Every person who earns money should pay tax. If you live in India and earn above the basic exemption limit, you must file an income tax return. You must collect your income details, check the correct form, fill it online, verify it, and submit it to the Income Tax Department. The process is easy, especially with online filing (e-filing). Knowing how to file an income tax return on time helps avoid penalties and brings many benefits. You can get refunds, loans, and even visa approvals easily. Filing ITR is not only a duty but also helps in planning your finances. Every year, the Income Tax Department gives updates on the new ITR rules and slabs. You must follow them to file your return properly.
What is an Income Tax Return?
An income tax return is a form where you share your income and tax paid with the government. It shows how much you earned, what deductions you claimed, and how much tax you paid.
Why do people file ITR?
People file ITR to report their income officially. It is a legal rule. If you earn more than the limit set by the government, you must file it. Even if your income is below the limit, filing ITR gives you many benefits like refunds and proof of income.
You can file ITR even if you have no tax liability. This helps you get TDS refunds. It is useful for students doing internships or freelancing. It also helps when you apply for loans, scholarships, or visas.
The Income Tax Department gives seven types of ITR forms. Each form is for a different income type. For example, salaried people use ITR-1. Business owners use ITR-3 or ITR-4. You must choose the correct form while filing.
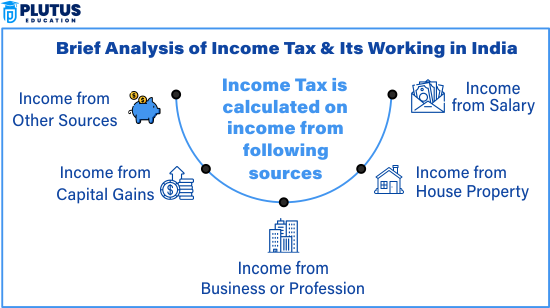
Step-by-Step Guide on How to File Income Tax Return
You can file your income tax return easily by following some clear steps. You need to collect all required papers first. Then log in to the income tax website and choose the correct form. You must fill in your income and claim deductions. After checking, you can submit and verify your return.
Step 1: Collect Documents
You must keep all documents ready before filing.
- Form 16 (for salaried people)
- Salary slips
- Bank statements
- PAN card and Aadhaar card
- Form 26AS (Tax credit statement)
- Investment proofs
- Rent receipts (if claiming HRA)
- Interest certificates from banks
These documents help you fill the form correctly. They also support your claims in case the department checks your return later.
Step 2: Register or Login to the Income Tax Portal
Visit the official website: https://www.incometax.gov.in
- If new, register with your PAN
- If already registered, log in using your PAN and password
The portal has all the tools needed to file your return.
Step 3: Choose the Right ITR Form
Select the ITR form that matches your income type.
| ITR Form | For Whom |
| ITR-1 | Salaried individuals with income up to ₹50 lakh |
| ITR-2 | Individuals with capital gains or multiple properties |
| ITR-3 | Business or professional income |
| ITR-4 | Presumptive income scheme (small businesses) |
Choosing the right form is important to avoid mistakes.
Step 4: Fill in Income Details
Enter details like:
- Salary income
- Income from house property
- Other income (interest, gifts)
- Business income
- Capital gains (if any)
The portal may auto-fill some details from Form 26AS and AIS.
Step 5: Claim Deductions
Add deductions under Chapter VI-A like:
- Section 80C – Investments in LIC, PPF, ELSS
- Section 80D – Health insurance
- Section 80TTA – Interest on savings account
- Section 80E – Education loan interest
These reduce your tax and increase refund chances.
Step 6: Calculate Tax and Pay if Needed
Use the tax calculator on the portal. If tax is due, pay using challan ITNS 280. Enter the challan details in the form.
Step 7: Verify and Submit
Check all entries again. Then submit the return.
After submission, verify it. You can e-verify using Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or send the signed ITR-V to CPC, Bangalore.
Income Tax Slabs and Filing Deadlines
Income tax slabs show how much tax you pay based on your yearly income. The government updates these slabs every year in the budget. There are two systems: the old and the new tax regime. You must file your ITR before the due date to avoid late fees. Knowing these slabs helps you plan better.
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2024-25 (New Regime)
| Income Range | Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹3,00,001 – ₹6,00,000 | 5% |
| ₹6,00,001 – ₹9,00,000 | 10% |
| ₹9,00,001 – ₹12,00,000 | 15% |
| ₹12,00,001 – ₹15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above ₹15,00,000 | 30% |
You can choose between the old and new regime each year.
ITR Filing Deadlines
- Individuals: 31st July of the assessment year
- Audit cases: 31st October
- Revised return: 31st December
File before the deadline to avoid late fees under Section 234F.
Benefits of Filing Income Tax Return
Filing your ITR gives you many useful benefits. It helps you claim a refund if you paid extra tax. It also works as income proof for loans and visas. You can carry forward losses if you file on time. Most importantly, it shows that you follow the law.
- Claim Refunds: If TDS is deducted more than needed, you get a refund. But you get it only after filing the return.
- Proof of Income: ITR acts as income proof. It helps in applying for home loans, education loans, or car loans.
- Helps in Visa Applications: Many countries ask for ITR receipts for the last 2-3 years while applying for visas.
- Carry Forward Losses: If you file ITR on time, you can carry forward losses to future years. This helps in reducing future tax.
- Avoid Penalties: If you file late, you may pay up to ₹5,000 as a fine. Filing on time saves that money.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Filing ITR
Many people make errors when they file their ITR. These include using the wrong form, entering wrong bank details, or forgetting to verify. Even a small mistake can delay your refund. So, you must double-check everything. Filing correctly saves time and avoids trouble later.
- Wrong ITR Form: Using the wrong form leads to rejection. Know your income type and choose correctly.
- Not Reporting All Income: Even small interest from banks must be reported. Hiding income can cause penalties later.
- Claiming False Deductions: Do not claim deductions without proof. The tax department may ask for them later.
- Forgetting to Verify: Your return is not complete until verified. E-verification is the easiest and fastest.
- Wrong Bank Details: Always enter the correct IFSC and account number. Wrong details delay your refund.
How to File Income Tax Return for Salaried Employees
Salaried employees can file their ITR using Form 16. Most of their tax data is available in that form. They should match it with Form 26AS before filing. They must also claim deductions like HRA, 80C, and 80D. Filing on time ensures faster refunds and avoids fines.
- Use Form 16 Correctly: Form 16 has all your salary and TDS details. Match it with Form 26AS before filing.
- Claim HRA and Deductions: Use rent receipts and medical bills to claim benefits. Don’t forget 80C and 80D deductions.
- File on Time: File before July 31 to avoid penalties and get faster refunds.
How to File Income Tax Return FAQs
What is the last date to file an income tax return?
The last date for individuals is 31st July of the assessment year.
Can I file ITR without Form 16?
Yes, use salary slips, bank statements, and Form 26AS instead of Form 16.
What happens if I miss the ITR deadline?
You may pay a penalty up to ₹5,000. You also lose some benefits like carrying forward losses.
Do students need to file ITR?
If their income crosses the exemption limit or they want TDS refund, they should file ITR.
How can I verify my ITR?
You can verify using Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or by sending a signed ITR-V to CPC, Bangalore.


