price Levels: Individuals and businesses often forecast their future demand according to the expected level of inflation or deflation. For instance, when individuals expect prices to go up, they may increase their current purchases to avoid paying higher prices in the future.
- Interest Rates and Credit Supply: Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, which will likely be followed by an increase in ex ante demand for goods, particularly durable goods such as automobiles or houses.
- Income and Employment Expectations: Consumers are likely to spend more if they expect their income to increase or if employment levels are high. Conversely, people reduce their expenditures if they foresee economic downturns.
- Consumer Confidence: When consumers feel confident about the economy, they spend more, thereby increasing aggregate demand. However, pessimistic expectations lead to reduced spending and lower demand.
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies may influence the expectation of demand. Government spending or tax reduction may enhance confidence and demand. However, austerity measures have a contrary effect.
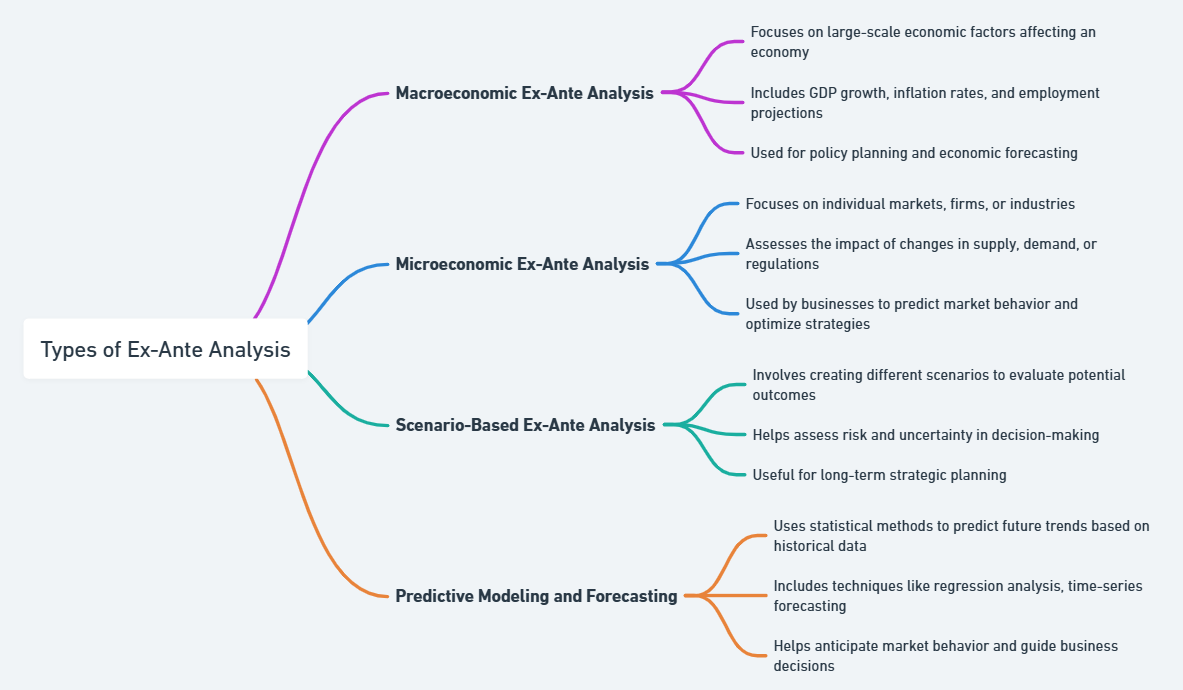
Types of Ex-Ante Analysis
Ex-ante analysis, on the other hand, pertains to the process where future outcomes are predicted based on the theoretical or historical data in advance of the happening. It projects future market conditions through various methods of making such predictions, including consumer behavior models and other kinds of economic indicators. Among the primary types of ex-ante analysis commonly utilized in economics and business include:
1. Macroeconomic Ex-Ante Analysis
Macroeconomic ex-ante analysis is used in the forecasting of the behavior of an entire economy. In this analysis, variables like growth in GDP, inflation, unemployment, and interest rates are predicted. Economists and government officials use statistical models to predict these variables that in turn guide their policy decisions. For example, if an economy is projected to grow at a certain rate, the government would then make adjustments in the fiscal or monetary policies to keep the inflation under control or encourage further investment.
2. Microeconomic Ex-Ante Analysis
Microeconomic ex-ante analysis analyzes the conduct of individual firms or markets. It can predict demand in the future, cost structure, and the dynamics of competition. Businesses will use models based on microeconomics to estimate the quantity they would sell at various prices. They could also forecast the responses of other firms toward a price adjustment or new product launch.
3. Scenario-Based Ex-Ante Analysis
In scenario-based ex-ante analysis, different possible outcomes are usually considered. Analysts mostly build up different scenarios as a result of different assumptions for significant variables. For example, they may create best-case, worst-case, and most likely cases for market growth, consumer spending, or political stability. That kind of analysis is very effective if the environment is quite uncertain because it allows the preparer of decisions to anticipate a variety of different potential future states.
4. Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Predictive modeling makes use of statistical techniques in forecasting future demand. These are most often used in businesses in the prediction of customer behavior, sales trends, or even inventory needs. Analysts feed historical data into complex algorithms that will create predictive models, and then generate an estimate of future demand.
Ex-ante analysis is essential for businesses and policymakers to understand potential market outcomes before they occur. By anticipating future trends, they can make informed decisions that reduce risk and optimize performance.
Advantages of Ex-Ante Demand
- Informed Decision-Making: Ex ante demand analysis provides insights that enable businesses, governments, and economists to make better-informed decisions. By predicting future demand, companies can adjust their production schedules and inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overproduction.
- Resource Optimization: Advance demand forecasting allows businesses to optimize resources. Whether it is labor, raw materials, or production capacity, companies can plan for increases or decreases in demand, ensuring efficient operation.
- Strategic Planning: Ex ante demand analysis helps businesses and policymakers prepare long-term strategies. By knowing what might happen in the future, they can prepare for the opportunities or threats that will arise in the near future.
- Risk Mitigation: Anticipating shifts in demand may help businesses prepare for times of economic downturn or catch the wave of a boom in the market. One may predict a recession by reducing production as demand is going to be low.
- Implementation of Policy: Governments use ex-ante demand analysis for designing fiscal and monetary policies. By estimating future aggregate demand, policymakers can adjust tax rates, interest rates, and government spending programs.
Disadvantages of Ex-Ante Demand
- Uncertainty: Another limitation of ex ante demand analysis comes in the form of uncertainties in estimating the future prevailing market conditions. Even highly sophisticated models are not sure to grasp variables that remain unforeseen in the equation, including natural disasters or political changeovers and sometimes global crises.
- Data Limitation: To develop accurate ex ante demand analysis, strong data is required. Lacking, stale, or inaccurate data tends to produce faulty predictions, which can lead to the wrong set of decisions.
- Assumption-Dependent: Many analyses of ex ante are done based on assumptions that do not necessarily come to fruition in the future. An example would be an analysis that assumes that consumer behavior will be just like before, but tastes or behaviors may change and lead to inaccurate demand forecasts.
- Overdependence in Predictions: It also shows overconfidence in ex ante models. Sometimes businesses have aggressive decisions that will later prove to be inappropriately taken if real demand turns out to differ in a significant way.
While ex-ante demand analysis offers significant benefits, it’s important for decision-makers to be aware of its limitations and the uncertainties involved. A balanced approach that considers both ex-ante predictions and flexibility in strategy can lead to better long-term outcomes.
Difference Between Ex Ante and Ex Post Demand
Ex ante demand and ex-post demand are two distinct concepts that play an essential role in understanding economic behavior. The primary difference lies in the timing and basis of the demand measurement.
Ex Ante Demand
Ex ante demand is a forward-looking concept that predicts the amount of demand for something under certain expected future conditions. It is based on prediction, assumption, and modeling of how much of something will be demanded at a given price in the future. This demand is essential for planning and decision-making since it gives businesses and policymakers the foresight needed to adjust their strategies.
Ex Post Demand
Ex post demand is based on observed actual demand that takes place after the fact. It measures the actual quantity of goods and services bought in the market. This demand ex post is critical for knowing how well demand forecasts have aligned with real-life conditions. After-market data, be it sales reports or market surveys, give a more lucid picture of how accurate the predictions were.
| Feature | Ex Ante Demand | Ex Post Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Pre-event, based on forecasts and assumptions | Post-event, based on actual market data |
| Use | Strategic planning and forecasting | Evaluation of forecast accuracy and market conditions |
| Data Basis | Predictions, assumptions, and models | Actual consumer behavior and transactions |
| Uncertainty Level | Higher due to reliance on future predictions | Lower, as it is based on real, observed outcomes |
Ex ante demand allows businesses to make decisions proactively, while ex post demand is useful for post-analysis, helping businesses assess how well their predictions matched the real outcomes.
Ex Ante Demand FAQs
What is Ex Ante Demand?
Ex ante demand refers to the predicted demand for goods and services before the actual market events occur. It is based on forecasts considering factors such as consumer behavior, expected income, and market conditions.
What is the difference between Ex Ante and Ex Post Demand?
Ex ante demand is a forecasted or predicted demand based on future expectations, while ex post demand measures actual market demand that occurs after the event, reflecting real consumer behavior.
How is Ex Ante Aggregate Demand calculated?
Ex ante aggregate demand is calculated by estimating the total planned expenditure in the economy, considering factors like expected income, price levels, interest rates, and government spending.
What are the advantages of Ex Ante Demand Analysis?
Ex ante demand analysis allows businesses and governments to make informed decisions, optimize resources, mitigate risks, and plan strategically for future economic conditions.
How accurate are Ex Ante Demand forecasts?
Ex ante demand forecasts depend on available data and assumptions. While they are valuable for planning, they can be uncertain and influenced by unexpected events or changes in consumer behavior
.


