Trade, an activity essential to any economic system, involves buying, selling, or exchanging goods and services. Trade links markets, encourages growth, and increases personal standards of living. A shopkeeper selling groceries next door and a multinational corporation trading on many continents make trade work to allocate resources efficiently, create innovative products, and build global partnerships. This article explains and examines the classes of trade, trade importance, and practical cases to enlighten students, businesspeople, and professionals on how trade touches their lives.
What is Trade?
Trade is more than mere exchange; it facilitates resource access, encourages specialization, and creates economic ties. Thus, it is an engine of economic growth for two reasons: it allows nations and corporations to procure what they lack and to exchange what they have in excess. Trade creates innovation and jobs through international cooperation in a truly interdependent modern context.
Definition of Trade
Trade is voluntary and involves selling and buying goods and services between parties. It can be local in a city or cross international borders. Whether selling handmade products locally over the Internet or exporting vehicles to other countries, trade is essential for generating value or income.
Purpose of Trade
Regardless of scale, trade satisfies needs and wants that local production cannot meet. In other words, it allows for more efficient and profitable use of resources by exchanging surplus for desirable products unmatched by forms of production, because of which production involves greater overhead. It thus provides liquidity between producers and consumers by making products available and accessible.
Role of Trade in Economic Systems
Trade forms the basis of all economic systems, whether capitalist, socialist, or mixed. It enhances production efficiency, offers a pricing mechanism, and provides competitive encouragement. Trade permits specialists in geographic regions to concentrate on industries with comparative advantages.
How Trade Improves Resource Allocation?
Trade helps in the due process of the flow of ultimate scarcities. Countries and businesses can concentrate and organise the production of those goods to achieve maximum efficiency concerning their better use, trading for all shared goods with an emphasis on eliminating waste for productivity. This creates a win-win situation regarding cost savings and productivity improvement globally.
Increased Trade and Wider Markets
Trade allows a business to operate beyond the local market, to the national or even international stage. Such borders create huge income possibilities and economies of scale, allowing a larger company to design products and strategies based on divergent exposure to various consumer preferences.
Types of Trade
Trade may be divided into different types according to purposes, scales, participants, and regions. Understanding all these types enables individuals and companies to make better decisions about when and where to buy or sell goods and services. These types range from a daily media of trade in a local market to corporate exchanges in volumes so high that they are of the utmost importance to every economy.
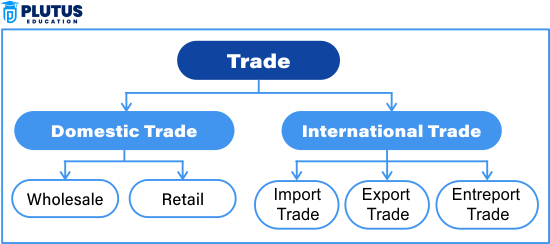
Domestic Trade
Domestic trade is the term used for transactions carried out inside the territory of the same country, including buying and selling operations between persons, companies, and retailers guided by analogous laws and currency systems. It supports the functioning of national economies and generates occupational opportunities for the local market.
Main Characteristics of Domestic Trade
Domestic trade is bound by the laws applicable in the country, in the local currency, with fewer regulatory hurdles. It aids regional development, boosts the small and medium enterprises sector, and ensures speedy delivery, emphasising after-sales service.
Retail Trade
Retail trade sells goods or services in tiny amounts at a retail price to final consumers. This trade is most visible in shops, malls, and online marketplaces. Retailers purchase their products from wholesalers and thus mark up prices over wholesale prices to earn a profit. This adds to the comfort and ease for the average buyer.
Wholesale Trade
Wholesale trade is the making and receiving of goods in bulk. A wholesaler buys products from a manufacturer and sells them to retailers or institutional buyers. This decreases unit costs, and retailers can efficiently achieve control over stock for better economic handling. This is just one part of the supply chain.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Trade
Many trading transactions happen between two businesses, termed B2B deals; for instance, the textile manufacturer can supply fabrics to a garment exporter. Typically, characteristics that define B2B deals are volumes, contractual terms, and longer sales cycles, making them the essence of industrial trade relations.
International Trade
International trade links countries together and makes the global market accessible. In other words, it allows nations to import things they lack and export stuff they can produce efficiently. His exchange brings up productivity and enriches diplomatic relations while ensuring technological progress. Any business seeking global expansion should learn the types and modes of international trade.
Definition of International Trade
“International trade” defines the buying and selling goods and services across boundaries. It allows countries to benefit from each other’s strengths, such as labour, resources, and/or innovations. International laws, treaties, and trade organisations govern this trade.
Import and Export Trade
Imports flow into a country from outside, while exports are goods brought to other countries. For example, India imports oils and exports textiles. These activities generate revenue, solve shortages, and balance production with demand.
Trade Agreements and Tariffs
Trade agreements are important instruments for governments to reduce trade restrictions, for instance, by establishing free trade areas or customs unions. Tariffs are levies on imports that may protect local industries while burdening consumers. Therefore, such policies change the geographical structure of trade concerning the nature of trade flows involved and the strategies they evolve in the different geographies.
Global Supply Chains
Modern manufacturing, for example, involves many countries. An automobile is designed in Germany, built in India, and sold in the United States. Such systems are called global supply chains or interlinked production, which depend on efficient international trade to connect them.
Currency and Exchange Rates
Different currencies may make dealings international; thus, exchange rates are essential. Home currency gain will cause a loss from exports due to the competitive pricing of imports. Companies can manage such currency shocks through hedging or a pricing strategy.
Special Forms and Modern Types of Trade
Trade is defined as being beyond physical or traditional markets. In today’s diversified economy, trade, which is modern and specialized, plays a pivotal role. Such include the e-commerce site, stock market commodities, and other traditional systems like barter, which many area people still subscribe to.
Barter Trade
Barter is trade without money through direct replacement of goods or services. It is one of the oldest forms of trade, still having an informal or remote economy. Unlike standardised pricing, barter offers a practical alternative when a currency is unavailable.
E-Commerce Trade
E-commerce involves digitally buying and selling goods and services through platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, and Alibaba. It is speed, accessibility, and comfort for companies and consumers. This latest trade model has high-growth opportunities from digital wallets, mobile apps, and 24-hour access.
Capital Market Trade
Capital trades involve selling and buying securities like shares and bonds in exchanges such as the BSE and NSE. This type of trade is proper in mobilising businesses’ capital while providing avenues of wealth generation for investors. Plutus Education offers expert-led capital market courses, which facilitate hands-on trading knowledge for learners.
Commodity Trade
Natural resources such as oil, gold, or wheat are exchanged through this trade. Commodities being traded in a special fashion depend on global market conditions. Traders keep price risks through futures contracts, which are important to the global economy.
Why is Trade Important for Economic and Social Development?
Trade moves much more than products. It transforms economies, creating jobs and income, transferring technology, and improving living conditions. Importantly, trade teaches countries how to strengthen their local industries and build stronger global networks. Thus, trade is development’s non-negotiable pillar.
Fosters Economic Growth
Trade increases economic output because of greater market access and access to materials and technologies. This creates a strong investment environment and new industries. More trade-oriented countries grow faster and easily attract foreign investment.
Creates Employment Opportunities
In the trade services such as warehouse and shipping, retail, and finance, millions of jobs are created. International trade creates job openings in export sectors, which are, most of the time, high-paying and skill-intensive, hence building human capital.
Enhancing Living Standards
Trade liberalization has expanded consumers’ rights to goods at lower prices, fostered more competition, and improved quality. Today, the consumers have access to international brands and innovations, majorly due to trade liberalization.
An Additional Access to Basic Need
There is nothing a country can produce that suits all its needs. Trade allows countries to import essentials such as food, energy, and medicines. This provision becomes crucial for maintaining stability during crises or shortages.
Encourages Growth in Technology and Industry
Companies adopt state-of-the-art technologies and increase productivity while being exposed to competition in global marketplaces. As much as trade exposes domestic firms to innovation and upgrades, it also does so at an international best practice level.
Types of Trade FAQs
1. What are the main types of trade?
They include domestic, international, e-commerce, capital market, commodity, and barter trade.
2. How does international trade benefit a country?
It increases GDP, supports job creation, and provides access to resources and technologies not available locally.
3. What is the difference between wholesale and retail trade?
Wholesale trade sells goods in bulk to businesses, while retail trade sells smaller quantities directly to consumers.
4. What are the advantages of e-commerce trade?
E-commerce offers convenience, global reach, cost efficiency, and 24/7 accessibility for buyers and sellers.
5. How does trade contribute to economic development?
Trade drives innovation, improves efficiency, creates employment, and raises living standards in developed and developing economies.


