Financial and non-financial incentives play a critical role in motivating and performing employees in business and management. Knowing the difference between financial and non-financial incentives will allow organizations to strike a balance that increases productivity without diminishing employee satisfaction. This article delves into the definition of incentives, classification, and different types of financial and non-financial incentives that businesses can utilize to increase employee engagement and motivation.
What Are Incentives?
Incentives are the rewards or motivational benefits that encourage employees to reach higher levels of productivity and efficiency. They act as catalysts for achieving organizational goals and can be monetary or non-monetary. Incentives are crucial in attracting talent, retaining employees, and fostering a culture of commitment and hard work. These rewards can be broadly categorized into two main types: financial incentives and non-financial incentives.
Financial Incentives
Financial incentives are the monetary rewards offered to employees to stimulate enhanced performance. These, therefore, directly affect the amount of earnings received by the employees. It is thus an actual reward to the employees for their contributions toward the success of the firm. Financial incentives will align employee interests with those of the organization by giving rewards based on measurable grounds.
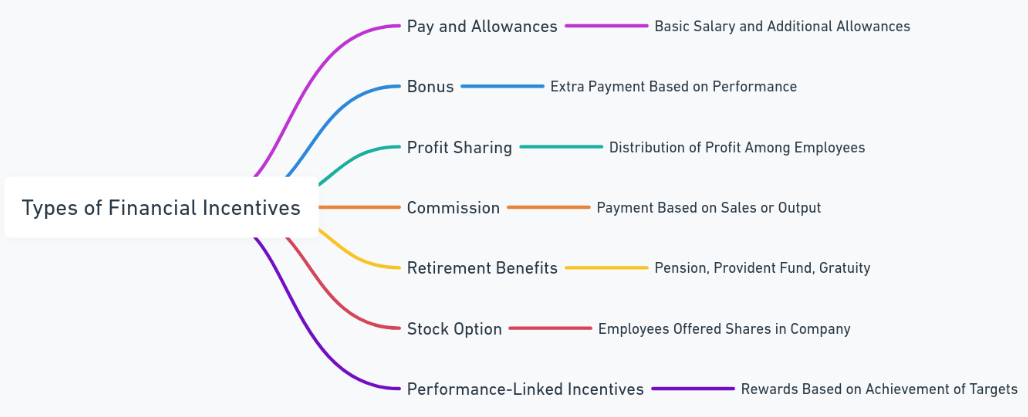
Types of Financial Incentives
Financial incentives include rewards that are combined with monetary incentives or need money to be paid. These incentives can take any possible shape and form. Following are some of the very common financial incentives.
Basic Salary
Any job mainly provides monetary benefits through its salary or wage. Such is considered a direct reward for service rendered and should be remitted periodically so that workers can use these payments for their sustenance and individual responsibilities, providing a more basic motivator.
Bonuses
Bonuses are additional payments given for achieving certain milestones, often tied to performance metrics or business achievements. Commonly given annually, bonuses can also be tied to specific projects or quarterly results to encourage sustained performance.
Profit Sharing
Companies may offer employees a share in the company’s profits as an incentive. Profit sharing schemes motivate employees by giving them a stake in the company’s success, fostering a sense of ownership.
Commission
Primarily used in sales roles, commissions are percentage-based rewards that employees earn on sales they generate. This financial incentive motivates employees to increase sales, directly impacting their earnings.
Stock Options
Stock options allow employees to purchase company shares at a lower price than the market value, incentivizing them to stay with the company. It also aligns employee interests with shareholder interests, as both benefit from stock price appreciation.
Retirement Benefits
Pension plans and retirement funds provide long-term financial security, motivating employees to remain with the organization over a longer duration.
| Type of Financial Incentive | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Salary | Regular payment for work done |
| Bonuses | Additional reward for achieving specific goals |
| Profit Sharing | Employee shares in the company’s profits |
| Commission | Earnings based on sales or performance |
| Stock Options | Right to buy company stock at a discount |
| Retirement Benefits | Long-term savings plans or pensions |
Non-Financial Incentives
While financial incentives directly appeal to the tangible needs of employees, non-financial incentives cater to intrinsic motivators like recognition, job satisfaction, and growth. Non-financial incentives help create a positive work environment where employees feel valued beyond their financial compensation.
Types of Non-Financial Incentives
Except for money, there are several techniques by which a firm can induce good behavior change and compel the staff to work efficiently. Below are some of the commonly practiced forms of non-cash incentives:
Recognition and Appreciation
Acknowledging an employee’s efforts through awards, public appreciation, or a simple “thank you” note can significantly boost morale. Recognition programs instill a sense of achievement and reinforce positive behaviors.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Offering growth paths, promotions, and career development opportunities shows employees that their future in the company is promising, thus encouraging loyalty and long-term commitment.
Flexible Working Conditions
Flexible hours, remote work options, or the ability to adjust schedules can significantly enhance job satisfaction, helping employees balance work and personal life effectively.
Job Enrichment and Enlargement
Job enrichment involves adding more challenging tasks to an employee’s role to increase their engagement. Job expansion, on the other hand, expands the scope of their job, allowing them to work on varied tasks.
Work-Life Balance Programs
Companies that emphasize work-life balance through wellness programs, paid time off, or on-site fitness facilities show employees that they care about their well-being, making them feel more valued.
Autonomy and Responsibility
Providing employees with autonomy in decision-making and holding them accountable for their work fosters trust and builds confidence, making them feel integral to the organization.
| Type of Non-Financial Incentive | Description |
|---|---|
| Recognition | Public or formal acknowledgment of performance |
| Career Advancement | Growth opportunities within the company |
| Flexible Working | Flexibility in work hours or location |
| Job Enrichment | Adding challenging tasks to the role |
| Work-Life Balance | Programs that support employees’ well-being |
| Autonomy | Granting responsibility and decision-making power |
A motivated workforce requires a balance of financial and non-financial incentives. Financial incentives satisfy the immediate need toward tangible ends, but non-financial incentives ensure longer satisfaction through intrinsic motivational factors. Incentive structures that are well-balanced improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention, which makes the workplace more cohesive and productive.
Financial and Non Financial Incentives FAQs
What is the difference between financial and non-financial incentives?
Financial incentives involve monetary rewards like bonuses and salaries, whereas non-financial incentives focus on recognition, flexible working conditions, and career development opportunities.
How do financial incentives improve employee performance?
Financial incentives provide a direct economic benefit that motivates employees to increase their productivity to receive rewards such as bonuses or profit sharing.
Why are non-financial incentives important in the workplace?
Non-financial incentives are essential for long-term employee satisfaction as they cater to intrinsic motivators such as recognition, personal growth, and work-life balance.
Can a balance of financial and non-financial incentives increase employee retention?
Yes, a mix of both incentives keeps employees motivated and satisfied, enhancing loyalty and reducing turnover.
What are examples of non-financial incentives?
Examples include flexible work schedules, recognition programs, career growth opportunities, job enrichment, and autonomy in work.