A partnership is a business arrangement where two or more individuals or entities can combine to carry on a business for mutual profit. Every partner contributes something—such as capital, skills, labor, or expertise to the business, and they share profits and losses according to an agreement. Partnerships are one of the most popular options as they allow the pooling of resources and reduce the burden on a single individual. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of partnerships, such as their definition, types, legal implications, advantages, and disadvantages, and more.
Partnership Definition
A partnership is an arrangement where two or more people agree to come together to achieve common goals. Each partner brings something to the table, whether it’s financial resources, expertise, or skills. The partners share the risks, profits, and responsibilities according to the partnership agreement.
This agreement describes the operation of the business, the distribution of profits and losses, and the settlement of disputes. A partnership does not have a separate legal identity from its owners, which means that partners are personally liable for the business’s debts and obligations.
Partnerships can be formed for short or long periods of business purposes as well as simple or complex agreements representing business structures. All the partners need to understand their respective roles and responsibilities as they may lead to conflict.

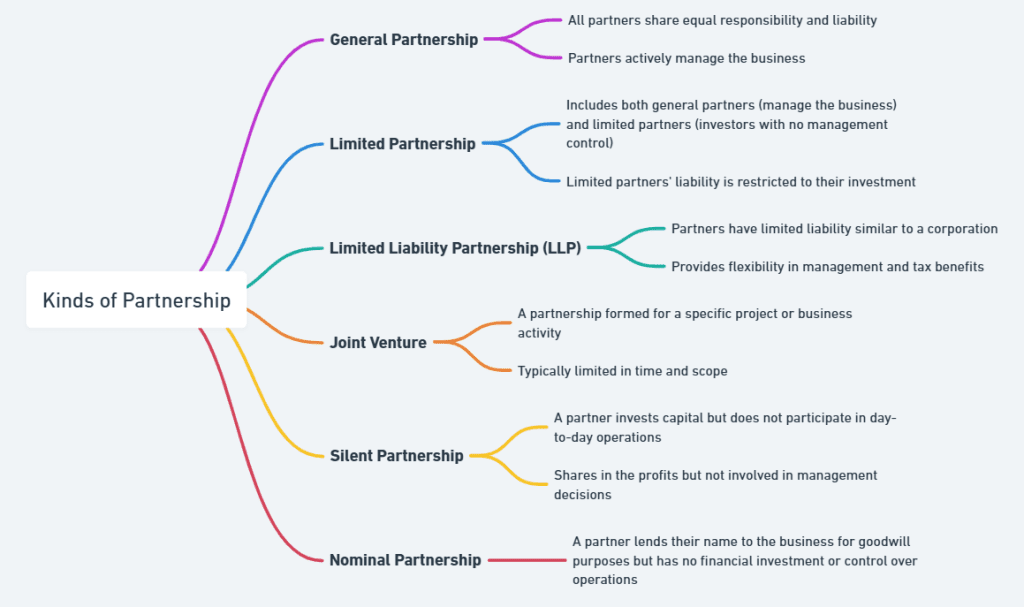
Kinds of Partnership
Different kinds of partnerships serve various business needs. Understanding the types of partnerships will help you choose the best structure for your business.
General Partnership
In a general partnership, all partners will share the burden of undertaking the management of the business and equally be held liable for any debts or obligations that arise with the business. It is the most common type of partnership whereby an equal say in the operation will be shared in matters of profit and losses as agreed upon in the partnership.
Limited Partnership
A limited partnership consists of two types of partners: general partners and limited partners. The general partners have complete control over the business and are liable for the debts personally, while the limited partners contribute finances but do not participate in the day-to-day operations. Their liability is limited to the amount they have invested.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP is a combination of a general partnership and a corporation. In an LLP, all the partners have limited liability, where they are not liable individually for the debts of the business. This is to their advantage because their property will not be seized due to losses or lawsuits faced by the business.
Joint Venture
A joint venture is the temporary partnership formed for a specific project or business goal. Unlike other types of partnerships, joint ventures are usually short term and dissolve once the project or objective has been completed. The partners involved usually share the resources, risks, and rewards proportionally.
Partnership Act
The Partnership Act is a law that has provisions for the regulation of partnership rights, duties, and obligations. The act provides legal direction for how partnerships should be created, managed, and terminated. It has provisions covering profit and loss sharing among the partners, the roles the partners have towards each other, and the settlement of disputes among partners.
In most countries, the Partnership Act governs the default rules for partnerships. But partners are at liberty to draft a partnership deed that overrides certain aspects of the act, depending on their agreement.
The Partnership Act ensures that there is clarity and transparency in the partnership structure. It also serves to protect the interests of both partners and third parties by clearly defining the business operations and the obligations of each partner.
What is Partnership Deed?
A partnership deed is essentially a legal document that expresses the terms and conditions under which the partners have formed the partnership. Such an agreement is important since it sets out the role of every partner, sharing of profit and loss, duration, and how to dissolve in case of a split.
A partnership deed is necessary for the administration of disputes and to avoid misunderstandings. It is a proof of the agreement between partners and may be presented in court in case legal action is needed. The deed may have terms about ownership of assets, contribution of capital, decision-making processes, and other important operational details.
Although not compulsory in some cases, a partnership deed is highly recommended as it prevents future conflicts. If the business faces legal or financial issues, it will protect the partners.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Partnerships
Partnerships offer several benefits but also come with their share of challenges. Below are some of the advantages and disadvantages that you should consider when entering into a partnership.
Advantages
- Shared Responsibility and Resources: One of the biggest advantages of partnerships is that partners share the responsibility of running a business. This ensures one partner doesn’t have to bear the entire burden. Hence there is better management and efficiency.
- Pooling of Skills and Expertise: Each partner brings diverse skills and knowledge into the business. Partners working together in a business often complement their strengths to ensure better decision-making and problem-solving.
- Formation Ease: The formation of a partnership is relatively easier than establishing a corporation. There are fewer legal requirements and less bureaucracy, which makes the process more informal and efficient.
- Flexibility: Partnership allows more flexibility in terms of decision-making, management, and division of profits. Partners have the freedom to structure the business to suit their needs and preferences.
- Tax Benefits: Partnerships are generally offered favorable tax treatment. The business itself is not taxed, but rather, the profits or losses are split among partners who report their portion on their tax returns.
Disadvantages
- Unlimited Liability: In a general partnership, all partners have unlimited liability. That is, personal assets may be used to settle business debts or legal obligations, putting the partner’s wealth at risk.
- Potential for Disputes: In any business with more than one person, there is always the possibility of disagreements or disputes. These can be over decisions, profit-sharing, or other operational issues.
- Lack of Stability: A partnership may dissolve if one of the partners decides to leave or dies. This lack of continuity can be very disturbing to the business and its operations.
- Limited Capital: A partnership may have less access to capital than a corporation. Since the business is funded by the partners themselves, raising funds becomes more difficult.
Difference Between Partnership and Company
While both partnerships and companies are forms of business organizations, they differ in several key aspects. Here is a brief comparison of the two:
Partnership
- Formed by two or more individuals or entities.
- Partners share management responsibilities and are personally liable for debts.
- The business does not have a separate legal identity from its owners.
- More flexible and simpler to set up compared to a company.
- Profits and losses are directly passed to the partners for tax purposes.
Company
- A separate legal entity from its shareholders.
- Shareholders own the company, while directors manage it.
- Limited liability for shareholders; personal assets are protected.
- More complex and costly to set up and maintain.
- Companies are subject to corporate taxes and other legal regulations.
| Feature | Partnership | Company |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Entity | Not a separate legal entity | Separate legal entity |
| Liability | Unlimited liability for partners | Limited liability for shareholders |
| Formation | Easy to form | Complex formation process |
| Capital Raising | Limited capital | Easier to raise capital |
| Taxation | Pass-through taxation | Corporate taxation |
| Decision Making | Partners share control | Directors manage the company |
| Profit Distribution | Shared among partners | Distributed to shareholders |
What is Partnership FAQs
What is the main advantage of a partnership?
The main advantage of a partnership is the ability to pool resources, skills, and expertise. This collaboration can lead to more effective management, better decision-making, and shared responsibilities, making it easier to run the business.
What is a partnership deed?
A partnership deed is a legal document that outlines the roles, responsibilities, profit-sharing, and terms for operating a partnership. It acts as an official agreement to avoid disputes and clarify expectations between partners.
What is the difference between a partnership and a company?
A partnership involves shared management and unlimited liability for its owners, whereas a company is a separate legal entity with limited liability for its shareholders. Companies also face more complex formation processes and regulatory requirements than partnerships.
What are the types of partnerships?
The main types of partnerships include general partnerships, limited partnerships, limited liability partnerships (LLP), and joint ventures. Each type offers different levels of responsibility, liability, and involvement in business operations.
What is the Partnership Act?
The Partnership Act is the legal framework that governs partnerships. It outlines the rights, duties, and liabilities of partners and serves as a guide for resolving disputes and managing business operations.


