Macroeconomics plays a vital role in understanding the performance, structure, and behavior of an economy as a whole. It focuses on broad aggregates such as national income, GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, and fiscal policies. Governments, policymakers, economists, and central banks use macroeconomic theories and models to design national strategies and make economic decisions. However, despite its usefulness, macroeconomics has its own set of limitations that reduce its accuracy, applicability, and effectiveness in the real world. These limitations of macroeconomics arise due to the complexity of economies, the unpredictable behavior of human agents, differences in regional realities, and the challenges in gathering and interpreting data. As economies become more interconnected and complex, macroeconomics often struggles to provide clear and timely guidance.
What is Macroeconomics?
Before diving into the limitations, it’s important to briefly understand what macroeconomics is and what it tries to achieve. Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with the economy as a whole. It looks at aggregate indicators and policies that affect an entire nation or region, rather than focusing on individual consumers or businesses (which is the focus of microeconomics).
The Goals of Macroeconomics Include:
- Ensuring economic growth through GDP expansion
- Maintaining price stability by controlling inflation
- Reducing unemployment through policy and planning
- Achieving balance in the external sector (trade, exchange rates)
- Managing fiscal and monetary policy effectively
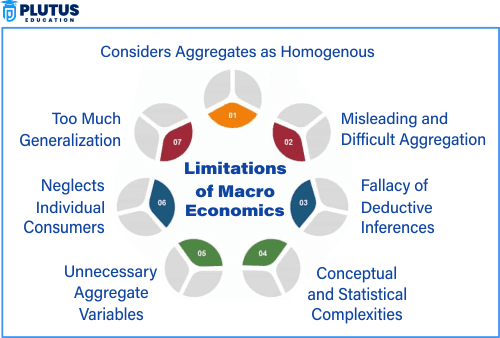
Limitations of Macroeconomics
To accomplish these goals, economists use models, forecasts, and statistical tools. However, the real-world application of these tools often reveals certain shortcomings.
Macroeconomics helps analyze the overall functioning of an economy through aggregates like GDP, inflation, and employment. However, it comes with several limitations that affect its real-world accuracy. Its models often rely on unrealistic assumptions and fail to account for regional and social differences. Delayed data, policy lags, and unpredictable human behavior further reduce its reliability. Understanding these limitations is essential for making informed and balanced economic decisions.
1. Overgeneralization of Economic Models
One of the most commonly cited limitations of macroeconomics is that it often overgeneralizes. Most macroeconomic theories rely on assumptions that do not apply uniformly across all economies or social structures.
Why Overgeneralization Is Problematic
Macroeconomic models are designed to simplify reality. To make models manageable and mathematically solvable, economists use generalized assumptions like:
- All agents are rational
- Markets are competitive
- Prices adjust automatically
- All economies behave similarly
While these assumptions help build theoretical frameworks, they do not always reflect reality.
Real-World Examples:
- A policy that works well in a developed country with a strong financial system may fail in a developing country with a large informal economy.
- Inflation control measures used in Western economies might not be effective in economies where prices are heavily influenced by subsidies or political factors.
Result:
Such generalizations can lead to policies that are either ineffective or even harmful in some contexts. Therefore, the limitations of macroeconomics must be considered when applying models to real-world problems.
2. Inaccuracy and Delays in Data Collection
Another significant limitation is data dependency. Macroeconomic analysis relies heavily on national-level statistics such as GDP, inflation rates, employment figures, and fiscal deficits. However, data collection and interpretation often suffer from delays and inaccuracies.
Reasons for Data Inaccuracy:
- Time lags between data collection and publication
- Use of outdated base years in GDP computation
- Lack of reliable data in rural and informal sectors
- Errors in sampling and estimation
Impact on Policy Decisions:
Delayed or incorrect data can lead to misinformed policies. For example:
- If unemployment data is underestimated, a government might not roll out job creation schemes in time.
- If inflation is misreported, the central bank might take the wrong stance on interest rates.
This shows that macroeconomics is only as reliable as the data it uses, and that is a major limitation when timely decisions are needed.
3. Difficulty in Measuring Non-Market Activities
A key limitation of macroeconomics is that it does not effectively capture non-market activities. GDP and national income calculations typically exclude economic activities that do not involve market transactions.
Examples of Non-Market Activities:
- Household chores and caregiving (especially by women)
- Informal or unregistered employment
- Barter transactions
- Volunteer work and social contributions
Why This Matters:
Excluding these activities gives an incomplete picture of economic health. For instance, in many developing countries, a large part of the workforce operates in the informal sector. Ignoring these activities may cause policymakers to overlook the needs of a huge segment of the population.
Furthermore, unpaid work done at home or in the community contributes to well-being and economic stability, yet macroeconomic models usually ignore it.
4. Time Lag in Policy Implementation and Effects
Even when macroeconomic policies are correct in theory, they suffer from time lags in implementation and effectiveness.
Three Main Types of Lag:
- Recognition Lag – Time taken to recognize that an economic problem exists.
- Implementation Lag – Time taken to design and implement a policy.
- Impact Lag – Time taken for the policy to show results.
Consequences:
- By the time a policy is implemented, the economic situation may have changed.
- Delayed impact may lead to confusion or a lack of public trust in policies.
- Policies like interest rate adjustments may take 6–18 months to influence inflation or investment levels.
Thus, time lag is a major limitation of macroeconomics in rapidly changing environments where immediate action is needed.
5. Inability to Predict Human Behavior
Economic models often assume that individuals, firms, and governments behave rationally. However, human behavior is unpredictable, and emotions like fear, greed, and panic play a significant role in economic decisions.
Real-World Observations:
- Stock markets crash due to panic selling, not rational analysis.
- Consumers hoard goods during uncertainty, causing artificial inflation.
- Governments may make politically motivated decisions that go against economic advice.
This unpredictability weakens the accuracy of macroeconomic forecasts. Models can’t fully capture these human elements, which adds uncertainty to any economic prediction or policy recommendation.
6. Limited Focus on Income Inequality and Social Welfare
Macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth and fiscal deficit do not reflect the distribution of income and wealth in society. A country’s GDP may be rising, but if the benefits go only to the top 10% of the population, it results in widening inequality.
Why This Is a Concern:
- Rising inequality can lead to social unrest.
- Policies based solely on GDP may ignore poverty, education, and health issues.
- Economic growth without inclusive development is not sustainable.
While macroeconomics provides tools to measure and analyze aggregates, it often fails to address the quality of growth or whether it benefits all sections of society. This makes it incomplete for comprehensive development planning.
7. Environmental and Sustainability Blind Spots
Traditional macroeconomic models do not factor in environmental degradation or sustainability. Natural resources are often treated as unlimited or external to the economy.
Examples of Overlooked Environmental Costs:
- Depletion of groundwater or forest resources
- Air and water pollution from industrial output
- Climate change risks and carbon emissions
Economic growth measured in GDP may rise at the cost of long-term ecological damage. This is why many experts advocate for green accounting or sustainable macroeconomic models, which are not yet mainstream.
8. Global Influences Make Predictions Uncertain
In today’s interconnected world, a crisis in one country can affect others. Global oil prices, interest rate changes in the US, or a war in Europe can all impact local economies. Macroeconomics has limited tools to account for these external shocks.
External Factors That Disrupt Macroeconomic Models:
- Global commodity price changes
- Trade wars and tariffs
- Pandemic outbreaks
- Political instability in major economies
These unpredictable external influences reduce the reliability of macroeconomic predictions. Even the best policies may fail when global headwinds are strong.
Limitations of Macroeconomics FAQs
1. What is macroeconomics mainly used for?
Macroeconomics studies the economy at a large scale and helps policymakers manage issues like inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
2. Why is overgeneralization a limitation of macroeconomics?
Because it applies the same models to different economies, which may not share the same structures, needs, or challenges.
3. How does time lag affect macroeconomic policy?
Time lag causes delays between recognizing problems, implementing solutions, and seeing results—making policies less effective.
4. Can macroeconomics predict all economic outcomes?
No. Human behavior, external shocks, and data limitations make exact predictions impossible.
5. Why doesn’t macroeconomics reflect income inequality?
It focuses on aggregates like GDP and national income, which do not show how wealth is distributed across different social groups.