The average revenue formula is an important concept in economics, especially to understand the revenue structure of a firm. Average revenue refers to the revenue a firm generates per unit of output sold. In other words, it is the total revenue divided by the number of units of goods sold. This means is a tool businesses use to figure out how much revenue they bring in selling one unit of the product. This concept is, therefore, very important for the management of companies in making correct pricing decisions and trying to estimate possible earnings.
What is Average Revenue?
The average revenue of a firm is the amount of revenue earned per unit of output sold. It shows the efficiency of a business in generating revenues from each product or service sold.
Key Features of Average Revenue:
- AR equals price if all units sold are sold at the same price.
- If the firm is a price taker—for example, a perfect competitor—AR is constant.
- In monopoly or monopolistic competition, it is natural that AR declines as more units are sold owing to the downward-sloping demand curve.

Why is the Average Revenue Formula Important?
The average revenue formula plays a critical role in economic decision-making for both businesses and policymakers. Here’s why it is important:
Revenue Estimation
The average revenue formula helps businesses project how much revenue each unit will generate at a particular time. This way, the businesses are then in a position to compute their likely total revenue at specified volumes of sales.
Pricing Decisions
Average revenue helps companies determine their pricing strategy. If average revenue drops drastically with every more unit sold, then it reflects that the firm may need to redesign the pricing or promotional strategies.
Market Structure Analysis
Average revenue behaves quite differently in different market structures like perfect competition or monopoly. In a perfectly competitive system, average revenue equals the price of the product, and the demand curve that the firm faces is horizontal. However, where a monopoly or monopolistic competition exists, the curve is inclined downward so that average revenue decreases with an increase in units sold.
Profit Maximization
The company can add the average revenue to the costs as calculated in the form of marginal revenue and marginal cost to get to the level of profits. Average revenue is compared with average costs, and through the comparison, a business can understand whether it is recording profit or loss.
Understanding Elasticity
This measure is referred to as average revenue. Elasticity may be defined as the degree of responsiveness of consumers to price changes. If a minimal change in price results in a big change in average revenue, then the firm will likely be in an elastic part of the market, where small price changes would affect total sales significantly.
What is the Average Revenue Formula?
The average revenue formula is expressed as:
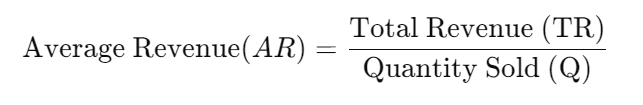
Where:
- Total Revenue (TR) represents the total income a firm earns by selling its goods or services.
- Quantity Sold (Q) refers to the total number of units sold.
Example Calculation:
Assume a firm sells 200 units of a product, and its total revenue is ₹10,000. Using the average revenue formula, we calculate:
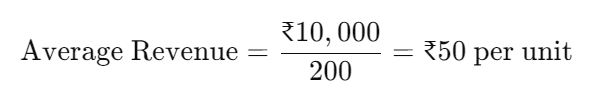
This means that, on average, the company earns ₹50 for every unit sold.

How to Calculate Average Revenue?
The process of calculating average revenue is straightforward:
Step 1: Determine Total Revenue
Average revenue is determined with the help of total revenue. Total revenue is considered to be the total money that will be obtained from selling goods or services. It can be calculated as follows:
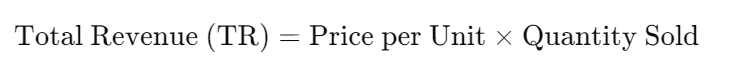
Step 2: Identify Quantity Sold
Once one can determine the total revenues, then one can determine the quantity of units sold. The total number of goods or services sold in a period.
Step 3: Apply the Formula
Finally, divide the total revenue by the quantity sold using the average revenue formula:
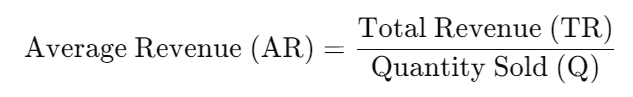
Example:
If a company sells 150 products at ₹40 each, the total revenue is:
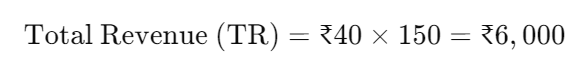
Then, using the formula for average revenue:
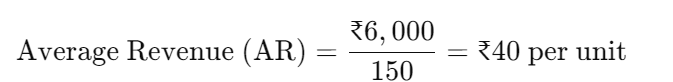
Thus, the average revenue is ₹40, indicating that each unit contributes ₹40 to the total revenue.
Practical Use:
- Small Businesses: Calculate how efficiently they are generating revenue from each sale.
- Large Firms: Measure the overall performance in terms of revenue per unit to assess pricing strategies.
| Variables | Example Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue (TR) | ₹6,000 | The income from selling 150 units |
| Quantity Sold (Q) | 150 | Total number of units sold |
| Average Revenue (AR) | ₹40 | Revenue generated per unit sold |
Conclusion
In short words, the average revenue concept is one of the fundamental ideas that any business or firm would be interested to know to optimize its prices, understand the market structure, and maximize revenue. It reflects the firm’s price power in the market under varying levels of competition. Average revenue analysis leads a business to strategic decisions on pricing, output, and market entry.
Average Revenue Formula FAQs
What is the difference between total revenue and average revenue?
Total revenue is the total income from selling goods, while average revenue is the revenue earned per unit sold.
Can average revenue be negative?
No, average revenue cannot be negative, as it represents the amount of income generated per unit sold, which is always a positive number unless no revenue is generated.
How does average revenue differ in different market structures?
In perfect competition, average revenue equals price and remains constant. In monopolistic competition and monopoly, average revenue declines as more units are sold.
What happens to average revenue when prices decrease?
When prices decrease, average revenue also decreases, as it is directly tied to the total revenue generated per unit.
How is average revenue useful in pricing decisions?
Average revenue helps businesses understand how much they earn from each unit sold, which is critical in determining optimal pricing strategies to maximize profits.


