Controlling in management is crucial to guaranteeing business activities adhere to intended goals. It matches performance against goals and monitors performance and corrective action where appropriate. With proper control, organisations can succeed by increasing efficiency and eradicating errors. He makes most businesses stay on track and updates their strategies when needed. It gives managers insights into decision-making and the organisation’s development through knowledge of management’s other functions.
What is Controlling in Management?
Control in Management monitors actual performance against planned targets and takes corrective measures if necessary. It makes organisational activities geared towards business objectives.
Controlling is the management function responsible for monitoring and measuring performance to ensure the accomplishment of business goals.
Controlling in management ensures that all activities align with organisational objectives by checking performance and making the required improvements. It is a constant process involving frequent checking and corrective measures to rectify deviations. It is a look-ahead position that enables companies to adjust to changing situations. Effective control maximizes operating efficiency, reduces wastage, and optimizes the use of resources for improved productivity and growth.
Function of Controlling in Management
Management is used to control organisational activities through controlling. The management process is necessary for effective control and successful attainment of goals. The following are the basic functions:
- Setting Performance Standards: Managers define performance objectives and targets to assess achievement. Standards provide a yardstick to determine employees’ productivity, finances, and business efficiency. Having realistic and attainable standards makes it easy to run businesses. Updating performance standards from time to time enables organisations to keep up with industry trends and evolving business requirements.
- Measuring Real Performance: Performance is evaluated using financial reports, productivity reports, and quality audits. Periodic reviews assist in locating areas of weakness and areas for improvement. Firms utilise KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to monitor progress. Proper measurement of performance assists managers in making accurate decisions and allocating resources effectively.
- Comparison with Standards: Managers compare planned and actual results to recognise performance gaps. Deviations are corrected if they do arise to get operations back in line. This helps ensure that companies are highly efficient. Regular monitoring aids in detecting minor problems before these become full-blown issues.
- Identifying Deviations and Corrective Actions: Managers identify causes of performance failures and implement necessary changes for improved results. Preventive measures are taken to avoid repeating mistakes and maintain business stability. Productivity and employee performance improvements are guaranteed through prompt corrective measures. Companies that correct deviations early create long-term success and sustainable growth.
- Guaranteeing Continuous Improvement: The control enables the companies to sustain competitiveness through modification of process and efficiency. It helps for better decision-making and removes errors in routine processes. Companies focusing on continual improvement evolve with market demand. An organised controlling helps frame a stable base for the enduring, lasting success of the business.
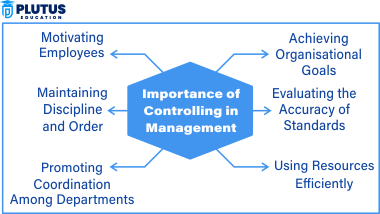
Importance of Controlling in Management
Controlling is critical for success in business because it ensures that organisational efforts are aligned with strategic objectives. Some things matter very much, like whether organisation goals are met, whether standards are validated, whether resources are optimised, whether people are motivated, etc.
- Realisation of Organisational Objectives: Controlling directs organisation on the right track by checking whether the planned activities are being performed correctly. It makes sure that progress is made in achieving company goals. If there are deviations, corrective actions are taken to improve performance. This impedes the organisation in overcoming their targets on time and cost-effectively.
- Assessment of the Validity of the Standards: A good control system enables companies to test if their established standards are practicable and feasible. It tracks the changes in the business environment and will allow firms to adjust their benchmarks when necessary. Periodic assessment ensures the company sustains high performance and is responsive to market trends.
- Utilising Resources Effectively: Controlling minimises waste and guarantees proper use of resources. It checks how employees, funds, and materials are utilised to avoid unnecessary losses. Operations maintenance to fit the company objectives may reduce expenses and enhance general productivity.
- Employee Motivation: Controlling informs employees of performance expectations. Workers know how and when their contributions will be appraised and compensated if they realise how their efforts will be judged and rewarded. A systematic control system enhances worker morale and challenges employees to meet company expectations.
- Enforcing Discipline and Order: An effectively applied control system guarantees discipline in the workplace. It monitors the activities of employees and prevents fraud, mismanagement, or dishonesty. It makes companies implement policies to create a culture of responsibility and professionalism.
- Encouraging Coordination Between Departments: Controlling facilitates various departments to collaborate towards shared goals. It gives a specific direction to employees so that there is no confusion and repetition of work. Good coordination between groups results in improved efficiency and smooth business processes.
Nature of Controlling in Management
Control is a critical managerial function that conforms business operations to organisational objectives. It enables firms to track performance, detect variances, and take remedial measures to enhance efficiency and development.
- Goal-Oriented: Controlling makes sure all business operations follow established goals. Each process and decision is to enhance performance and profitability. Controlling keeps firms on track toward their goals and prevents unnecessary straying. An effective control system ensures that resources are effectively utilised for business success.
- Continuous and Ongoing: Controlling is not a singular task; it operates on all levels of management. Constant checking maintains business operations smoothly and efficiently. Managers keep reviewing performance regularly in search of loopholes. It is through continual practice that companies can learn and improve over time.
- Forward-Looking: Controlling allows businesses to foresee future threats and take preventive measures. Companies can predict future problems by examining market trends and internal performance. A strong control system reduces uncertainty and encourages business sustainability. Future planning is made easy when businesses have clear visions of their operations.
- Flexible and Adaptable: The controlling process allows firms to adjust their strategies based on market conditions. When there are sudden changes, timely decisions help in maintaining stability. Flexibility in controlling ensures companies remain competitive. Adaptability assists companies in surviving in changing environments and reacting to customer needs efficiently.
- Integrated with Other Functions: Controlling goes hand-in-hand with planning, organising, and leading functions. It integrates all the departments of the business to run smoothly together. An integrated control system encourages efficiency and prevents mismanagement. Successful coordination among various functions results in higher productivity and company growth.
Control Techniques in Management
Effective control measures enable companies to quantify performance, utilize resources optimally, and attain sustained success. They ensure economic stability, quality management, and functional effectiveness with the least threats and optimal decision-making.
- Budgetary Control: Businesses set budgets for finance to control expenses and use resources efficiently. Budgeting allows profitability to be monitored and effective cost management. Effective budgeting guarantees that expenditure is within business objectives and against excess spending. Continuous review of budgets enables companies to make knowledgeable financial decisions and modify strategies where necessary.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Income, balance sheets, and cash flow statements give information about a company’s financial condition. They help companies analyse financial risks and opportunities for growth. Ongoing financial analysis leads to accurate decision-making and the ability to carry out long-term financial planning. Investors and shareholders utilize these statements to determine how stable and profitable a company is.
- Performance Appraisal: The productivity of employees is assessed by performance appraisals and feedback meetings. The appraisals and feedback identify strengths and areas of improvement. Rewards, promotions, and incentives motivate and induce improved performance. A formalised appraisal system guarantees equitable assessment and helps maintain a healthy work culture.
- Quality Control Measures: Firms use ISO standards, Six Sigma processes, and periodic inspections to ensure product quality. These processes help ensure customer satisfaction and create a brand reputation. Quality control avoids defects, reduces returns, and gains consumer confidence. Periodic checkups and improvements help companies compete in the market.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Companies track KPIs such as sales revenue, customer retention, and market share to measure business performance. These indicators help measure overall effectiveness and set future goals. Regular tracking of KPIs helps companies make informed decisions. A good KPI monitoring system helps companies stay on the right track towards growth.
- Internal and External Audits: Ongoing internal audits ensure that all firm policies and sector standards are being followed. External audits help maintain accuracy in finances, and transparency. Regular audits detect fraud, decrease risks, and encourage ethical behavior. Companies can earn the confidence from investors and consumers with rigorous audit methods.
- Inventory Control: Methods such as Just-in-Time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) assist in controlling stock effectively. Efficient inventory management reduces storage expenses and prevents product wastage. Firms maintain an optimal stock level to meet customers’ requirements without having a surplus. Efficient inventory management increases supply chain effectiveness and profitability.
Controlling in Management FAQs
1. What is controlling in management?
Controlling in management is monitoring performance against goals, followed by corrective action for business success.
2. What are the types of control in management?
The primary management control types are budgetary control, financial audits, quality control, performance appraisals, and inventory control.
3. What is the process of controlling in management?
Management control consists of the steps to establish standards of performance, measure performance, compare results and take corrective actions where needed.
4. Why is the management of control important?
Management has to manage goals to be achieved, increase efficiency, identify errors and let enterprises adjust to market changes.
5. What are the most significant aspects of controlling in management?
The aspects of controlling in management are planning, measurement of performance, comparison against standards, correction, and continuous improvement.


