General insurance plays a pivotal role in mitigating the financial risks associated with unforeseen events. It provides coverage against losses and damages that can arise due to accidents, natural disasters, health emergencies, or legal liabilities. Unlike life insurance, which focuses on long-term financial planning and life risk coverage, general insurance deals with the protection of tangible and intangible assets for a defined period. Understanding the features of general insurance is crucial for making informed decisions about securing oneself and one’s assets.
What is General Insurance?
General insurance is a financial arrangement where an individual or organization pays a premium to an insurer in exchange for coverage against specific risks. These risks are often associated with the loss of assets, medical emergencies, or liabilities. The policyholder is compensated for the actual losses incurred during the policy’s term, up to the insured amount, ensuring they can recover and stabilize financially.
Unlike life insurance, general insurance does not involve the element of savings or investment. It operates on the principle of indemnity, which ensures that the insured is compensated for the actual loss incurred without profiting from the claim. This makes general insurance a practical tool for safeguarding one’s financial interests against unpredictable events.
For example, if a homeowner faces damages due to a fire, their property insurance will cover the cost of repair or replacement as specified in the policy. Similarly, health insurance covers medical expenses arising from illnesses or injuries, reducing the financial burden on the individual.
Features of General Insurance
The distinctive attributes of general insurance make it a vital financial instrument for risk management. Each feature contributes to its functionality and relevance in providing financial security.
Risk Coverage
The primary purpose of general insurance is to cover specific risks. These risks can range from natural disasters, theft, and accidents to health emergencies or legal liabilities. For instance, property insurance shields homeowners from financial losses due to fire or floods, while motor insurance protects vehicle owners from repair costs or third-party liabilities.
Time-Bound Contracts
General insurance policies are typically valid for a specific period, often one year. At the end of the term, the policyholder can renew the policy based on their current requirements and risk assessment. This feature ensures that the coverage remains relevant and up-to-date with changing circumstances.
Premium Payments
To avail of coverage, policyholders must pay a premium to the insurer. The premium amount depends on various factors, such as the type of coverage, the value of the asset insured, the risk involved, and the insurer’s assessment of the likelihood of a claim. Premium payments can often be customized to suit the policyholder’s financial capabilities, allowing flexibility in payment frequency.
Contractual Agreement
General insurance operates based on a legal contract between the insurer and insured. This agreement clearly outlines the terms, conditions, inclusions, exclusions, and the coverage limit. The policy document serves as a binding agreement, ensuring clarity and accountability for both parties.
Indemnity Principle
A cornerstone of general insurance is the principle of indemnity, which ensures that the insured is compensated only for the actual loss incurred. This prevents the policyholder from gaining a financial profit from their claims. For instance, if a stolen car is covered by motor insurance, the policy will compensate the policyholder for the car’s current market value and not more.
Tailored Policies
General insurance policies can be customized to address specific risks and requirements. This flexibility allows individuals and businesses to choose coverage that aligns closely with their needs, whether it involves securing health, property, vehicles, or liabilities.
Absence of Savings or Investment Component
Unlike life insurance, general insurance does not function as a savings or investment vehicle. Its sole focus is risk coverage, ensuring that financial losses due to unexpected events are mitigated effectively.
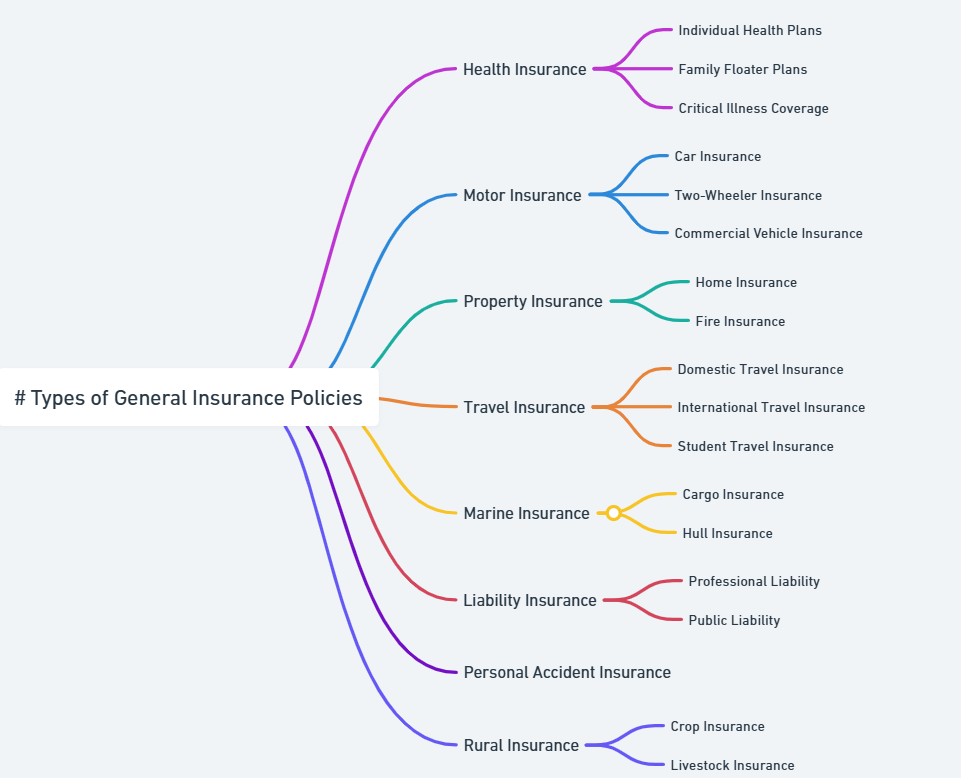
Types of General Insurance Policies
General insurance encompasses a diverse range of policies designed to meet different risk management needs. Each policy type caters to specific scenarios, ensuring comprehensive financial protection.
Health Insurance
Health insurance is one of the most sought-after forms of general insurance. It provides financial coverage for medical expenses arising from illnesses, surgeries, or accidents. The policy can include hospitalization, medication, diagnostic tests, and even preventive care in some cases. Health insurance may also cover critical illnesses, ensuring policyholders receive adequate financial support during life-threatening health conditions.
Motor Insurance
Motor insurance is mandatory for vehicle owners in most countries. It covers damages to the vehicle, third-party liabilities, and personal accidents. Comprehensive motor insurance policies provide extensive coverage, including theft, natural calamities, and accidental damages. This ensures that vehicle owners are protected from significant financial setbacks.
Property Insurance
Property insurance safeguards homes, offices, and other properties against damages caused by natural disasters, theft, fire, or vandalism. It offers financial compensation for repair or replacement, ensuring that property owners can restore their assets without incurring severe financial losses.
Travel Insurance
Travel insurance provides coverage for emergencies during travel, such as medical expenses, trip cancellations, lost baggage, or travel delays. It is especially beneficial for international travelers, offering financial security in unfamiliar territories.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance protects individuals and businesses from legal liabilities arising from accidents, negligence, or damages caused to third parties. Businesses often opt for employer liability or public liability insurance to cover potential risks.
Marine Insurance
Marine insurance covers goods during transit by sea, air, or land. It safeguards against losses or damages to the cargo, ensuring that businesses can transport goods without financial risks.
Personal Accident Insurance
This type of insurance compensates policyholders for injuries, disabilities, or fatalities resulting from accidents. It ensures financial stability for the insured or their family during unforeseen circumstances.
Benefits of General Insurance
General insurance offers a multitude of advantages, underscoring its importance in financial planning and risk management.
- Financial Security: General insurance acts as a financial safety net, covering significant expenses that arise due to unforeseen events. It ensures that policyholders do not have to deplete their savings or incur debt to manage unexpected costs.
- Asset Protection: Whether it is a home, vehicle, or business property, general insurance protects valuable assets from damages or losses. This ensures their longevity and usability, contributing to financial stability.
- Legal Compliance: Certain types of general insurance, such as motor insurance and employer liability insurance, are mandatory by law. Complying with these requirements ensures that individuals and businesses avoid legal penalties.
- Risk Transfer: Insurance transfers the financial burden of risk from the policyholder to the insurer. This allows individuals and businesses to focus on growth and daily operations without the constant worry of potential losses.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that one is financially protected against unexpected events provides peace of mind. Policyholders can navigate life’s uncertainties with confidence, knowing that their financial interests are secured.
Features of General Insurance FAQs
What is general insurance?
General insurance provides short-term financial coverage against risks other than life, including health, motor, and property insurance.
How is general insurance different from life insurance?
Unlike life insurance, general insurance covers non-life risks and is a short-term contract without savings or investment components.
Why is general insurance necessary?
It mitigates financial losses due to unforeseen events, protects assets, and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
Can I renew my general insurance policy?
Yes, most general insurance policies are renewable annually, allowing adjustments to coverage as needed.
What does the principle of indemnity mean in general insurance?
It means the insured is compensated only for the actual loss incurred, preventing them from profiting from a claim.


