Consumer rights are crucial because they help protect buyers against unfair trade practices, fraud, and exploitation. These rights allow consumers to have fair treatment, quality products, accurate information, and the ability to make decisions. In this world where business organizations aim at profits, consumer rights act as a shield, ensuring that companies engage in ethical practice. The fundamental importance of consumer rights is giving people the strength to demand quality, safety, and honesty in the marketplace. Without such rights, businesses can exploit buyers through poor-quality products, false advertising, and exorbitant prices. Thus, understanding the importance of consumer rights develops an awareness of the powers one holds as a consumer, creating a fair and balanced economy.
What is Consumer Rights?
Consumer rights refer to protection governing fairness, safety, and transparency that the buying public deserves when purchasing goods and services. These rights tend to curb businesses from taking advantage of consumers and thus create ethical market practices. Consumer rights are limited to purchases and services that most of us use daily, like banking and healthcare, education, and online applications.
With this knowledge, consumers can make intelligent decisions, detect bad practices, and act appropriately. For example, if a product is faulty or a service has not been unprovided as guaranteed, consumer rights empower the individual to lodge complaints, demand refunds, or even seek legal recourse.
History of Consumer Rights in India
Ancient traders did observe ethical trade rules to avoid exploitation, but there was no formal legislation for consumer protection. The growth of trade and commerce made necessary an orderly and systemic protection of the consumers. Industrialization in India during post-independence days marked an excellent tempo for development; simultaneously, there was an inherent lack of orderliness in consumer protection schemes.
| Year | Event | Significance |
| 1962 | U.S. President John F. Kennedy’s Speech | Introduced the idea of consumer rights globally |
| 1986 | Consumer Protection Act (CPA) Passed | Gave legal power to protect Indian consumers |
| 1991 | Economic Reforms in India | Increased need for stronger consumer laws |
| 2002 | Amendment to Consumer Protection Act | Strengthened consumer forums and legal processes |
| 2019 | New Consumer Protection Act Introduced | Modern laws covering e-commerce and digital issues |
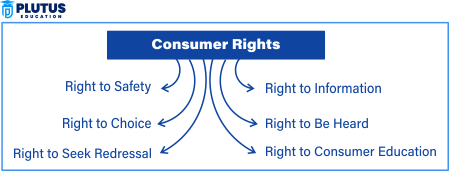
What are the 8 Consumer Rights and Responsibilities?
There are specific rights concerning a consumer that protect from unfair practice. These rights ensure they are appropriately treated and receive quality products and proper information. Let’s look in detail into the 8 rights of the consumer.
Right to Safety
Consumer rights must be protected from products or services hazardous to their health or life. For instance, food items have to meet safety standards so that one does not face any health problems.
Right to Information
Consumers are entitled to know everything regarding products they buy, such as price, quality, composition, shelf life and service conditions. This enables them to make the right choices.
Right to choose
Customers can exercise options within products and services available at competitive prices. They are not compelled to purchase an item when its alternative is available.
Right to be heard
Consumers are free to lodge grievances if there are any problems. The concerns are heard, and businesses and the government take suitable steps.
Right to Redressal
When there is some deficiency in the product or poor quality service, the consumers should get a substitute or appropriate reimbursement. Consumers can also resort to consumer courts to redress such complaints.
Right to Consumer Education
Consumers should be educated about their rights and duties. Awareness campaigns, advertisements like “Jago Grahak Jago,” and school curriculums are helpful.
Right to a Safe Environment
The consumer has the right to live and work in a safe and, sustainable, healthy environment. Consumers are protected against pollution and unwholesome trade practices.
8. Satisfaction of Basic Needs
All consumers have a right to obtain fundamental goods and services such as food, water, shelter, and health, considered necessities for human survival.
| Right | Meaning |
| Right to Safety | Protection from harmful products |
| Right to Information | Access to complete and accurate product details |
| Right to Choose | Freedom to select from a range of products |
| Right to Be Heard | Opportunity to express complaints |
| Right to Redressal | Right to seek compensation for grievances |
| Right to Consumer Education | Learning about consumer rights and responsibilities |
| Right to a Healthy Environment | Living in a safe, pollution-free environment |
| Right to Satisfaction of Basic Needs | Access to essential goods and services |
Needs and Importance Of Consumer Rights
The need for consumer rights awareness has never been greater. As the number of products and services increases, consumers are exposed to fraud, poor-quality goods, and unethical business practices. Consumers can easily be exploited if they are not aware.
Protection Against Unfair Practices
Many businesses use misleading advertisements, false claims, and hidden charges to deceive consumers. Consumer rights awareness helps people identify these tricks and take action. Knowing your rights means demanding fair treatment, accurate information, and honest dealings.
Empowerment of Consumers
An educated consumer is an empowered consumer. Knowledge equips people with the confidence to question sellers, demand product information, and reject shoddy goods. It also empowers consumers to demand restitution if they are cheated or injured by a product or service.
Facilitating Ethical Business Practices
Legitimate businesses thrive when consumers know what rights they are entitled to. They tend to avoid unscrupulous practices because customers can report them for unfair practices. This way, companies ensure that quality is maintained and transparent procedures are followed. This creates a healthy marketplace where both buyers and sellers benefit.
Importance of Consumer Rights in India
The benefits of consumer rights in India are enormous, creating a marketplace that values fairness, transparency, and accountability. It forms the foundation of a just and fair market, where a consumer can believe in what they are purchasing and consuming.
Protection of Consumer Interests
Consumer rights protect people from fraud, low-quality goods, and unfair business practices. It ensures that the consumer gets value for their money and is not misled by false promises. For instance, if a company advertises a specific phone with certain features but delivers something else, the consumer can demand a refund or replacement. Without consumer rights, businesses could take advantage of buyers without a return consequence. They give laws that create legal ramifications to hold companies accountable.
Increase in Consumer Confidence
Confidence will be more present in consumers buying goods and services when they perceive they can get legal support. They shall not fear exploitation or deception with the confidence that they will take legal remedies if needed, thus positively boosting their economic activities.
For example, online shopping is popular due to strong consumer protection policies. A person can rely on an e-commerce website as they can return the products or get their money back in case of any mistake.
Promoting Business Transparency
Consumer rights make the business operation transparent and honest. Companies must disclose the details about their products, such as ingredients, pricing, and safety measures so that the consumer can make informed decisions.
Legal Recourse for Grievances
Consumer rights provide legal avenues for resolving disputes. Consumers who face fraud, poor service, or defective products can file complaints with consumer courts. In India, the Consumer Protection Act of 2019 simplifies this process, allowing consumers to seek justice quickly.
These legal protections make businesses shun unethical practices. Companies understand that consumers can legally sue them; therefore, companies will have high standards of quality and service to avoid being taken to court.
Responsible Social Action
Consumer rights push companies to act toward society responsibly. Companies are supposed to understand the impact their products and services have on the environment. For instance, restrictions on plastic packaging encourage eco-friendly alternatives.
Socially responsible businesses receive public support and create strong brand identities. They contribute to sustainable development, which benefits the economy and the environment.
| Consumer Rights | Consumer Responsibilities |
| Right to Safety | Ensure products are used correctly |
| Right to be Informed | Read product labels and understand information |
| Right to Choose | Make informed choices based on comparisons |
| Right to be Heard | Provide feedback and voice concerns |
| Right to Redress | Seek legal remedies if rights are violated |
| Right to Consumer Education | Stay informed about consumer laws |
| Right to Healthy Environment | Support eco-friendly products and practices |
| Right to Basic Needs | Demand access to essential goods and services |
8 Consumer Rights in India with Examples
Consumer rights in India are designed to protect individuals in all transactions, from daily shopping to significant financial investments. These rights apply to products, services, online transactions, and government services.
| Consumer Right | Real-Life Example |
| Right to Safety | A faulty mobile phone battery causing injury can be reported. |
| Right to be Informed | Labels on food items showing ingredients and expiry dates. |
| Right to Choose | Multiple brands of toothpaste available in a store. |
| Right to be Heard | Filing a complaint about poor service at a restaurant. |
| Right to Redressal | Getting a refund for a defective washing machine. |
| Right to Consumer Education | Awareness programs about online frauds. |
| Right to a Healthy Environment | Laws against factories causing pollution near homes. |
| Right to Satisfaction of Basic Needs | Government schemes providing clean drinking water. |
How Do You File a Complaint Under Consumer Rights?
Consumer rights complaints are a simple process to help consumers get justice in case of defective products, poor services, unfair trade practices, or misleading advertisements. Consumers can file complaints against manufacturers, service providers, retailers, or e-commerce platforms.
| Step | Description |
| Identify the Issue | Clearly understand the problem with the product or service. |
| Gather Documents | Collect bills, receipts, warranties, and communication records. |
| Contact the Company | Try resolving the issue directly with the company’s customer support. |
| Draft a Complaint | Write a formal complaint with details of the issue and documents. |
| Approach Consumer Forum | File a complaint with the District, State, or National Forum based on claim value. District Consumer Disputes Redressal Forum (up to ₹ one crore)State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (₹1 crore to ₹10 crore)National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (above ₹10 crore) |
| File Online | Use the E-Daakhil Portal to file digital complaints. |
| Attend Hearings | Participate in court proceedings and follow up until resolution. |
Importance Of Consumer Rights FAQs
What is consumer rights?
Consumer rights are legal protections that ensure fairness, safety, and transparency for people buying goods and services. They help prevent fraud and promote ethical business practices.
What are the 8 consumer rights?
The 8 consumer rights are the right to safety, to be informed, to choose, to be heard, to redressal, to consumer education, to a healthy environment, and to satisfy basic needs.
What is the importance of consumer awarness?
Consumer awareness is crucial as it enables individuals to make informed decisions better while recognizing unfair practices and exercising their rights.
What is the history of consumer rights in India?
The history of consumer rights in India starts with the Consumer Protection Act of 1986, which aimed to protect consumers from unfair practices. The act was amended in 2019 to address the modern challenges in e-commerce and digital transactions.
What are the importance of consumer rights in India?
The consumer has protection against fraud, legal recourse for grievances, improved product quality, and greater consumer confidence. These rights provide fairness and transparency in business practices.


