Considering an industry classification means considering different sectors as contributors to the economic development of a country. The industry differs in terms of what it produces, how it operates, and who owns or manages it. Grouping industries based on type, raw materials, ownership, and size helps policymakers, entrepreneurs, and students to analyze roles, challenges, and economic impacts. Possible industries include a village-based handicraft unit or a multi-billion-dollar steel plant industry that fits into a defined category. This guide breaks down the four major classifications of the sectors along with real-world examples and characteristics to make the learning situation practical and insightful.
What is an Industry, and What Is Its Role in the Economy?
A general understanding of industries is needed before it would be appropriate to study the different kinds of industries. An industry is a collection of businesses that produce similar goods. provide similar services or extract similar natural resources. Industries are the backbone of the economy of any country, creating jobs, delivering goods, and contributing to the gross domestic product. The industries range from traditional agriculture and textiles to more advanced IT and biotech. Although some industries give lesser GDP contributions than others, they are in no way less important in ensuring sustainable development, innovation, and competitiveness in global trade.
Classification of Industry Based on Types of Activities
Industries can first be grouped by what they do—whether they extract natural resources, manufacture goods, or provide services. This is one of the most common and foundational ways to classify them.
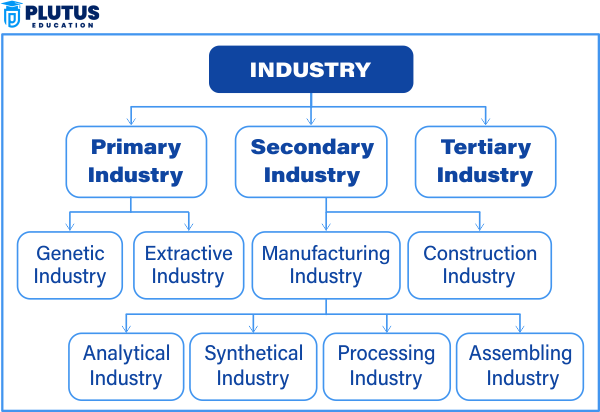
Primary Industry
Primary industries are directly involved in using natural resources. They extract or harvest raw materials from the earth, oceans, or forests. Agriculture, fishing, mining, and forestry are classic examples of this type. These industries form the base of the economy and supply raw materials to other sectors.
Secondary Industry
Secondary industries take the outputs from primary industries and convert them into finished or semi-finished products. Both manufacturing and construction sectors are included. Factories producing cars, textiles, or processed food belong in this category. Such industries are crucial for economic growth and urbanization.
Tertiary Industry
Tertiary industries provide services rather than goods. They connect producers and consumers through trade, communication, healthcare, and education. Examples include banking, hotels, transport, and retailing. These industries act as catalysts for improving the standard of living and economic efficiency.
Classification of Industry Based on Raw Material
Yet another very important basis for classifying industries is the certain raw materials they employ. This classification gives clues about each sector’s resource dependency and environmental impact.
Agro-Based Industry
Some raw materials for agro-based industries are agricultural products themselves. For instance, cotton textiles, sugar, and milk processing are activities under this definition. They are generally near the agriculture fields to minimize transport costs since they are highly climate—and crop-yield-sensitive.
Mineral-Based Industry
These industries use minerals and metals as their primary inputs. Steel plants using iron ore or cement factories using limestone are examples. They are often located near mining zones and require heavy investment in infrastructure and machinery.
Forest-Based Industry
Forest-based industries utilize timber, resin, bamboo, and various forest products. Paper production, furniture production, and handicrafts are all examples. These industries often provide sustenance for rural economies and depend on sustainable resource utilization to avoid deforestation.
Marine Based Industry
Not only fish processing plants, pearl farming, and offshore oil drilling fall under marine-based industries, but others as well. The typical geographical feature of these industries is that they are built along coasts and are very specialized in the technology used for operating in an environment that is normally marine.
Classification of Industry Based on Ownership
Ownership determines who controls resources, makes decisions, and enjoys the benefits of profits. This classification gives insight into the intent behind industry operations—profit, public welfare, or a blend of both.
Public Sector Industry
Public sector industries are owned by the government and operate under its ownership. Hence, their primary concern is not profit but public welfare. For instance, Indian Railways and ONGC fall under this category. The funding of public sector industries is usually through taxes, and it assures every citizen access to these services, even in less profitable or difficult-to-reach locations.
Private Sector Industry
These are industries owned and run by an individual or private company with the main aim of making a profit. Examples of such companies include Reliance, Infosys, and Tata. Private industries make an important contribution by encouraging innovation and competition while making a big difference in the GDP and employment.
Joint Sector Industry
Such industries can be defined as public-private partnerships. This model ensures efficiency and social welfare. A classic example is Maruti Suzuki, which was originally an undertaking between the Government of India and Suzuki Motors. Risks are shared while balancing profit and public interest.
Classification of Industry Based on Size
An industry’s measure is the scale of its operations, investment, output, and number of employees. It shows how well an industry can serve the local, national, or global markets.
Large-Scale Industry
These are usually very large industries, either national or global. Examples include steel plants, automobile manufacturers, and refineries. They require massive investment in advanced technology and, therefore, significantly increase employment capacity and export volume.
Small-Scale Industry
They work with minimal capital and are primarily local markets. Examples are garment units, bakeries, and tool-making shops. This is important for obtaining local employment, and government schemes for micro and small enterprises often support such industries.
Cottage Industry
A cottage industry is a small, home-based unit where production processes depend mainly on traditional methods and manual labor. Examples include handloom weaving, pottery, and embroidery. As these industries help preserve cultural heritage, they also become a source of income for rural and semi-urban areas with minimal investment.
Classification of Industry FAQs
1. What is the classification of industry?
Industries are classified based on type, raw materials, ownership, and size. This helps understand their function, scale, and contribution to the economy.
2. How are industries categorized based on ownership?
Industries can be public (government-owned), private (individually owned), or joint sector (both Government and private partnership).
3. What are examples of raw material-based industries?
Agro-based (cotton textiles), mineral-based (steel plants), forest-based (paper mills), and marine-based (fish processing) are examples of raw material-based industries.
4. Why is a classification of industry important?
It helps economists, policymakers, and businesses analyze industry roles, identify strengths, and make informed decisions for development and investment.
5. What are small-scale industries?
These are industries with limited capital and workforce, often serving local markets. Examples include handicrafts, local manufacturing, and small food processing units.


