Business services are the cornerstones of modern economic systems because they support organizations operating in various industries. Business services are non-tangible activities that help businesses reach operational efficiency and growth. From IT support and human resource management to logistics and marketing solutions, the nature of business services enables companies to focus on their core activities while outsourcing specialized tasks to experts. These services are now considered essential because of the efforts of businesses to stay competitive, keep pace with technological changes, and respond to customer needs within a dynamic market environment.
What Are Business Services?
Business services are one of the categories of intangible offers, that assist businesses in conducting their operations. Since they lack physical forms, unlike physical products, they play a role in maintaining and enhancing business process efficiency. These include services like IT solutions, financial advisory, legal consultation, logistics, and marketing.
Business services essentially relate to adding value to an organization by bringing expertise, efficiency, and reliability to its business processes. Business services assist companies in saving on costs, staying focused, and improving productivity by delegating specific tasks to outside or internal service providers.
For instance, a firm may utilize a payroll management service that would take care of employees’ salaries, tax deductions, and compliance. This means that the company’s HR department can focus on talent acquisition and employee development. On the other hand, a company’s technological infrastructure could be kept safe and functioning through an IT service provider, which enables smooth business operations.
Nature of Business Services
The nature of business services is characterized by specific attributes that distinguish them from physical goods. These attributes define how these services are produced, delivered, and consumed.
Intangibility
Business services can never be seen or touched and cannot be stored as they exist only in terms of expertise, processes, or actions. For example, a financial consultant’s advice and the software solutions designed by an IT firm are intangible in nature. This intangibility often makes it challenging to measure the quality of services, but it also stresses the importance of trust and expertise in service delivery.
Inseparability
Business services are generally consumed as well as produced at the same time. It is impossible to separate a service such as consulting or customer support from its process of delivery. The interaction between the customer and the service provider usually results in a unique experience for every client. For example, when a business receives a marketing strategy from a consultant, it is both engaging with the service and consuming its benefits in real time.
Variability
Quality varies dramatically, depending on the service provider, context, and particular needs of the customer. The quality of service would depend on several factors: the skills of employees providing the service, the tools utilized, and client expectations, for example. Thus, two different companies that might have accessed the same IT support service might still experience a different degree of satisfaction, based on the specific requirements of their interaction with the service team.
Perishability
Services cannot be stockpiled and used at some later time. When a business does not avail itself of a service at the time that service is offered, then that service is lost. Unoccupied consulting hours or unused training sessions represent a lost resource for the service provider. That perishability forces businesses to plan and schedule services to ensure the most value is received.
Client-Specific Customization
Unlike standardized goods, business services are often tailored to meet the unique requirements of individual clients. A logistics service provider might create a custom supply chain solution for a retail company, while a legal advisor may offer tailored compliance strategies for a healthcare organization. This customization ensures that the services align closely with the client’s goals and challenges.
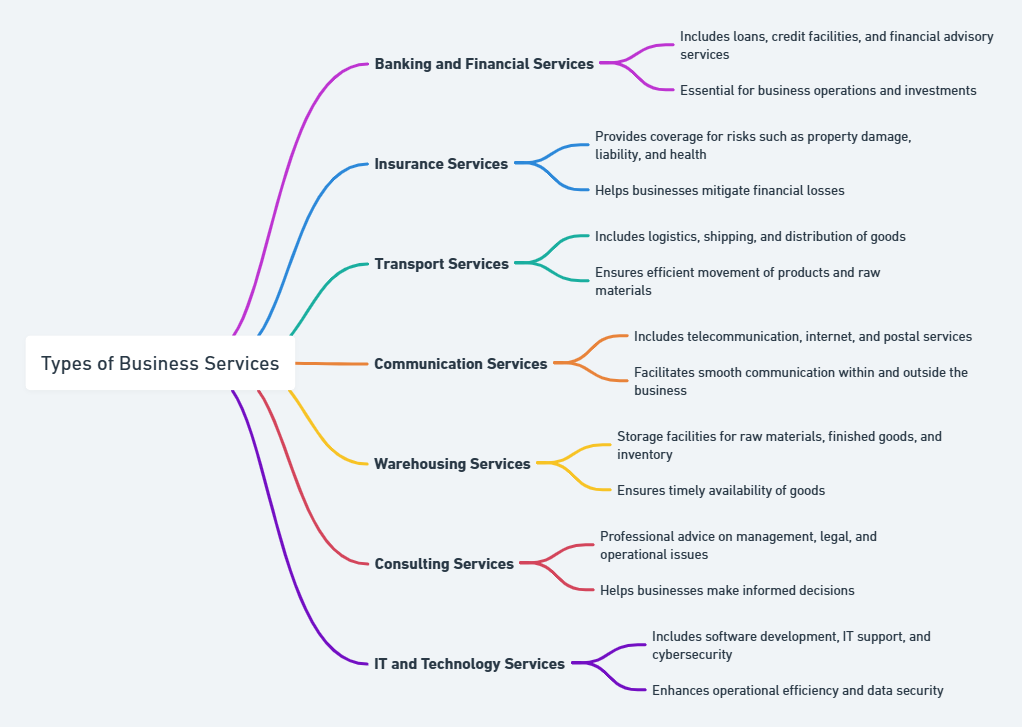
Types of Business Services
Business services encompass a wide range of functions that cater to various organizational needs. These services are crucial for ensuring smooth operations and achieving strategic objectives.
Professional Services
Professional services include advice and solutions from qualified professionals, for example, law, accounting, and consulting. Such services are essential to the resolution of complex business issues and compliance with the regulatory requirements.
For example, legal services assist in contract drafting, resolving disputes, and maintaining regulatory compliance. Accounting services also encompass financial reporting, tax planning, and audits, which allow organizations to maintain financial health and transparency.
IT Services
IT services are a must-have in the digital age. In this regard, it manages infrastructure, cybersecurity, software development, and data analytics. IT services are considered to be a factor by which businesses can benefit the most from technology.
For example, an online shop uses IT services like maintaining a website, customers’ personal data security, and online smooth transactions. Also, cloud computing facilities are more flexible and scalable since they allow most businesses remote access to information and applications.
Financial Services
Financial services involve banking, investment advisory, and insurance services. All these services will help the business manage its finances and reduce risk by making wise investment decisions. For example, a bank could provide a loan to expand, and an insurance company will cover damage to property or liability claims.
Human Resource Services
HR services manage the workforce in an efficient manner. These services include recruitment, payroll processing, employee training, and performance management. Outsourcing the HR functions of a business can save that time and channel it for strategic activities.
For example, a startup might use a recruitment agency to find skilled employees quickly, while a larger corporation could outsource payroll management to ensure timely and accurate salary disbursements.
Logistics and Supply Chain Services
Logistics services involve the movement, storage, and distribution of goods. These services are critical for businesses that deal with physical products. A logistics partner might handle inventory management, transportation, and order fulfillment, ensuring that products reach customers efficiently.
For instance, an online retailer relies on logistics services to manage its warehouse operations and deliver products to customers across different regions.
Marketing and Advertising Services
Marketing services help businesses promote their products and build brand awareness. These services include market research, digital marketing, content creation, and public relations. A strong marketing strategy ensures that businesses connect with their target audience effectively.
For example, a digital marketing agency might develop a comprehensive campaign involving SEO, social media, and email marketing to boost a company’s online presence and drive sales.
Importance of Business Services in Modern Enterprises
Business services are the backbone of contemporary enterprises. They allow organizations to:
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing non-core activities, businesses can concentrate on their primary goals and expertise.
- Enhance Efficiency: Specialized service providers bring expertise and advanced tools, improving operational efficiency.
- Reduce Costs: Outsourcing services can be more cost-effective than maintaining in-house capabilities.
- Adapt to Change: Business services offer the flexibility to scale operations and adopt new technologies, helping businesses stay competitive.
Nature of Business Services FAQs
What are the primary characteristics of business services?
Business services are intangible, inseparable from their consumption, variable in quality, perishable, and customized to client needs.
Why are IT services critical for businesses today?
IT services enable businesses to leverage technology for efficiency, data security, and innovation, ensuring competitiveness in the digital era.
How do logistics services benefit businesses?
Logistics services streamline the supply chain, ensuring timely delivery of goods, optimal inventory levels, and reduced operational costs.
Can marketing services help small businesses?
Yes, marketing services like SEO and social media campaigns enable small businesses to reach their target audience effectively and affordably.
What role do professional services play in business growth?
Professional services provide expertise in legal, financial, and strategic domains, helping businesses make informed decisions and comply with regulations.


