The average total cost formula is very vital for both businessmen and the student to understand the nature of cost behavior about the quantity of goods or services. Average total cost (ATC) is defined as total cost divided by the units of output. It has greatly contributed to the decision-making process since it informs business people about pricing strategy, profitability, and the general health status of finances. In effect, the ATC helps one know whether the business is operating efficiently or whether there is a need to improve something to ensure production cuts at optimal cost.
What is Average Total Cost?
The Average Total Cost, or ATC, is the sum of all fixed and variable costs combined in terms of total cost per unit of output. In simpler words, ATC is the sum of all costs needed in the production of a certain amount of output divided into that number of units of output.
Mathematically, the formula is:

Where:
- ATC = Average Total Cost
- TC = Total Cost (sum of fixed and variable costs)
- Q = Quantity of output produced
For now, let’s just say total cost is the sum of all costs involved with production:
- Fixed Costs (FC): these do not change with the level of output; for example, rent, salaries
- Variable Costs (VC): these change with the level of output; for example, raw materials, and direct labor.
Thus, another way to express the ATC formula is:
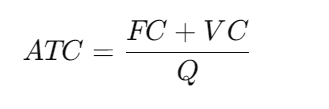
This formula yields an insight into the efficiency with which a company produces goods and services. More efficient production is understood to be indicated by a lower ATC, whereas a higher ATC may demonstrate a tendency towards inefficiencies.
How To Find Average Total Cost?
To find the average total cost, follow these steps:
Determine Fixed and Variable Costs
- Identify all fixed costs, which are those that do not change regardless of the level of output.
- Determine variable costs, which are costs that change with production level.
Calculate Total Cost
Combine fixed and variable costs for total cost, TC.
Measure Output
Determine the total units of output produced, Q.
Apply the Average Total Cost Formula:
Divide the total cost, TC, by the level of output, Q using the above formula.
Example:
Consider a small factory producing 1000 units of a product.
- Fixed Costs (FC) = $5000
- Variable Costs (VC) = $3000
Thus,
TC=FC+VC = 5000+3000 = 8000
Using the ATC formula:
ATC = 8000 / 1000 = 8
So, the average total cost per unit is $8. This means it costs the factory $8 to produce each unit.
Long-Run Average Total Cost Formula
The formula for the long-run average total cost is different from that for the short-run. All costs are variable in the long run because there are no fixed costs. All factors of production are variable in the long run.
In the long run, firms make decisions such that the average total cost is minimized based on the scale of production. The formula remains the same.
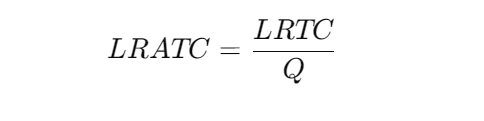
Where:
- LRATC = Long-run Average Total Cost
- LRTC = Long-run Total Cost
- Q = Quantity of output
The long-run average total cost curve often exhibits economies and diseconomies of scale:
- Economies of Scale: As production increases, average total costs decrease.
- Diseconomies of Scale: After a firm passes some level of production, it may be detrimental to increase the production further as higher costs per unit are incurred.
In a perfectly competitive market, firms are engaged in adjusting their level of output such that their ATC is equal to the market price in the long run: either maximize profit or minimize cost.
The Significance of Average Total Cost in Business
The average total cost is very important the business managers need to understand, which includes the following:
- Pricing Strategy: The business must price above average total cost to make a profit. In case prices are below average total cost, then the business suffers losses.
- Evaluating Efficiency of Operations: It shows that the business is producing efficiently with lower ATC, where the decision for allocation of resources is taken.
- Long-Term Planning: The business makes decisions on production capacity, investment plans, and competitiveness in the market by using average total cost for the long run.

Factors Influencing Average Total Cost
Multiple factors affect the average total cost:
- Scale of Production: Generating at high levels can absorb fixed costs over more units, therefore decreasing the ATC.
- Technological Change: By increasing production efficiency, technology can reduce variable costs.
- Economies of Scale: At higher levels of production, businesses may enjoy bulk purchasing, greater labor productivity, or increased use of equipment, therefore lowering the ATC.
- Input Costs: Changes in labor, raw material, and other inputs’ costs directly affect the variable component of the ATC.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the average total cost formula is very crucial in cost efficiency determination by businesses so that they may make sound decisions, either in production or pricing. Companies will, therefore, be able to maximize profitability and subsequently enhance competitiveness by constantly monitoring the ATC both in short and long-run scenarios. The concept of ATC, therefore, is pivotal in all perfectly competitive and monopolistic competitions and forms a crucial basis for an explanation of a company’s cost structure and its implications on market behavior.
Average Total Cost Formula FAQs
What is the formula for average total cost?
The formula for average total cost is:
ATC = TC / Q
Where TC is the total cost and Q is the quantity of output produced.
What is the difference between average total cost and marginal cost?
Average Total Cost (ATC) is the total cost per unit of output, whereas Marginal Cost (MC) is the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of output.
How do you find long-run average total cost?
The long-run average total cost is calculated by dividing the long-run total cost (LRTC) by the quantity of output (Q):
LRATC = LRTC / Q
Why is average total cost important in pricing decisions?
Average total cost is crucial because businesses must price their products above the ATC to ensure profitability. Pricing below ATC can lead to financial losses.
What factors influence average total cost?
Factors such as production scale, technological advancements, input costs, and economies of scale significantly influence the average total cost.

