Decentralisation in management is the distribution of authority and the power to lower levels of management instead of higher levels. Thus spreading responsibility across an organization. In this approach, managers or employees at any level can choose, which pushes for more autonomy and swifter response to any business need. The only fundamental difference between centralization and decentralisation in management is the concentration of authority. In a centralized management system, the decision-making power is very much centralized; that is, minimal input is left to lower levels, whereas in decentralisation, authority is diffused down the hierarchical levels. Centralization and decentralisation are fundamental management concepts through which a business firm decides the method of its decision-making as an out organization of the size, scope, or requisition.
What Is Decentralisation?
Decentralisation means handing over the decision-making powers and authorities to lower or middle management groups within an organization. It reduces the involvement of top-level management in more minor decisions. Thus, a significant improvement in operational efficiency was realized. The department heads and regional managers who are low in the hierarchy are given decision-making freedom. To choose their market area, and the actions are consistent with local conditions and needs.
This concept is important in public and private organizations in India. For instance, the Indian government has supported decentralisation to allow power decentralisation and streamline administration. In India, the industries are continually growing in complexity. Decentralisation now forms an integral part of these businesses. Large business ventures usually favor decentralisation as a better tool for efficient management. As its geography is too extensive to handle efficiently from a single nerve center.
Role of Decentralisation in India
The Indian government has started taking measures of power decentralisation within a few areas . This is to support governance and economic growth. The powers of decentralised decisions directly influence regional areas . This have made state governments differ as they design their policies to meet local needs. In such ways, there have been developments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure regarding delivery services.
Decentralisation also suits the Indian private sector since the regional branch or its manager can make decisions individually. Retail, manufacturing sector – knowledge about a local market or quick response and decision at an appropriate time, indeed, can create a great deal of difference between winning or losing in a contest. Decentralisation for these companies helped even Tata, Infosys, and Reliance run large-scale activities across diverse regional locations.
Pros and Cons of Decentralisation in Management
Decentralisation in management is defined as distributing the decision-making power from top to lower or middle-level management. This organizational structure gives middle and lower management managerial powers to make decisions independently. Without much dependence on top-level executives. Even though there are several merits to decentralization, it also has its drawbacks. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of decentralization in management helps business entities decide whether the management style fits their purposes or operational requirements.
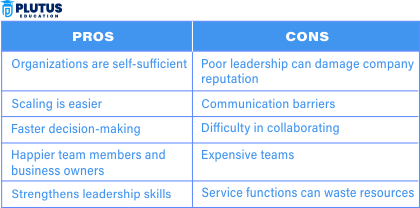
Pros of Decentralisation in Management
Decentralisation in management is defined as distributing the decision-making power from top to lower or middle-level management. Let us now check the pros of decentralization.
Speedy Decision-Making
Decentralisation is one of the top routes to speeding up decision-making. The lower the levels, the more influential the managers and the less they depend on top-level authorities for approvals. Therefore, they can respond to issues immediately. In specific industries, firms need to respond to customer needs or changes in the market as fast as possible to survive in business.
Increased Flexibility and Responsiveness
Decentralisation makes organisations flexible and responsive to local market requirements. Regional or branch managers, being closer to the operational levels of a business, are more aware of their specific markets. They make decisions tailored to the particular requirements of their customers. This can improve adaptability to changing environments and consumer demand.
Higher Motivation and Job Satisfaction
When employees and the managers at more subordinate levels within the organization experience a feeling of being appreciated and trusted, they will become empowered to become more motivated . They also are now satisfied with their jobs and have much morale in an organization. Since decisions and responsibilities motivate good performance, as called upon by the employees to deliver their best,
Fosters Innovation
Decentralisation offers an innovative environment. Because, if the subordinate managers are given freedom, they take up new ideas, strategies, and solutions. They are challenged to think outside the square and may develop imaginative products, services, or business strategies. The variety of thoughts at different levels is a continuous improvement and innovation in the organization.
Improved Customer Service
Decentralisation can be done quicker and closer to the point of service. Where customer needs may be responded to. Since a lower-level manager knows their day-to-day operation and customers’ wants and needs, responding to complaints can be quick. Customer service provides better satisfaction to the needs of customers,. This may eventually mean a competitive edge in customer-driven industries.
Cons of Decentralisation of Management
Decentralisation in management is defined as distributing the decision-making power from top to lower or middle-level management. Let us now check the cons of decentralization.
Inconsistent Decision Making
A significant disadvantage of decentralization is inconsistency in the organization’s decision-making processes. Distributed authority causes more problems since many levels have decision-making authority and tend to implement different alternatives to solving the same problems or issues. Such uniformity affects brand image, productivity, and quality customer service delivery.
Coordination Problems
Because the decision-making process is spread over so many levels, aligning across several departments or business units would be difficult. An extensive organization without centralized control might not perceive an integrated nature of objectives and strategies in the system. Without this integration, one would sometimes have redundant efforts, missed opportunities, or conflicting objectives between branches or units.
Lack of Control
When decentralization is implemented, the top management cannot take notice of even a single decision from the organization itself. So, in delegating power to all the necessary matters, senior managers may not learn about every issue that emerges in a company. The chances of increasing their risk level depend on possibilities. In contrast, lower-level managers start working against their significant goals and primary values. In this situation, management control does not allow them to enforce a company-wide policy and strategic direction.
Resource Replication
In a distributed system, every division or sub-section could operate independently and use the same resources for administration, research, or marketing. Resource replication may cause inefficiencies because of duplication of work done by one section without knowing that some other unit has already done it. It wastes time and money because the central organization has no inter-unit control.
Inability to Handle Large Groups
With more power being concentrated in the hands of lower-level managers, the top management is now required to keep track of more diverse groups of decision-makers. This calls for a bigger team to deal with, which might increase the complexity of the organization’s size. It is generally very challenging to develop a set of core principles or guidelines that all managers can adhere to uniformly without being seen as micromanagers, requiring great trust and effective organizational communication.
Decentralisation in Management FAQs
- What is decentralisation in management?
Decentralization in management refers to the distribution of decision-making authority to lower levels of an organization.
- What are the most essential benefits of decentralization?
It provides quicker decision-making, higher adaptability, and quality responses to customers.
- What are the disadvantages of decentralization?
It leads to inconsistent decisions, coordination problems, and loss of control.
- When does decentralisation perform best?
Decentralisation performs best when there are complex organizations involving a broader type of diversification. Also, where responses are needed faster, innovation is required.
- How does decentralization impact innovation?
Decentralization fosters innovation as it allows the managers to make creative, independent decisions.


