Data is crucial in every field, whether business, science, or technology. The sources of data provide the foundation for decision-making, research, and analysis. These sources help individuals and organizations collect the information necessary to make informed choices, generate insights, and solve problems.
Data comes from various sources, each serving different purposes and offering unique benefits. Understanding the sources of data is essential for anyone involved in research, analysis, or data-driven decision-making. Data can be broadly categorized into internal and external sources, with each offering its strengths and weaknesses.
In this article, we will explore the concept of data, the different sources from which it can be obtained, and how these sources play a crucial role in different industries and research.
What is Data?
Data refers to raw facts, figures, or statistics that are collected for analysis. It can exist in various forms, such as numbers, text, images, audio, or even video. In essence, data provides the foundation for knowledge and understanding.
Data is often categorized into two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative data includes descriptive attributes, while quantitative data deals with measurable numbers. Both types of data are essential in decision-making and can be collected from various sources like surveys, observations, or experiments.
In research, data is vital for concluding, testing hypotheses, and proving theories. Without data, it would be difficult to develop solutions to problems, make predictions, or evaluate outcomes. Therefore, understanding where data comes from is an essential part of any analytical process.
What Are the Sources of Data?
The sources of data are the places or systems where data is collected, stored, and accessed. These sources can vary based on the nature of the data needed and the specific industry or research area. Data sources are generally categorized into two major groups: internal and external.
Internal Sources of Data
Internal sources of data refer to the data that an organization collects and stores internally. These sources are typically generated within the company and are directly related to the organization’s operations.
Internal sources of data can come from a variety of places, such as:
- Company databases: These contain records related to customers, sales, inventory, and employees.
- Financial records: Includes data related to profits, expenses, and balance sheets.
- Employee feedback: Organizations collect data from employees to improve internal processes or customer service.
- Surveys: Companies often collect data through surveys sent to their employees, customers, or other stakeholders.
One of the key benefits of internal sources is that organizations have full control over this data. They can ensure the data is relevant, accurate, and tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, internal data is often collected over a long period, providing a rich history that can be analyzed for trends and patterns.
The downside is that internal sources may not provide enough diversity in the data. For instance, company data may be limited in scope and may not represent external factors affecting the organization. It is often necessary to combine internal data with external data to get a full picture.
External Sources of Data
External sources of data refer to data that is collected from outside the organization. These sources are especially useful when an organization needs information about trends, competitors, market conditions, or customer behaviors that go beyond its operations.
Examples of external data sources include:
- Government reports: These include census data, economic indicators, and demographic reports published by government agencies.
- Market research: Reports and data gathered from industry analysts or research firms.
- Social media: Platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram provide vast amounts of data about consumer behaviors and opinions.
- Third-party databases: Many organizations provide data related to industries, consumer behavior, or global trends, such as Nielsen or Statista.
The advantage of using external sources is that they allow organizations to access a broader range of data that they might not have internally. However, external data often comes with limitations, such as privacy concerns, accuracy issues, or lack of control over how it is collected.
Experimental Sources of Data
Experimental sources of data involve collecting data through controlled experiments or observations. These sources are commonly used in scientific research, clinical trials, and studies where researchers manipulate variables to observe outcomes.
Key examples of experimental sources of data include:
- Laboratory experiments: Controlled settings where variables are manipulated to observe their effects.
- Clinical trials: Medical experiments where data is collected about treatments, drugs, or interventions on participants.
- Surveys and questionnaires: Researchers may create experiments using surveys to understand responses based on different factors.
Experimental data is considered highly reliable because researchers can control the conditions under which the data is collected. However, it may not always represent real-world conditions, as controlled settings may differ from natural environments.
Types of Data Sources
The sources of data can be broken down into several types based on how the data is collected, processed, and applied. These sources help organizations decide on the methods they will use to gather data, analyze it, and make decisions.
Primary Data Sources
Primary data sources involve data that is collected firsthand for a specific purpose. This data is original and has not been previously processed or analyzed.
- Surveys: Organizations conduct surveys to gather opinions, feedback, or demographic data directly from individuals.
- Interviews: In-depth one-on-one interviews provide qualitative data.
- Experiments: Experimental research in a controlled environment.
- Fieldwork: Data collected in real-world settings or natural environments.
Primary data sources are often more time-consuming and costly to gather but provide highly relevant, specific data. The data made to a specific problem or research question.
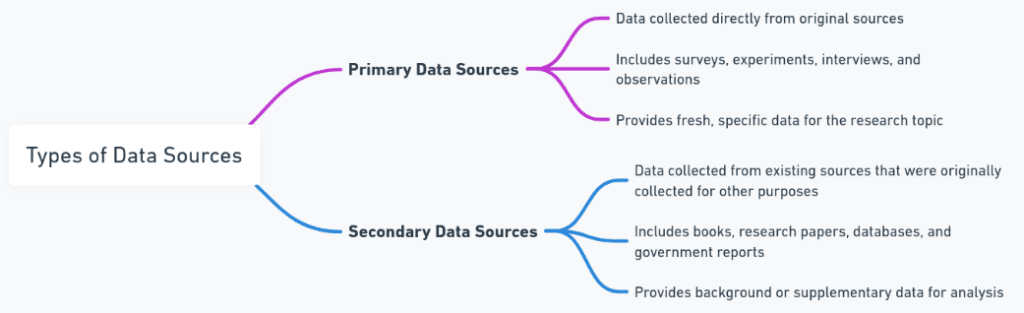
Secondary Data Sources
Secondary data sources consist of data that has already been collected and processed for some other purpose. Researchers or organizations use secondary data to save time and resources.
- Published reports: Government agencies, think tanks or industry groups often release reports with reusable data.
- Academic research: Studies, journals, or dissertations published by universities.
- Public databases: Open data from various sectors, such as health, economics, or transportation.
Secondary data sources can be very useful in providing a broad understanding of a topic or situation. However, these sources may not always align with the specific needs of the researcher.
Tertiary Data Sources
Tertiary data sources refer to data that has been summarized or compiled from primary and secondary data. This type of data is useful for quick insights but lacks the detail of primary or secondary sources.
- Encyclopedias: Offer summarized data on various topics.
- Indexes: List sources of data or reports without providing raw data.
- Data directories: These catalog various datasets across different domains.
Tertiary sources are useful for a general overview, but researchers often need to refer to primary or secondary data sources for detailed analysis.
Sources of Data FAQs
What are the primary sources of data?
Primary sources of data include surveys, experiments, fieldwork, and interviews. These sources provide original, firsthand data specifically collected for a particular study or project.
What are the differences between internal and external sources of data?
Internal sources of data come from within an organization, such as sales records or customer databases. External sources refer to data collected from outside the organization, like government reports or market research.
What is experimental data?
Researchers collect experimental data through controlled experiments, manipulating variables to observe outcomes. This type of data is often used in scientific studies and clinical trials.
How do secondary data sources help businesses?
Secondary data sources, such as published reports or academic studies, provide pre-collected data. Businesses can use this data to save time and resources, although it may not always cater to specific needs.
What is the role of tertiary data sources?
Tertiary data sources provide summarized or compiled data, often from primary and secondary sources. They are useful for getting an overview of a topic but lack detailed insights.


