When undertaking legal and financial matters, in the law and finance world, the terms dissolution of partnership and dissolution of firm hold a meaning of their own; the two words are frequently interchanged. Dissolution of partnership and dissolution of firm refer to possible changes occurring within a partnership business; however, the terms differ significantly because of their nature, outcomes, and legal implications. Therefore, it is essential for the partners, accounting professionals, and business law students to know what the differences entail.
Knowing if a partnership has been dissolved only for reconstitution or entirely does affect the ultimate fate of the business. Still, it also affects how well the legal formalities regarding asset alliances, liabilities, and taxation will be adhered to. An in-depth study of these two terms will now follow.
What is Dissolution of Partnership?
Dissolution of Partnership refers to a change in the relationship between existing partners. This can happen because of the retirement or death of a partner, the admission of a new partner, or some alteration of the profit-sharing ratio. The business, however, continues to operate under the same name, so we call it a reconstitution rather than closure.
This type of dissolution focuses more on internal restructuring than closing the business. A new partnership agreement or deed is usually created after the dissolution. However, even though the composition of partners may change, or terms may be altered, the firm retains continuity with its clients, goodwill, and legal commitments.
Change in Partner Composition
One of the most common causes of partnership dissolution is a change in partner composition. Well, this might include retirement, admission, or the death of a partner. So the old agreement is dissolved, and a new one is created to reflect the partner changes.
Suspending the old agreement does not make the firm dissolve. Instead, the business continues to function, and services are provided to the market, so there are no disruptions, and the company continues to operate under the legal designation.
Reconstitution of the Partnership Deed
The deed must be updated whenever there is a change in the partnership terms, capital contributions, or profit-sharing ratios. Thus, the old deed is dissolved, and a new one is created.
For this reason, transparency exists, and legal compliance is maintained, as the partners agree to the changes. Even though the firm is undergoing internal changes, its external existence remains intact.
What is Dissolution of Firm?
The Dissolution of Firm refers to the end of the partnership business itself. It means shutting down all operations, liquidating assets, settling liabilities, and ending the firm’s legal existence. This, thus, signifies complete termination of the business rather than its reconstitution.
Dissolution of the firm must be by all partners’ consent or due to other unavoidable circumstances, such as insolvency, mutual agreement, or through a court order. The procedure is detailed, involves steps by law to be formally followed, and affects the internal arrangement and the business’s disposition in the marketing arena.
End of Business Operations
Dissolution of a firm refers to the stage at which it ceases to conduct its business, discontinues all contracts, and exits the market. A legal partnership ceases to exist. This proceeds with notifying the clients and stakeholders, fulfilling pending orders, and ensuring that it has closed ties with the market responsibly and legally.
Disbandment of Accounts and Legal Formalities
There must be a settlement to pay off outstanding debts and liabilities and to distribute any remaining profits between partners. Also, all tax liabilities, dues, and employee salaries are determined. This will then be followed by legal deregistration and notification to relevant authorities. Depending on the partnership agreement, if, by chance, the assets do not suffice to pay debts left behind by the firm, the partners might have to contribute personally toward settling such obligations.
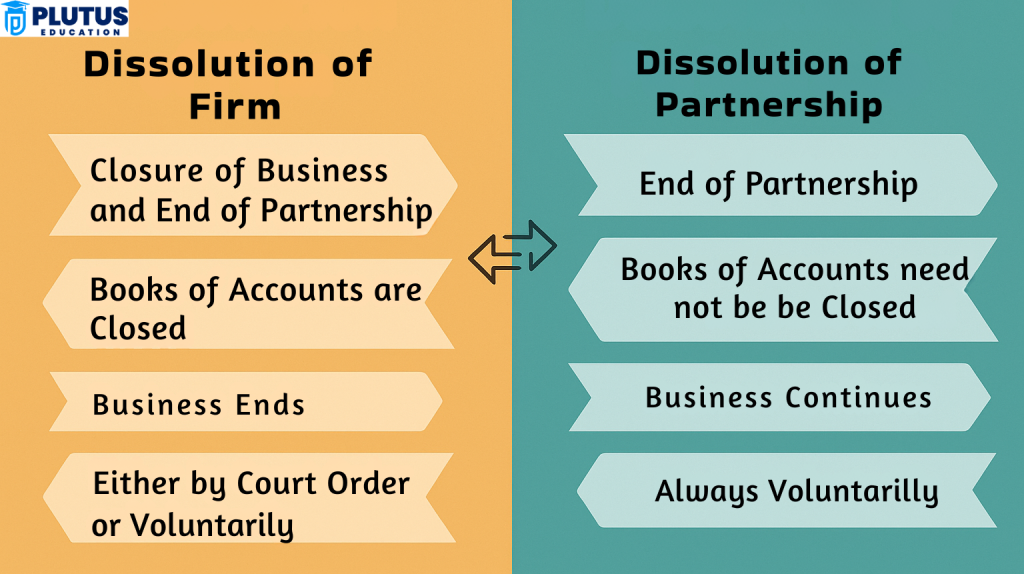
Difference Between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of Firm
Though the words sound so alike, as far as the fate of business continuity was concerned, they’re different in legalities. A dissolution of partnership transforms the internal relationship of a partnership, while the whole enterprise ceases to exist through dissolution. Thus, it is essential to know that for compliance with laws and sound financial planning. Unscrupulousness in understanding the terms will culminate in wrong filings, disputes, or tax complications.
Effect of Dissolution on Business Continuity: Partial Continuity
In the dissolution of a partnership, the firm continues functioning with a change in the agreement. In contrast, with the dissolution of a firm, the whole business activity is terminated, and its existence becomes nonexistent. Here is the central distinguishing point between operational planning. One is adjusting, while the other demands complete closure and liquidation.
Need for Restructure and Reorganisation
The dissolution of a partnership entails creating a new deed that records changes in ownership, profit-sharing, or roles. On the other hand, firm dissolution does not permit reconstitution, since the business ceases to exist. Therefore, while the former allowed the industry to mature, the latter led to permanent cessation.
Legal Closure Requirements
A partnership dissolution may not require formal legal procedures unless specified in the partnership deed. However, dissolving a firm requires legal compliance, including winding up proceedings, filing with the Registrar, and asset liquidation. This reflects the severity and finality of firm dissolution in legal and operational contexts.
Asset Handling
Since the business continues, no liquidation of assets is required in a partnership dissolution. However, all assets are sold during firm dissolution, and proceeds are used to clear debts and distribute the remaining amount among partners. The handling of finances plays a central role in differentiating the two.
Causes and Triggers
A change in the profit-sharing ratio, admission or retirement of a partner, or completion of the agreed term leads to partnership dissolution. Firm dissolution arises from mutual consent, legal mandate, or the accomplishment of business objectives. This shows that firm dissolution is often intentional and final, while partnership dissolution is more adaptive and routine.
| Aspect | Dissolution of Partnership | Dissolution of Firm |
| Definition | A change in the relationship among the existing partners of a firm. | A complete closure of the partnership business and its legal existence. |
| Effect on Business | Business continues to operate under the same firm name. | Business operations come to a permanent end. |
| Nature of Change | Internal reconstitution (structural change). | Final termination of the firm and all its activities. |
| Need for Reconstitution | A new partnership agreement is drafted to reflect changes. | No reconstitution, as the business ceases to exist. |
| Legal Status of the Firm | The firm continues to exist legally. | The legal status of the firm is terminated. |
| Cause/Reason | Admission, retirement, partner death, or profit-sharing ratio change. | Completion of purpose, mutual consent, insolvency, or court order. |
| Asset Liquidation | Not required, as the business continues. | Required. All assets are sold to pay off liabilities and settle partner accounts. |
| Liabilities Settlement | No immediate requirement to settle liabilities. | All liabilities must be settled before the firm can be dissolved. |
| Legal Formalities | May not require legal filing unless re-registration is needed. | Requires formal legal procedures, including notice to the Registrar of Firms. |
| Continuity of the Firm Name | The firm continues with the same or modified partnership deed. | The firm name and identity are permanently closed. |
| Existence of Business Entity | The business entity remains intact and functioning. | The business entity is dissolved and struck off from the records. |
| Resulting Partnership | A new partnership is formed with changed terms and/or partners. | No further partnership is formed under the same firm. |
| Court Involvement | Usually not required unless disputes arise. | Often involves legal intervention, especially in cases of insolvency or disagreement. |
| Example Scenario | A partner retires, and the remaining partners continue the business under a new agreement. | All partners agree to close the business due to a lack of profitability or purpose completion. |
| Involvement of Creditors | Not directly involved unless changes affect repayment obligations. | Creditors must be paid off before any distribution of remaining assets to partners. |
| Relevance in Daily Operations | It commonly occurs as businesses evolve and change their structure. | Less frequent, usually a result of strategic or financial decisions. |
Why Knowing the Difference Matters?
Dissolution of partnership and dissolution of firm are two concepts that hold vital importance for businesspersons, students, and lawyers. While both denote changes within a partnership arrangement, the main difference lies in the degree of damage/influence on the business’s continued existence. In the dissolution of a partnership, the point of focus for reconstitution allows the firm to exist; on the other hand, the dissolution of a firm marks the complete cessation of all business activities and legal existence. Thus, with a proper grasp of these concepts, a partner can make conscious choices leading to legal compliance, ensuring asset and liability management success. While restructuring or winding up the partnership or firm, the decision will significantly depend on what is relevant to the future goal of the business and its legal implications.
Modes of Dissolution of Partnership
There are many methods of dissolving partnerships, and many do not interfere with the firm’s continuity. These methods show the flexibility of partnership law and the ability of the firm to adapt while maintaining its legal and market presence. Each method meets various business requirements and situations to ensure that the many partnership structures can transform without having to close the business for good.
By Mutual Agreement
Partners might mutually agree to change the terms of the partnership by admitting a new partner or varying the capital. This will amount to the partnership’s dissolution but not the firm’s. This is the most common and flexible type of dissolution that allows an efficient and amicable restructuring of business affairs.
By Operation of Law
Where events such as a partner’s death, bankruptcy, or incapacity occur, automatic dissolution of the partnership agreement takes effect. Surviving partners may choose to carry on the business under a new deal. The law recognizes these events as disruptive and allows for such reconstitution as may be desired by the remaining partners.
On Expiry of Term or Completion of Purpose
If the partnership was set up with a specific duration in mind or for a particular project, dissolution occurs automatically upon such completion. The partners will then have a choice of dissolving the firm or continuing operations under a new agreement, should there be any future scope for collaboration.
Changes in Profit-Sharing Ratio
Any significant amendment to the ratio in which profits are shared might require a new deed to be drawn. This will dissolve the partnership, but the business may continue without interruption. This way, the company can realign the reward system based on merit, market changes, or changing roles.
Retirement from Partnership or Admission of a Partner
Once a new partner is admitted or an old one is expelled, a new agreement has to be executed, thereby dissolving the partnership. However, the name and operation are usually unaffected. Thus, the business continues to evolve with partners without disrupting customer relations.
Dissolution of Partnership vs Dissolution of Firm FAQs
What is the dissolution of a partnership?
It refers to a change in the agreement among partners, typically due to admission, retirement, or a shift in terms, while the firm continues to operate.
What leads to the dissolution of a firm?
A firm may be dissolved due to mutual agreement, insolvency, completion of purpose, court orders, or when partners permanently shut down operations.
Does dissolution of a partnership require legal closure?
No. It typically does not involve legal closure, as the business continues under a new agreement. However, proper documentation and deed changes are essential.
What are the key modes of dissolution of a partnership?
These include mutual agreement, operation of law, expiry of term, change in profit-sharing ratio, and admission or retirement of a partner.
What happens to the assets in a dissolution of a firm?
Assets are liquidated to pay off liabilities, and any remaining amount is distributed among partners according to their capital contribution or agreement terms.


