Leasing is a financing system that is a big leap for the entrepreneurs and individuals that need to buy assets and don’t want to spend all the money themselves. They can use the building, the car, the tools for a set time and make the regular payments at the same time. Leasing is the most common in the real estate industry, where tenants rent the homes and offices, and in business, where companies lease machinery or vehicles. By knowing what a lease actually is, people and companies are enabled to do business with their finances smartly, avoid the huge front costs and manage their resources properly. This article offers to its readers the explanation of leases, the different types, how they function and the benefits of them in thorough details.
What is a Lease?
A lease is a legal agreement that enables a person or a company to utilize an asset or an estate that belongs to another party for a predetermined period while payment for the time is made. A lease is the most commonly used tool when it comes to renting property, vehicles, and equipment. The main function of leasing is to help individuals and businesses to access high-cost assets that they would not be able to buy outright otherwise.
Leasing deals set out the basic elements, such as rent amounts, the duration of the contract, responsibilities, and penalties for any violations. Understanding what a lease is and both the landlord’s and the tenant’s rights are is essential. It is the agency that ensures that both parties live up to their promises and solve disputes.
Lease Definition
A lease is a contract that involved the two parties, lessor (owner) and lessee (user). Where a lessee gets the right to use an asset for a specific time and pays a fixed amount. The lease agreement contains conditions such as payment terms, maintenance duties, and renewal options.
Based on the agreement, leases can be either long-term or short-term. The lease document is legally binding and represents both the parties’ rights. Businesses and individuals use properties, equipment, and vehicles leases to control their expenses and thereby, gain more financial flexibility.
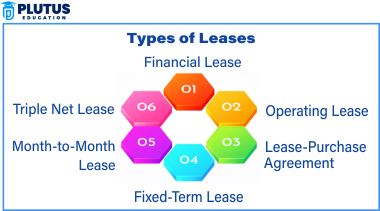
Types of Leases
There are several contract terms and asset types that areleased by three distinguished lease types. Without knowledge of a lease type, if it is a lessee or lessor, then for their needs it is one among the best options to choose.
1. Financial Lease
Financial leases, which are also known as capital leases, are contracts that run over a long period of time during which the lessee enjoys some rights that are comparable to ownership rights. Furthermore, the lessee is required to pay for the insurance and maintenance and also might have to bear some tax liability. The most common areas where it is utilized include machinery, along with real estate, and vehicles, all of them offering long-term stability.
2. Operating Lease
An operating lease is a lease agreement that does not extend to the transfer of ownership upon its expiry; it involves the return of the asset to the owner. The lessor takes care of its upkeep. It is utilized for office spaces, equipment, and vehicles.
3. Lease-Purchase Agreement
A lease-purchase agreement provides the lessee with the right to lease an asset and then purchase it at the conclusion of the lease period. The lease payments are typically considered to be partial payments for the cost of owning the goods that makes it an attractive alternative for those who plan to purchase the goods. This type of lease is found in real estate and second-hand vehicle sales. Lease-purchase agreements are flexible, but they also call for close attention to contract terms which may result in unexpected costs. The tenants should learn about the financial commitments and the purchase terms beforehand by doing real estate contract review. In the case of a lease-purchase agreement, the lessee pays rent and has the right to buy the asset with the help of the last rent payment. This is a popular way of acquiring automobiles and homes.
4. Fixed-Term Lease
A fixed-term lease is a lease with a specific start time and end date. The lessee is bound to remain through to the end of the lease period, unless they have the option to break it. This type of lease is very secure for rental agreements and other lease terms, and is therefore the choice of many for apartments, some commercial properties, and equipment rentals. Rent prices are fixed for the most part throughout the lease, thereby giving tenants a“ heads-up” view of their financial obligations. However, early termination of the lease may lead to a loss of money or the deposit. They are best for those who wish for the long-term in case there are any unexpected changes. They provide a guarantee to the landlords and the tenants that the rights and obligations are clear and stipulated the entire lease period.
5. Month-to-Month Lease
This is a short-term lease where the tenant or landlord can end the contract with little notice, usually 30 days. It is applied primarily for rental houses where tenants require temporary shelter or landlords want temporary occupancy. It offers convenience and flexibility to both parties. But it might be accompanied by frequent rent revisions and fewer securities than long-term leases. Month-to-month leases are best suited for those who are not sure of their long-term housing situation or for landlords who wish to retain control over rent levels and tenant choice.
6. Triple Net Lease
As already mentioned, a lease involving net three is widely used in the commercial real estate sector where the tenant is liable for the rent, property maintenance, taxes, and any insurance claims. The landlord, on the other hand, takes on the responsibility of paying the landlord by way of the tenant paying for the rest of the financial burden. The property segment benefits those investors who wish to receive a constant flow of money without any operating expenses. Businesses attach great significance to long-term stability and thus, the NNN lease is the most common, although they still have to count in other costs besides the rent. Thorough financial planning is the key when such agreements are being signed, as tenants are the ones who pay for the main property expenses. In other cases, triple net leases are suitable for either the corporations that wish to dominate the property maintenance and the tax planning or the tenants who might prefer to take on the two significant costs themselves.
How Do Leases Work?
Leasing is basically a highly structured negotiation process that also includes formal contract agreements and payment. This is how one usually rents it out:
1. Lease Agreement Formation
- The lease agreement between the lessor and the lessee will include discussions about things such as the payment of rent, contract duration, and who will have what responsibilities.
- The most important piece of work on the lease was the creation of a formal document, which includes all of the terms.
2. Signing the Lease
- When either or both of the tenants and the landlord have signed the lease, then it is considered to be a legally binding contract.
- One of the situations in which a lessee may be required to deposit security before being allowed to move in or to use the asset is very common too.
3. Payment Terms
- The tenant shall be bound to pay the lump sum on a monthly or quarterly basis.
- Few leases have the insurance and maintenance expenses included in the prescribed amount.
4. Maintenance and Usage
- Using the asset as per the terms by the lessee is a matter of good practice and is the best way to keep the asset in good condition.
- In some leases, the lessor takes care of maintenance.
5. Lease Expiry or Renewal
- Let us assume that the tenant wants to break the deal and walk away he instead pays the penalty. But the tenant might retain the asset or renegotiate the lease placing the interest in the asset on the rest (subject to availability).
- Furthermore, some leases allow early termination at a penalty fee.
Advantages of Leasing
There are various major advantages of leasing. Being well-posed to financial flexibility, management of cash flow, and the reduction of ownership burdens are the major advantages of leasing respectively. Both individuals and businesses see leasing as a way to save money.
Lower the Initial Costs
Leasing allows people to use a lot of things that were otherwise out of their reach because they did not have the money to buy them right away. This is especially the case for companies that need machinery, vehicles, or office space but do not have the capital to buy them immediately.
Predictable Expenses
The agreements for the lease typically come with set monthly payments, which makes it easy for both individuals and companies to plan how they will spend their money. In fact, unlike owning something where maintenance and repairs are possible unanticipated expenses, a lot of times are furnished with those services.
No Maintenance Hassles
In many cases, a lot of the leases that you might want to have a part of the maintenance are already included so you do not have further costs or responsibilities. The lessor is responsible for repairs and ensures the asset is well taken care of.
Flexibility in Asset Management
Short-term leases give the flexibility of frequently updating equipment and other assets by the company. In this case, it is advantageous for businesses working in the technology industry and those that need to keep up with technological advancements.
Tax Benefits
Companies tend to ignore the fact that lease payments are normal operating expenses and therefore can be deducted from the expenses before taxes. Leasing, thus, offers a tax-efficient choice for companies that are trying to handle their expenses in a strategic manner.
Access to High-Value Assets
Leasing is the process of renting out instead of buying or otherwise obtaining property, machinery, or vehicles that are valuable at a cost that individuals or companies might be unable to afford. Expansion and operating efficiency are possible without huge investments.
Relevance to ACCA Syllabus
Leases are covered under IFRS 16, which is a key standard in ACCA’s Financial Reporting (FR) and Strategic Business Reporting (SBR) papers. Lease accounting is ACCA candidates’ key to preparing financial statements and meeting international accounting standards compliance. It is essential to tunnely and discern financial reports, depreciation schedules, and off-balance-sheet impact valuation are the financial factors that are crucial for interpretation of the lessee’s financial situation. The negotiation of a bond commission on the stated face value of a bond is worth the difference.
What is a Lease ACCA Questions
Q1: Which IFRS standard deals specifically with leases?
A) IFRS 15
B) IFRS 9
C) IFRS 16
D) IFRS 13
Ans: C) IFRS 16
Q2: Under IFRS 16, how is a lease recorded in the lessee’s financial statements?
A) As an expense in the income statement only
B) As a liability and a right-of-use asset
C) As an off-balance sheet transaction
D) Only as a contingent liability
Ans: B) As a liability and a right-of-use asset
Q3: Which of the following is NOT a criterion for classifying a lease as a finance lease?
A) The lease term covers the major part of the asset’s useful life
B) The present value of lease payments is substantially all of the asset’s fair value
C) The asset is returned to the lessor at the end of the lease term
D) The lessee gains ownership at the end of the lease term
Ans: C) The asset is returned to the lessor at the end of the lease term
Q4: What impact does IFRS 16 have on financial ratios?
A) Increases return on assets (ROA)
B) Reduces EBITDA
C) Increases debt-to-equity ratio
D) Increases net income
Ans: C) Increases debt-to-equity ratio
Relevance to US CMA Syllabus
The US CMA (Certified Management Accountant) syllabus includes lease accounting under Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control. CMAs must understand lease classifications, financial statement impact, and lease expense recognition. Lease-related decisions influence cost control, capital investment, and financial strategy, which are key elements in managerial accounting.
What is a Lease US CMA Questions
Q1: Under US GAAP (ASC 842), which of the following is a key feature of an operating lease?
A) The lessee records both an asset and a liability
B) The lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis
C) The lessee gains ownership of the asset at the end of the lease
D) The asset is classified as a capital expenditure
Ans: B) The lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis
Q2: How does a finance lease impact the financial statements under US GAAP?
A) Lease payments are expensed when paid
B) Interest and amortization are recorded separately
C) The lease is treated as an off-balance sheet liability
D) It has no impact on the balance sheet
Ans: B) Interest and amortization are recorded separately
Q3: What is the main difference between a finance lease and an operating lease under US GAAP?
A) Operating leases transfer ownership to the lessee
B) Finance leases result in balance sheet recognition of the asset and liability
C) Operating leases require depreciation of the asset
D) Finance leases are not recorded in financial statements
Ans: B) Finance leases result in balance sheet recognition of the asset and liability
Relevance to CFA Syllabus
The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) program covers lease accounting under Financial Reporting and Analysis. Candidates learn how leases affect financial ratios, earnings quality, and investment decisions. CFA professionals analyze whether a lease should be treated as an asset or liability when assessing a company’s financial health.
What is a Lease CFA Questions
Q1: How does capitalizing a lease impact a company’s debt ratio?
A) It decreases the debt ratio
B) It increases the debt ratio
C) It has no impact
D) It reduces total liabilities
Ans: B) It increases the debt ratio
Q2: Why do companies prefer operating leases under financial analysis?
A) To reduce reported expenses
B) To keep liabilities off the balance sheet
C) To increase return on equity
D) To avoid recognizing lease interest
Ans: B) To keep liabilities off the balance sheet
Q3: Under IFRS 16, what is the key advantage for investors analyzing leases?
A) All leases are treated as off-balance-sheet transactions
B) There is greater transparency in financial statements
C) Short-term leases are treated as assets
D) Lease payments are excluded from financial analysis
Ans: B) There is greater transparency in financial statements
Relevance to US CPA Syllabus
Leases are covered under the US CPA exam in the Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR) segment. Knowledge of lease accounting according to ASC 842 is vital for reporting and auditing. CPAs have to ascertain lease classifications, measure right-of-use assets, and analyze lease liabilities for proper disclosure.
What is a Lease US CPA Questions
Q1: In ASC 842, which of the following is NOT a lease classification?
A) Finance lease
B) Operating lease
C) Service lease
D) Sales-type lease
Ans: C) Service lease
Q2: How is an operating lease recorded on the books of the lessee under ASC 842?
A) As an expense only
B) As both a right-of-use asset and a lease liability
C) As a contingent liability
D) Not captured on the balance sheet
Ans: B) As a right-of-use asset and as a lease liability
Q3: What is a major difference between IFRS 16 and ASC 842 lease accounting?
A) ASC 842 mandates lessees to record leases as either finance or operating leases
B) IFRS 16 permits all leases to be treated as operating leases
C) ASC 842 does not mandatorily recognize leases on the financial statements
D) IFRS 16 does not distinguish between finance and operating leases
Ans: A) ASC 842 makes it mandatory for lessees to account for leases as finance or operating leases


