The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) designs and regulates the US CPA course syllabus, ensuring it meets global accounting standards. The CPA exam is conducted quarterly, giving candidates multiple opportunities throughout the year to attempt it. To prepare effectively, aspirants must gain a clear understanding of the detailed syllabus and exam pattern, which covers comprehensive subject matter relevant to modern accounting and finance practices. This syllabus includes critical topics such as auditing, taxation, financial accounting, and business concepts, equipping candidates with skills essential for professional success. Mastering the CPA syllabus not only prepares individuals for the exam but also positions them as leaders in the accounting profession—highly sought after across industries worldwide.
What is CPA?
CPA full form Certified Public Accountant. It is one of the most prestigious accounting qualifications under the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. In short, the CPA designation has been considered the top and most coveted proof of an individual’s capability in accounting principles, auditing, taxation, and financial analysis. In most countries in the rest of the world, a CPA designation is yet to be deemed as the epitome of perfection that many organizations in diverse industries seek after and earn.
CPA thereby reflects its value in public practice, corporate finance, and services to the government. Unlike other certifications, the CPA ranges from a broad series of skills and makes professionals extremely valuable to organizations. It proves not only expertise in technical details but also indicates the high levels of ethics involved. CPAs are business advisor consultants, steering financial decisions that are accurate as well as precise.
US CPA Syllabus
The US CPA syllabus outlines the topics candidates must master to succeed in each section. Below is a breakdown of the key areas for each section. This roadmap is assured by the CPA subjects concerning the preparation of candidates to address the real challenges in accounting. The CPA examination syllabus also structures its own with the three sections of the exam and completely encompasses the knowledge and skills expected of the CPA professional.
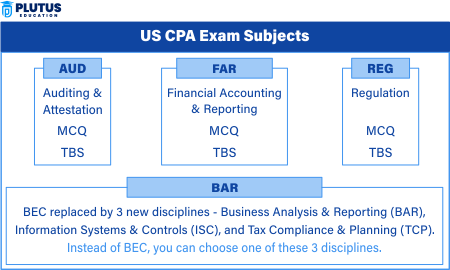
CPA Auditing and Attestation (AUD) Syllabus
AUD covers everything about auditing processes, ethics, and risk appraisal. Candidates must express their knowledge of audit procedures, professional standards, and responsibilities of an auditor. Topics include planning the audit, internal controls, evidence evaluation, and reporting findings. Ethical considerations are crucial in the accounting profession and are discussed at great length as well.
| Section | Topics | Weightage Range |
| Auditing and Attestation | Ethics, Professional Responsibilities, and General Principles | 15–25% |
| Assessing Risk and Developing a Planned Response | 25–35% | |
| Performing Further Procedures and Obtaining Evidence | 30–40% | |
| Forming Conclusions and Reporting | 10–20% |
CPA FAR Syllabus
The most challenging area is FAR, which includes a wide number of topics under the head of financial reporting such as US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Candidates should be aware of financial statements, consolidations, governmental and nonprofit accounting, and complex transactions.
| Section | Topics | Weightage Range |
| Financial Accounting and Reporting | Conceptual Framework, Standard-Setting, and Financial Reporting | 25–35% |
| Select Financial Statement Accounts (e.g., Assets, Liabilities, Equity) | 30–40% | |
| Select Transactions (e.g., Revenue Recognition, Leases, Investments) | 20–30% | |
| State and Local Governments | 5–15% |
CPA Regulation (REG) Syllabus
REG tests federal taxation, business law, and professional responsibilities. Some topics include individual and corporate taxation, estate taxes, and ethics. This section also tests knowledge of legal implications in business operations.
| Section | Topics | Weightage Range |
| Regulation | Ethics, Professional Responsibilities, and Federal Tax Procedures | 10–20% |
| Business Law | 10–20% | |
| Federal Taxation of Individuals | 15–25% | |
| Federal Taxation of Entities (Corporations, Partnerships, Estates) | 25–35% | |
| Federal Taxation of Property Transactions | 12–22% |
CPA Exam Pattern
The CPA exam follows a multi-format format so that the candidates are tested adequately.
- Multiple-choice questions (MCQs): These are objective-type questions with one correct answer.MCQs test the candidates on their theoretical knowledge and conceptual understanding.
- Task-Based Simulations (TBSs): TBSs are case-based, requiring candidates to apply knowledge to practical problems. Includes working with spreadsheets, preparing journal entries, or filling out tax forms.
- Written Communication (Only in BEC): This component tests the ability of the candidate to communicate effectively in a professional setting. Tasks involve writing memos, reports, or business letters based on given scenarios.
| Section | Section – Time | Multiple-Choice Questions(MCQs) | Tasked-Based Simulations (TBS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUD – Core | 4 hours | 78 | 7 |
| FAR – Core | 4 hours | 50 | 7 |
| REG – Core | 4 hours | 72 | 8 |
| BAR – Discipline | 4 hours | 50 | 7 |
| ISC – Discipline | 4 hours | 82 | 6 |
| TCP – Discipline | 4 hours | 68 | 7 |
Important Characteristics Of CPA Syllabus
1. Layout: The CPA exam consists of 3 segments, and each of these points towards distinct facets of accounting, business, and law. The different ones include the following:
- AUD: It consists of auditing activities, risk identification, and reporting.
- FAR: It contains details on frameworks, accounts, and transactions for reporting in the fields of finance accounting.
- REG: It focuses on federal taxation, ethics, and business law.
Each module is designed to include practical, theory-based, and application-oriented aspects of the subject:
- Practical: It resembles real-life scenarios, such as preparing audit reports, tax calculations, or financial statements.
- Theory-Based: It requires a good conceptual understanding of standards, principles, and regulations.
- Application-Oriented: It tests how the candidates apply theoretical concepts to practical problems, such as creating reports or analyzing case studies.
2. Focus: The CPA exam includes all fundamental professional standards and practices that form a very actual context. So, here is the core theme:
- Professional Ethics: States integrity, independence, and ethical obligation of an accountant.Focuses on the AICPA Code of Professional Conduct and rules of auditing ethics.Examines knowledge of ways to solve practical ethical problems associated with accounting practice.
- US Federal Taxation: Covers Individual, Corporate, and Entity Tax as per US Legal Provisions. It includes the tax arithmetic, deduction, and credit provisions in terms of the general compliance requirements of tax laws. Assesses candidates’ ability to solve complex tax scenarios.
- Financial Reporting Standards: GAAP and IFRS. Preparation, analysis, and interpretation of financial statements. Private and governmental accounting standards
- Business Concepts: BEC uniquely integrates governance, economic concepts, IT, and operational management.Teaches the candidate to think in a holistic way about the business environment.
CPA Eligibility
Meeting the CPA eligibility criteria is the first step in certification. Requirements vary by jurisdiction but typically include:
- Education: A bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field, with 120–150 credit hours (4–5 years). Some states require specific coursework in accounting, auditing, or taxation.
- Experience: 1–2 years of relevant work under a licensed CPA, typically in public accounting, auditing, or financial management, to ensure practical skills.
- Residency: Some jurisdictions require residency or a connection to the state, though many also accept international candidates.
| Eligibility Criteria | Details | Variations by Jurisdiction |
| Educational Requirements | Bachelor’s degree in accounting or related field. | Credit hours: 120–150 (equivalent to 4–5 years of education). |
| Specific coursework in accounting, auditing, and taxation may be required. | States may specify required courses (e.g., auditing, taxation). | |
| Experience Requirements | 1–2 years of relevant work experience under a licensed CPA. | Experience typically in public accounting, auditing, or financial management. |
| Practical, hands-on training ensures candidates can apply accounting principles in practice. | Jurisdictions vary in the type of work and CPA supervision required. | |
| Residency Requirements | Some states require candidates to live in or be connected to the state where they apply. | Some jurisdictions allow international candidates to apply; residency rules vary widely. |
CPA Course Duration
The CPA course duration is taken over 12 to 18 months, taking into account the time it takes to prepare for the exam, the scheduling of exams, and the individual study pace. It has four sections: Auditing and Attestation (AUD), Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR), and Regulation (REG), with a study time of 100–200 hours for each, adding up to around 400–800 hours.
Candidates have to finish all the sections within 18 months from the date they pass the first section. Most full-time students take only 12 months, but most working professionals will take longer. Good planning, knowledge of accountancy beforehand, and review materials such as Becker or Wiley will help candidates finish sooner. The inability to get the Notice to Schedule (NTS) will further prolong the schedule, thus making preparation and scheduling vital.
CPA Course Syllabus FAQs
What is the syllabus of CPA?
The US CPA syllabus covers three main areas: Auditing and Attestation (AUD), Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR) and Regulation (REG).
How to become a CPA?
One can become a CPA by finishing the education required, passing all four sections of the CPA exam, and gaining experience.
Can I complete CPA in 1 year?
If you are a full-time student, you may be able to complete the US CPA training & exams in less than a year. For working professionals who may not be able to dedicate study time on a daily basis, completing US CPA can take up to 18 Months or 1.5 years.
How long is the CPA course and how much does it cost?
The CPA course usually takes 12–18 months. The exam fee is between $1,500 and $3,000, not including other costs such as study materials.
Can I do CPA in 3 months?
Passing the CPA exam requires diligent preparation, dedication, and a strategic approach. By understanding the application and registration procedure, strategising a three-month study plan, and leveraging the support of coaching institutions, aspiring candidates can increase their chances of success.
Who earns more, CA or CPA?
In general, Chartered Accountants (CAs) tend to earn slightly more than Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) in India, particularly with experience and specialized skills.


