The capital market is another major feature wherein new securities such as equity and bonds will be raised and traded. The capital market plays an exceptionally key role in supplying the fund needed for business and government growth, repaying debts, and extending entities. Not only that, but it also helps the investors to earn income through dividends or interest. Therefore, understanding the capital market at a higher level, including its types, functions, and essential aspects, helps students, professionals, and investors make informed decisions in the new dynamic economic environment.
What is Capital Market?
The capital market is the financial arena where buyers and sellers trade financial instruments for the long term, such as shares, debentures, or bonds. It links those with surplus funds (investors) to those needing capital (businesses and governments). It offers an avenue for raising finances for private and governmental long-term needs, such as capital expenditures for infrastructure or technology.
Definition of Capital Market
Capital markets are areas where trade involves long-term assets from other sources, like shares, securities, and bonds. These kinds of markets support the collection of funds from savers to channel them toward businesses or institutions needing funds for purposes such as investment. Thus, they are controlled by governments to be a medium of trust and confidence for buyers and sellers.
How Capital Markets Function?
When money is needed, a company may issue shares or bonds. The capital market sells these new securities to investors in the secondary market, where they are bought and sold. The capital market enables fundraising, however, through continuous trading.
Capital Market Participants
Capital market participants comprise companies, government institutions, occasional investors, banks, mutual funds, and foreign investors. Each plays a specific role in the capital allocation, contributing to economic stability and wealth distribution.
Key Functions of the Capital Market
The capital market performs many functions, one of which is to keep the economy in good health. It strengthens savings and capital formation, creates investment opportunities, liquidity, and price discovery, and, when integrated, makes it an essential part of the financial ecosystem.
Raising Capital
The capital market provides a platform for companies and governments to raise capital by issuing shares (stocks) or debt (bonds). Companies and governments access funds that can be used to finance new ventures, pay off old debts, or expand, which creates an innovative way of establishing infrastructure or growing economies.
Investment Opportunities
Investors can use different instruments to keep savings in the capital market. Share dividends and bond interests are income from pensions for investing in the future. Retirement and wealth planning also take place here.
Ensuring Liquidity of Investments
The secondary market’s converting institutional assets into cash creates great liquidity for capital markets. This feature makes the capital market more prominent since participants can exit their investments under exigent circumstances.
Facilitating Price Discovery
Capital markets determine the fair value of securities based on demand and supply. Price is affected by many aspects, such as company performance, economic indicators, and investor feedback, leading to less bias and more informed investments.
Mobilizing Long-Term Savings
The capital markets mobilize savings for broad-based economic investments by availing to citizens safe investment alternatives. This will greatly empower the nation, drive entrepreneurship, and create financial discipline among citizens.
Types of Capital Market
As per some viewpoints, capital markets comprise the primary and secondary markets. The two markets are said to have complementary but different roles in the life cycle of a security from issuing to transacting.
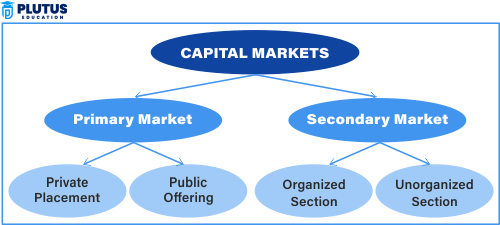
Primary Market
Where securities are issued for the first time, companies or governments raise funds directly from new sales of shares or bonds to the public. The first buyers of securities in the primary market become the initial owners.
Examples of Primary Market Activities
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): A private company offers its shares to the public for the first time. It is a means of raising capital.
- Private Placements: Selling securities directly or through a small group to institutional investors without a public offering.
Secondary Market
The secondary market is where securities already issued are bought and sold between investors. In such transactions, the company that issued the securities receives no money. This allows liquidity and the regular valuation of stocks and bonds.
Examples of Secondary Market Platforms
- Stock Exchanges: Platforms such as the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE) for real-time trading by investors.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Markets: Informal networks where securities not listed on formal exchanges are traded.
Importance of the Capital Market in Economic Development
On the one hand, the link to a capital market builds the country’s industrial development. On the other hand, it mobilizes investment and stabilizes the economy in times of crisis. It connects the savings, no matter how small or large, of people into different productive areas, empowering both institutions and people.
Supports Business and Infrastructure Development
Companies access finance through capital markets to scale operations, invest in R&D, or develop new product lines. As a result, innovation, job creation, and improved GDP are realized nationally.
Enables Wealth Creation for Investors
Investing in stocks and bonds can create wealth over time. Even small savers have mutual funds and index investments to help them access diversified portfolios and benefit from the long-term performance of capital markets.
Liquidity And Progressive Market Improvement
Capital markets are a forum for continuous buying and selling, thus allowing investors to enter and exit trades without necessarily experiencing a time lag between changes. The development of liquidity makes one feel comfortable with the market, makes it alive, and cares about price measurement efficiency.
Price Formation and Transparency Support
Price discovery mechanisms will ensure that the market value reflections of securities transactions are accurate. This will keep manipulation at bay, increase investor confidence, and create what can be termed a fair price for all.
Fostering Financial Inclusion and Discipline
Capital markets build a culture of saving and investing and inspire citizens to save for eventualities in the future. The proliferation of digital trading platforms and financial literacy programs steadily motivates greater citizen participation in the capital market.
FAQs on Capital Market
1. What is the capital market and its types?
A capital market is where long-term financial instruments like stocks and bonds are traded. It is divided into two types: the primary market (where new securities are issued) and the secondary market (where existing securities are traded).
2. What is a capital market in India?
In India, the capital market includes platforms like NSE, BSE, mutual fund houses, and bond markets regulated by SEBI. It helps raise business capital and gives investors access to long-term investment instruments.
3. What are the functions of the capital market?
Capital markets help raise capital, provide investment avenues, ensure liquidity, support price discovery, and mobilize long-term savings. These functions support economic and financial stability.
4. What is the difference between the primary and secondary markets?
In the primary market, securities are issued for the first time, and funds go to the issuer. In the secondary market, existing securities are traded between investors without involving the issuing entity.
5. Why is the capital market important?
The capital market supports economic growth by funding businesses, creating jobs, offering investment opportunities, improving liquidity, and establishing fair market prices for securities.


