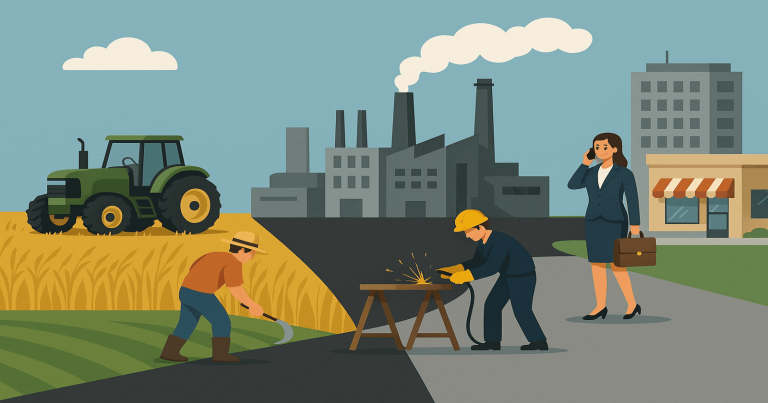
An economy means the system of making, using, and sharing wealth in a country. In simple words, it shows how a country produces goods, gives services, creates jobs, and earns money. Every country has its own economy based on its resources, people, and industries. India has a mixed economy. This means both the government and private people can run businesses. The economy of India is also developing, which means it is growing but still faces challenges like poverty, unemployment, and uneven development. People in India do many kinds of jobs. Some grow crops, some work in factories, and some offer services like teaching or running shops. All the jobs people do fall into different parts of the economy. These parts are called sectors of the Indian economy. Each sector plays an important role in the country’s growth. They help in earning income, creating jobs, and meeting people’s needs.
What are Sectors of Indian Economy?
Sectors in the economy are groups of economic activities. These are divided based on the type of work people do. When we understand these sectors, we can easily see how farming, factories, and services are linked.
There are mainly three sectors of Indian economy based on activities:
- Primary Sector – Uses natural resources.
- Secondary Sector – Converts natural things into products.
- Tertiary Sector – Offers services that support both of the above.
These sectors are not separate from each other. They work together. For example, wheat is grown in the primary sector, made into bread in the secondary sector, and sold in a shop through the tertiary sector.
Primary Sector of Indian Economy
The primary sector of the Indian economy includes all work where people use nature directly. Farmers grow crops using soil and water. Fishermen catch fish from rivers and seas. Workers take out coal, iron, and oil from the ground. Forest workers collect wood, fruits, and herbs. These jobs come directly from nature and do not use machines much.
Importance of the Primary Sector
People in villages do most of the work in the primary sector. Many families grow wheat, rice, and vegetables on small farms. They use cows and buffaloes for milk and help in farming. Some families keep goats and sheep. They use their wool and milk. Fishermen go to rivers and seas. They bring fish and prawns. Forest workers collect honey and wood.
The primary sector of Indian economy feeds the whole country. It gives food and raw materials to other sectors. It also gives jobs to a large number of people in India, especially in villages.
People also mine coal, gold, and salt from the land. They use tools and dig the ground to find minerals. These minerals help in making things like steel, power, and medicines. India has big coal and iron mines in states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
Problems in the Primary Sector
Farmers face many problems in this sector. They do not get enough water to grow crops. Many depend only on rain. Poor rains cause crop loss. Farmers do not use good seeds or machines. They work hard but earn little. They also do not get good prices for their crops.
Forest workers also face danger. Wild animals and harsh weather make their work hard. Fishermen face storms and dirty water. Many lose fish because of pollution in rivers and seas. Mining workers get hurt due to poor safety at work.
Growth of the Primary Sector
The government helps farmers with better seeds, loans, and free training. It builds canals, wells, and cold storage places. Farmers now learn about modern farming on mobile apps. Schools in villages teach about soil and farming. More children now help their parents in smarter ways.
Banks give farmers crop loans. The government also runs Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana to save farmers from crop loss. Forest laws help people collect forest goods safely. Fishermen get nets, boats, and cold storage to keep fish fresh.
Secondary Sector of Indian Economy
The secondary sector of Indian economy makes new things from the raw materials of the primary sector. People in this sector work in factories, construction, and small units. They turn cotton into clothes, wheat into bread, and wood into furniture. This sector includes all industries that make finished goods.
Role and Importance of the Secondary Sector
This sector helps build the country. People build roads, houses, and flyovers. Brickmakers, cement workers, and engineers do this work. Others work in factories that make paper, steel, and biscuits. The work needs tools, machines, and energy like electricity or oil.
Many people work in textile mills, food processing units, and automobile factories. Workers in the secondary sector use skills and machines. They earn more money than those in the primary sector. Cities grow when more factories open. Many small shops also grow near factories.
The secondary sector of Indian economy adds value to raw materials. It turns sugarcane into sugar and clay into bricks. The sector also boosts exports. India sells clothes, machines, and chemicals to other countries.
Key Examples of econdary Sector Industries
- Textiles: Uses cotton and jute to make clothes.
- Cement: Uses limestone and coal to make cement for houses.
- Automobiles: Uses metal to make cars and bikes.
- Steel Plants: Uses iron ore and coal to make steel rods and sheets.
These industries grow in cities like Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, and Bengaluru. Small factories also grow in towns like Kanpur, Surat, and Ludhiana.
Problems Faced in Secondary Sector
Factory workers often face unsafe working areas. They get low wages and no job safety. Many factories use old machines. They produce more smoke and waste. Some industries throw dirty water into rivers. These problems harm people and nature.
Power cuts stop work. Many small factories close due to lack of money or tools. People leave villages and rush to cities for jobs. Cities get crowded. Workers then live in slums.
Support to Secondary Sector
The government supports this sector with schemes like Make in India. It helps open new factories. It gives land, tax benefits, and training. It builds industrial parks and special zones.
Banks also give small loans to factory owners. Youth in cities now join skill training schools. They learn welding, machine work, and sewing. Women also join cottage industries to make food items, clothes, and crafts.
Tertiary Sector of Indian Economy
The tertiary sector of the Indian economy provides services. It does not make goods but helps both other sectors. People in this sector teach, drive, cook, sell, and take care of health. Banks, shops, transport, IT companies, and hotels also belong to this sector.
Growth and Value of the Tertiary Sector
The service sector helps farmers and factory owners. Teachers help children learn. Doctors care for health. Banks help with money. Drivers take goods from farms to shops. Shops sell goods to people. Mobile services and the internet help everyone stay connected.
The tertiary sector of the Indian economy grows very fast. In cities, most jobs now come from services. Software engineers, call center workers, and delivery agents earn money from services.
Many tourists come to India. They visit temples, palaces, and beaches. Hotels, guides, and shops earn from tourists. Transport workers take tourists around cities.
Examples of Services in the Tertiary Sector
- Education: Teachers in schools and colleges.
- Health Care: Doctors, nurses, hospitals.
- Banking: People working in banks and ATMs.
- Transport: Bus drivers, train staff, and flight workers.
- IT Sector: Software developers, data workers, and support teams.
- Retail: People working in malls, shops, and online stores.
Big cities like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Noida grow as IT hubs. They give jobs to youth. Women also find more jobs in offices, banks, and call centers.
Challenges in the Tertiary Sector
Not all people in this sector get good jobs. Some work as helpers or hawkers. They earn little. Many work long hours without holidays. Village areas do not have good schools, banks, or hospitals. People walk far to get services. Also, new services need internet, roads, and training. Villages lack these. So the gap grows between cities and villages. Poor people do not use good services.
Government Steps to Improve the Tertiary Sector
The government builds smart cities with better roads, hospitals, and schools. It opens digital service centres in villages. These centres help with online forms, farming tips, and banking. Banks now open more branches in small towns. They also give digital banking.
The IT sector grows fast. It earns foreign money and gives jobs. India exports software to the USA, UK, and Europe. Schools now teach coding and computers to kids. Online classes grow in cities and villages.
Sectors of Indian Economy FAQs
Q1: What are the sectors of the Indian economy?
The sectors of the Indian economy are primary (farming and nature work), secondary (factory and building work), and tertiary (services like teaching, health, and banking). These sectors show how people work and earn.
Q2: Why is the primary sector important for India?
The primary sector feeds the country and gives jobs in villages. It also gives raw materials like cotton, milk, and fish. These materials help factories and service jobs grow.
Q3: How does the secondary sector help the Indian economy?
The secondary sector makes goods from raw items. It builds homes, machines, and clothes. It creates better jobs and grows cities. It helps India earn money from exports.
Q4: What does the tertiary sector include?
The tertiary sector includes services like transport, health, education, and IT. People help others in this sector. It gives the highest number of jobs in cities.
Q5: Which sector is growing fast in India?
The tertiary sector grows the fastest in India. IT, banks, and health care grow fast. These services give better pay. They also support factories and farms to grow more.