The complete CA full form is Chartered Accountant. A Chartered Accountant is a highly respected financial expert trained to manage auditing, taxation, financial planning, accounting, and compliance functions. In India, the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is the official body that regulates the course and examination structure for CA aspirants. CA is one of the most in-demand professions in the world, offering stability, prestige, and excellent career growth. This detailed article explains the CA complete form in commerce, including eligibility, syllabus, career options, salary, responsibilities, and the exact steps to become a Chartered Accountant.
What is CA Full Form?
The CA complete form stands for Chartered Accountant, a globally recognized professional in the financial and accounting sectors. Chartered Accountants ensure that a business’s finances are managed accurately, lawfully, and profitably.
They help organizations manage taxes, financial statements, audits, cost controls, and fraud detection. CAs also work with individuals, assisting them with investments, tax filing, and legal compliance.
CAs are no longer limited to traditional accounting roles. Many work in senior leadership positions such as CFOs, investment bankers, or risk managers. They bring strategic value to companies and help in long-term financial planning.
CA Eligibility Criteria
To pursue the Chartered Accountancy course in India, students must qualify through either the Foundation Route (after Class 12) or the Direct Entry Route (after Graduation). Both entry points cater to different educational backgrounds and career paths.
Foundation Route (After 12th)
This route is ideal for students who have just completed their 12th standard, especially in the commerce stream. They must register with ICAI and complete a mandatory four-month study before appearing for the CA Foundation exam.
Once registered, ICAI provides study material, exam syllabus, and guidance under its Board of Studies. Students can take the Foundation exam after the four-month study period and proceed to the Intermediate stage upon clearing it.
The foundation route gives early exposure to professional subjects like accounting, law, economics, and math, helping students build a strong base.
Direct Entry Route (After Graduation)
This route allows graduates to skip the Foundation level and directly register for the Intermediate course. Commerce graduates must score at least 55%, while non-commerce students require 60% or more to be eligible.
Students who have passed the Intermediate stage of ICSI (Company Secretaries) or ICMAI (Cost Accountants) can also enter directly. Final-year students can register provisionally, provided they submit final marksheets within 6 months.
Direct entry is best suited for students who pursue CA after exploring other commerce or finance fields and want to save time.
CA Course Syllabus
The CA course includes three key stages—Foundation, Intermediate, and Final—designed to build theoretical knowledge and practical expertise. Each level is crucial and covers specialized finance, accounting, taxation, and auditing subjects.
CA Foundation Syllabus
The Foundation course consists of four papers covering fundamental commerce subjects. It tests conceptual understanding, analytical thinking, and communication skills.
- Principles and Practice of Accounting: This subject teaches accounting basics, journal entries, balance sheets, and profit-loss statements. It builds the core knowledge required in all future CA levels.
- Business Laws & Correspondence and Reporting: The first part focuses on legal concepts like contract law and business obligations, while the second part improves professional English and writing skills.
- Business Mathematics, Logical Reasoning & Statistics: This paper includes ratios, probability, and time value of money. It trains students in quantitative aptitude and decision-making.
- Business Economics & Commercial Knowledge: Students learn micro and macroeconomics concepts. The commercial knowledge section provides insight into business functions and corporate structures.
CA Intermediate Syllabus
It’s the second intermediate level with two groups of four subjects each. It furthers you into corporate laws, cost control, and taxation systems.
Group 1:
- Advanced Accounting: This covers advanced accounting practices for companies, including depreciation, share capital, and financial statements.Deals with specialized accounting topics such as partnership accounts, insurance claims, and accounting for business combinations.
- Corporate and Other Laws: The Curriculum teaches the Indian Companies Act, contract laws, and the legal aspects of business operations.
- Taxation: Includes Income Tax and GST. Students will learn to compute taxes and learn laws regarding taxes and how they are filed.
Group 2:
- Cost and Management Accounting: It helps understand costing techniques, budgeting, and performance management for better decision making.
- Auditing and Assurance: Focuses on audit planning, evidence collection, internal controls, and reporting. It prepares students to detect fraud and errors.
- Financial Management & Strategic Management: Students learn financial ratios, capital budgeting, and market analysis, which are essential for decision-making in business finance and strategic tools for planning and growth.
CA Final Syllabus
This is the last level and tests advanced knowledge, strategic thinking, and ethical practice. It includes two groups of four papers.
Group 1:
- Financial Reporting: Covers Ind AS (Indian Accounting Standards), business combinations, and financial statement analysis.
- Strategic Financial Management: Students learn about investment decisions, risk analysis, and portfolio management for long-term financial planning.
- Advanced Auditing and Professional Ethics: Teaches audit techniques, reporting requirements, and professional conduct expected from CAs.
- Corporate and Economic Laws: Focuses on SEBI regulations, FEMA, competition law, and economic reforms impacting business.
Group 2:
- Strategic Cost Management and Performance Evaluation: Helps in planning, controlling, and evaluating company performance through advanced costing techniques.
- Elective Paper (e.g., Risk Management, International Taxation): Students choose an elective based on their interest and future specialization.
- Direct Tax Laws and International Taxation: Covers income tax provisions, DTAA, and global tax frameworks affecting cross-border transactions.
- Indirect Tax Laws”: Covers GST, customs, and procedural compliance essential for businesses operating in India.
How to Become a CA in India?
To become a Chartered Accountant in India is that prestigious structured process guided by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India. There are Presses-to-clearing examinations at different levels, undertaking a practical training course, and complete other educational prerequisites. After Class 12, the student must do a CA Foundation course, then the CA Intermediate level, and finally the final CA level to become a chartered accountant. Apart from examinations, students also acquire articleship training to gain practical industry exposure. After qualification as a Chartered Accountant, one can enter into quite lucrative professions such as auditing, taxation, finance, and consultancy. It is counted among some of the most esteemed credentials in commerce.
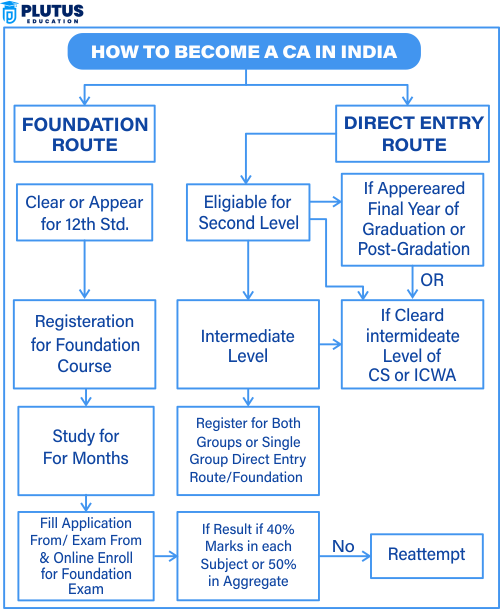
Step 1: Register for CA Foundation
After completing Class 12, students must register with ICAI for the CA Foundation course. This is the first step in the CA journey and is open to students from all streams. The registration should be done at least four months before the exam date. ICAI provides official study material for preparation. This exam forms the base for the entire CA course.
Step 2: Clear the CA Foundation Exam
The CA Foundation exam consists of four papers and is conducted twice a year in May and November. To pass, students must score at least 40% in each paper and 50% overall. The exam tests subjects like Accounting, Business Laws, and Economics. Once cleared, students become eligible for the Intermediate level. This step confirms your fundamental knowledge in commerce.
Step 3: Register for CA Intermediate
CA Intermediate has to be registered for by students who pass the Foundation. This course consists of two groups, with each having four subjects. Students can appear for one group at a time or for both groups together. Some of the significant subjects include Corporate Law, Accounting, and Taxation. The purpose of this level is to develop technical knowledge in the area of CA practice.
Step 4: Start Articleship After Group I
After passing Group I of the Intermediate exam and completing ICITSS training, students begin their 3-year articleship. This is on-the-job training under a licensed CA. It provides real-world experience in auditing, taxation, and financial reporting. Students learn to handle actual client work during this period. Articleship is a mandatory part of becoming a CA.
Step 5: Register for and Clear CA Final
During the second year of Articleship, students can register for the CA Final course. This is the last stage and consists of two groups with advanced-level subjects. After completing Articleship and clearing both groups, students can apply for ICAI membership. This marks the official completion of the CA course in India.
Top CA Institutes in India
While ICAI provides the course, these coaching institutes help students prepare better:
- ICAI (Official Body, PAN India)
- VSI Jaipur
- JK Shah Classes
- Aldine CA
- Navkar Institute
- Sriram Academy
- CHAMPS Academy
These institutes offer classroom and online coaching, mock tests, and study plans. Choose one based on your city, budget, and study preferences.
Role and Responsibilities of Chartered Accountant
The responsibilities of Chartered Accountants can vary widely depending on their specific role and targeted industry. They are essential players in financial management and business decision-making.
- Managing Audits: Chartered Accountants conduct the internal and external audits to ensure financial accuracy. They also assess internal controls in their audit and provide a report assessing the economic health of an organization.
- Tax Filing and Compliance: They conduct tax planning, prepare tax returns, and file them on time and accurately for businesses and individuals; they also act as agents for the taxpayers in tax assessment.
- Financial Reporting: They prepare balance sheets, profit-and-loss accounts, and financial statements used by the stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
- Consultancy and Budget Planning: They advise investment decisions, cost-saving measures, and business expansion, acting strategically in financial activities.
- Fraud Detection and Forensic Accounting: CAs investigate irregularities or discrepancies in the financial statements, undertake forensic audits, and track financial fraud within an organization.
Career Options After CA
There are various career options across sectors that one could pursue after CA. You can work in finance, consultancy, government departments, or provide services independently.
- Auditing and Accountancy: These primarily involve the analysis of financial statements, the verification of accounts, and the compliance of both with law and standards.
- Taxation: Works on approaches relating to the advisory and planning of taxation, as well as representation during assessments or in legal hearings.
- Risk Management: Risk managers would identify probable risks and recommend policies to protect the interests of the business while minimizing losses.
- Consultancy: Provide by CAs services on business solutions such as mergers and acquisitions budgeting, and financial projections.
- Corporate Finance & Investment Banking: The professionals manage investments on a grand scale, facilitate IPOs, raise capital, look into mergers, and acquisitions.
- Forensic Accounting & IT Systems: Some CAs are specialized in cyber audits and data protection and ensure that companies are digitally secure and compliant.
CA Salary in India
Chartered Accountants earn high salaries, which vary according to experience, skill set, and reputation of the company. The highest-paid professionals among recognized firms earn six and seven figures per year.
| Job Role | Average Salary (Per Year) |
| Finance Officer | ₹35 Lakhs |
| Account Executive | ₹25 Lakhs |
| Finance Manager | ₹10 Lakhs |
| Chartered Accountant | ₹7.25 Lakhs |
| Financial Analyst | ₹6 Lakhs |
| Assistant Account Manager | ₹5 Lakhs |
| Senior Accountant | ₹3.5–4 Lakhs |
Big firms like TCS, Infosys, KPMG, and Deloitte hire CAs with high packages. International postings offer even better compensation and perks.
CA Full Form FAQs
1. What is the full form of CA?
A Chartered Accountant (a finance professional licensed to manage accounts, taxes, audits, and financial planning.
2. What is CA salary?
A fresher CA earns ₹6- ₹8lpa. With experience, monthly salaries can exceed ₹23-₹25lpa.
3. What are primary roles of a CA?
A CA prepares financial reports, handles taxes, conducts audits, detects fraud, and offers financial advice to companies and individuals.
4. What is articleship in CA?
It is a three-year internship under a practicing CA. It provides practical exposure and is mandatory before appearing for the CA Final.
5. What are the three levels of the CA course?
The three stages are: CA Foundation (entry-level), CA Intermediate (mid-level), and CA Final (advanced professional level).
6. What is a CA for a job?
A chartered accountant is an internationally recognised financial professional who manages budgets, auditing, taxes and business strategies for clients. As a CA, you can work for businesses, the government and individuals


