Centralization and decentralization differ in their mode of distributing power across employees and decision-makers. In centralization, power stays in the top management, while in decentralization, this authority is spread over several levels. Knowledge of these two structures is essential for any organization bent upon operational efficiency, scaling up, or good management. Deciding whether to centralize or decentralize will influence everything from the speed at which decisions are taken to employee motivation and cost structure. This article explains both models in detail, along with their pros, cons, and key differences, to help you understand which structure will fit best for your business goals.
What is Centralization in Management?
Centralization refers to an organizational structure where the control and decision-making power are in the hands of top management. In this Structure, senior leaders take all the significant decisions and pass them down to middle and lower levels for execution. The flow of authority is clearly top-down, with limited autonomy at the operational level.
How Centralization Works in Organizations?
Centralized systems are predominantly found in manufacturing, military, or healthcare sectors, in which the requirement for standardization and uniformity is essential. The idea is to have an approach that can be followed uniformly by all departments. This model allows closer supervision, a more authoritative stance, and alignment of actions with long-term goals.
For example, decisions regarding pricing, marketing, or budgeting within a centralized corporation are made strictly by top executives, even if the issues are regionally based. While this sort of setup affords an organization greater control, it tends to restrict flexibility and prolong decision-making at the local level.
What is Decentralization in Management?
Decentralization is the transfer of decision-making authority to lower levels of the organizational hierarchy. It allows branch managers, team leads, or even employees to make Structure relevant to their roles. This Structure helps companies respond quickly to local needs and encourages innovation.
How Decentralization Improves Business Agility?
Increased autonomy within decentralized systems translates into quicker decision-making and motivation, as well as a more precise grasping of customer needs. Employees making choices on their own tend to demonstrate high levels of responsibility and accountability. This is especially relevant for large multinational companies with several geographical territories.
For example, a decentralized retail chain may allow regional managers to modify product assortments as a response to the prevailing local customer behaviour. This flexibility enables localized marketing and quick reactions to customer behaviour, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Nevertheless, all of these should operate within well-laid communication and alignment with organizational goals to avoid inconsistency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Centralization
Every Structure has its pros and cons. It is the same for centralization, having high control but at lower levels of flexibility.
Pros of Centralization.
Centralization requires that all departments operate under the same guidelines and policies, thereby raising confusion. Strategic priority dictates resource allocation, and the leaders can maintain a very high level of control over the financial and operational planning. This model is also beneficial when issues relate to crises and when there is a need to respond quickly with top-level direction.
Cons of Centralization.
The significant disadvantage is the speed of decision. The flow of approvals and instructions from the top down only creates bottlenecks. Employees at different levels feel less involved. Thus, morale decreases. The centralized organizations face a hard time adapting to local changes quicker as feedback loops are long and indirect.
Example: In such a large business, issues on field sales might take weeks to be resolved because of centralized processing. The delay could lead to discontent from customers and operational inefficiencies.
Benefits and Harms of Decentralization
New opportunities and challenges come with decentralization. While enabling quicker decisions and empowering the employee, it also brought about coordination problems.
Advantages of Decentralization
Businesses that use decentralized models respond rapidly to environmental changes. Such local teams make decisions that reflect the values of the ground realities. This not only improves service delivery but also builds trust among employees, increasing their morale. Ownership improves team morale. The CFA career opportunities model is one such example of how decentralized career avenues can really help clients in finance.
There is more engagement and innovation among those who participate in decision-making. The communication will flow both ways and will become more susceptible to quick responses because action can be taken proactively.
Disadvantages of Decentralization
Inconsistencies in policy and standards may develop in decentralized systems since every unit operates autonomously. Service and brand quality are challenging to maintain uniformly because every unit conducts operations independently. In addition, coordination costs may increase with administrative support needed by each unit.
Last, decentralization may lead to disorientation in alignment with the company’s overall goals. When local units rush after their targets without considering the big picture, it may cause an organization to lose strategic focus.
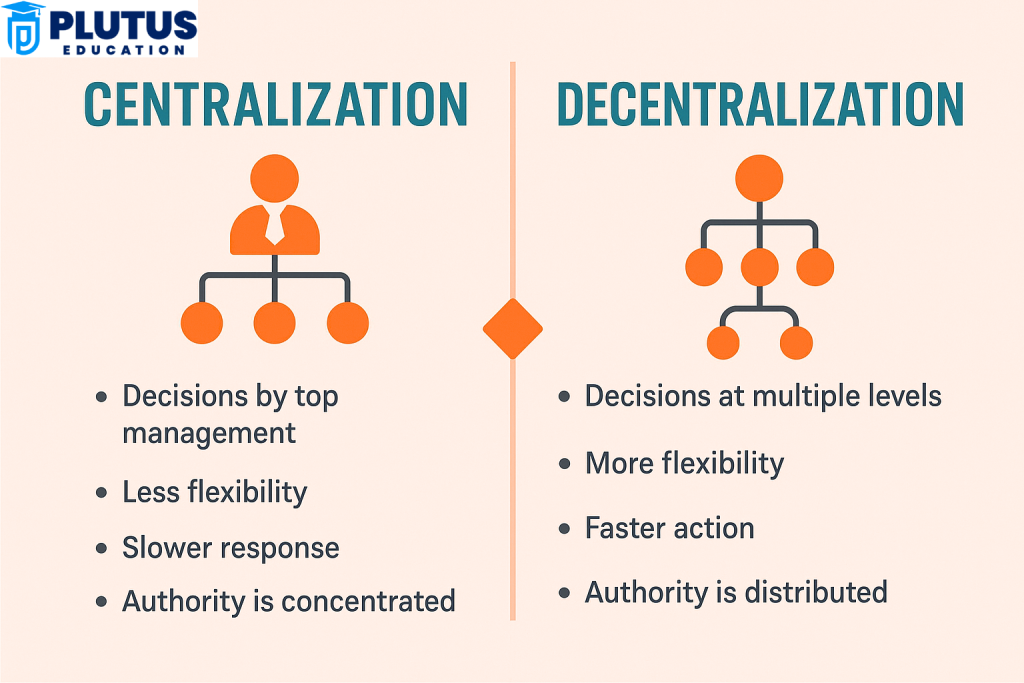
Centralization vs Decentralization
Understanding the Structure between centralization and decentralization becomes clearer when compared side-by-side. An organization’s size, goals, and nature of operations help determine the right model. For a new startup, centralization might work better. For a large FMCG company, decentralization is often more suitable.
| Aspect | Centralization | Decentralization |
| Definition | Authority and decision-making are concentrated at the top levels of management | Authority and decision-making are distributed across various levels of the organization. |
| Decision-Making Power | Held by senior executives or central authority. | Shared among lower and middle-level managers and employees. |
| Organizational Structure | Vertical and hierarchical; follows a strict chain of command. | Horizontal or flat; promotes flexibility and autonomy at different levels. |
| Speed of Decision-Making | Slower, as approvals go through multiple levels. | Faster, as decisions are made closer to the point of action. |
| Flexibility and Adaptability | Low; rigid processes make it hard to adapt to changes quickly. | High; readily adapts to local or situational changes. |
| Employee Involvement | Limited; employees execute rather than participate in decisions. | High; employees have a say in decision-making, increasing ownership. |
| Consistency in Operations | High; policies and procedures are uniform across the organization. | Variable; different units may operate with customized policies. |
| Cost Structure | Lower administrative costs due to centralized services. | Higher costs due to duplicated roles across departments or units. |
| Scalability | Less scalable in dynamic or global environments. | Highly scalable for large, geographically spread businesses. |
| Information Flow | Top-down; limited upward feedback. | Multidirectional, promotes open communication. |
| Risk and Control | Central authority monitors risk closely; more control. | More risk due to dispersed control and decision-making. |
| Innovation and Responsiveness | Innovation may be limited due to a lack of field insights. | Encourages innovation and quicker responses to local needs. |
| Accountability | Concentrated at the top; less ownership at operational levels. | Shared accountability; local managers take responsibility for outcomes. |
| Leadership Style | Authoritative and directive. | Participative and collaborative. |
| Best For | Smaller firms, or organisations that need control and consistency (e.g., manufacturing, military, aviation). | Large, diverse, or fast-moving businesses that need flexibility (e.g., retail chains, FMCGs, MNCs). |
| Examples | Government departments, nationalised banks, and centralized education systems. | Multinational corporations, franchises, and regional service providers. |
Choosing the Right Structure
There is no universal answer when deciding between centralization and decentralization. A company must evaluate its industry type, team size, geographic spread, and customer expectations. Many modern companies even adopt a hybrid approach, combining central decision-making with local execution power.
Hybrid Organizational Structures
This Structure enables the leadership team to maintain control over core strategic decisions while giving regional offices the freedom to operate independently. This model delivers the best of both worlds—consistency in vision and agility in action.
A global hotel company should set up branding and pricing in a central scope but decentralize customer service and staff management according to the needs of different regions. This would ensure that the brand image is well-synchronized but still responsive to local demands.
Difference Between Centralization and Decentralization FAQs
What is centralization in an organization?
Centralization is where the top management retains the authority to make decisions. The lower levels follow instructions with very little input in decisions.
What is decentralization in management?
Decentralized decision-making is given to the lower levels, which improves the responsiveness of the establishment and encourages the cooperation of employees.
Is it possible for a corporation to employ both centralization and decentralization?
Yes, most companies will be using a hybrid model comprised of a centralized plan with decentralized execution to ensure the balancing of control and freedom.
What are some benefits associated with decentralization?
Decentralization allows for faster decision-making, greater empowerment of employees, and better responsiveness to local market conditions.
Why does decentralization appeal to large enterprises?
Since the very nature of their operations involves the diversity of being in more than one region, decentralization allows a multinational corporation to react faster to the distinctive local needs of each of its operational territories, remaining competitive in each market.