Less common are the two instances when one may have spoken to the other and the other totally misunderstood him. The other day you may have received a message that further confused you. These instances illustrate just how important communication truly is. You might want to know what communication means. It involves sharing a thought, idea, emotion, or piece of information with another person. Communication helps individuals understand one another and, therefore, move together into action.
What is Communication?
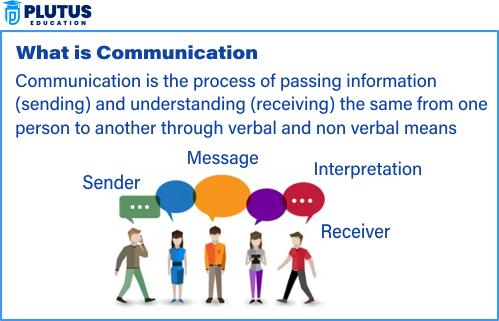
Communication is the process of giving and receiving information. It involves a sender, a message, a medium, a receiver, and feedback. Communication can be verbal or nonverbal, written or visual. It helps us share our ideas and understand others. Without communication, people cannot work together or solve problems.
For example, a teacher explaining a topic to students is communication. The students asking questions is also part of the communication. If both sides understand each other, the communication is complete.
Key Elements of Communication
To understand what communication is, you must know its main parts:
- Sender – the person who gives the message
- Message – the information or idea shared
- Medium – how the message is sent (voice, text, video)
- Receiver – the person who gets the message
- Feedback – the reply from the receiver
When all these parts work well, communication becomes easy.
So, communication is not just a skill. It is a powerful tool that connects people and helps them live and work better.
Importance of Communication
Communication helps people work better as a team. It builds trust and clears confusion. It also helps solve conflicts and supports decision-making. In schools, offices, and families, good communication creates strong relationships. It also makes people feel respected and understood. It is important because:
Helps in Building Relationships
Whether it’s at home, school, or work—strong relationships need clear and honest communication. When people talk openly, they understand each other better. It builds trust and removes doubts.
For example, parents and children bond better in a family when they share their thoughts daily.
Improves Work and Productivity
In schools, teachers explain lessons clearly so that students understand. In companies, managers give clear instructions to teams. When people know what to do and how to do it, work becomes faster and better.
Clear communication avoids mistakes and saves time.
Solves Problems and Conflicts
Many fights happen because of poor communication. When people listen to each other and speak politely, problems get solved easily. Good communication turns arguments into solutions.
Boosts Confidence and Leadership
People who speak clearly and listen well are often trusted more. They become better leaders, teachers, and friends. Confidence in communication helps in interviews, meetings, and public speaking.
Types of Communication
Communication happens in many ways. The type depends on how the message is shared—by speaking, writing, body language, or visuals. Each type serves a different purpose and setting, whether at school, home, or work.
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication uses spoken words to send messages. It includes face-to-face talks, phone calls, and group discussions. It is fast and can show emotions through tone of voice. People use it daily to give instructions, share ideas, and solve problems.
Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication uses body language, facial expressions, and gestures. It shows feelings without using words. A smile or a frown can say a lot. Eye contact and hand movements also help express thoughts. It supports and strengthens verbal messages.
Written Communication
Written communication includes letters, emails, reports, and texts. It helps share precise and permanent information. People use it in school, offices, and legal work. It helps keep records and reach many people at once. Correct spelling and grammar are essential.
Visual Communication
Visual communication uses pictures, signs, charts, and videos to share messages. It helps people understand data quickly. It is used in ads, reports, and instructions. It supports other forms of communication. Colourful and straightforward visuals work best.
Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication follows official rules and channels. It happens in meetings, reports, or official emails. Informal communication is casual and happens in friendly chats. Both are useful in different situations. The tone and language change with the setting.
Barriers of Communication
Even when people want to share ideas or messages clearly, problems can still arise. These problems are called barriers of communication. A communication barrier is anything that blocks, delays, or changes the meaning of a message. These barriers make it hard for the sender and receiver to understand each other properly.
Semantic Barriers
Semantic barriers happen when people misunderstand the meaning of words. Complex language or jargon confuses. People may use the same word differently. This leads to wrong messages being received. Simple words reduce this barrier.
Psychological Barriers
Emotions like fear, anger, or sadness cause psychological barriers. These feelings stop people from listening or speaking clearly. Stress or low confidence affects how we share ideas. Positive mood and empathy can reduce this barrier. Being calm helps communication.
Organizational Barriers
Organizational barriers happen when rules or structures block messages. Too many levels or unclear roles cause delays. Poor flow of information creates mistakes. Clear roles and open channels help fix this. Regular updates also reduce this problem.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers include distance, noise, or poor equipment. These make it hard to hear or see messages. Weak internet or background noise breaks understanding. Good tools and quiet spaces improve communication. Close contact also helps.
Cultural Barriers
Cultural barriers come from different customs, values, or beliefs. What is normal in one culture may confuse another. Language and behavioral differences cause mistakes. Respect and learning about other cultures help. Open-mindedness builds better communication.
Communication FAQs
What is communication and explain?
Communication is the process of exchange of information, ideas, thoughts, or feelings among individuals or groups. It involves sending and receiving messages through different means, such as verbal, nonverbal, and written means. Clear communication provides clarity and understanding, leading to bonding and cooperation.
Who defined communication?
Davis and Newstrom, in 1985, defined communication as the transfer of information and understanding from one person to another person. It is the bridge between people. Johnson in 1986 saw the concept as a means for one person to relay a message to another, expecting a response.
What are 4 types of communication?
The four principal categories of communication are verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual. These categories include the ways we employ spoken language, body language, written words, and visuals.
What are barriers to communication?
Communication barriers are elements that disrupt the process of sending an effective message, resulting in misinterpretation or a failure of communication. They may be physical, psychological, emotional, cultural, or language-based. They may disallow a message to be received as meant or slow down the receiver in interpreting the message appropriately.


