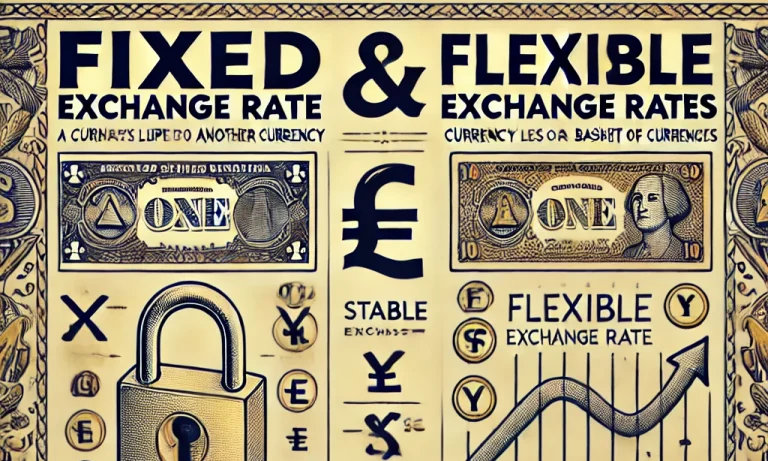
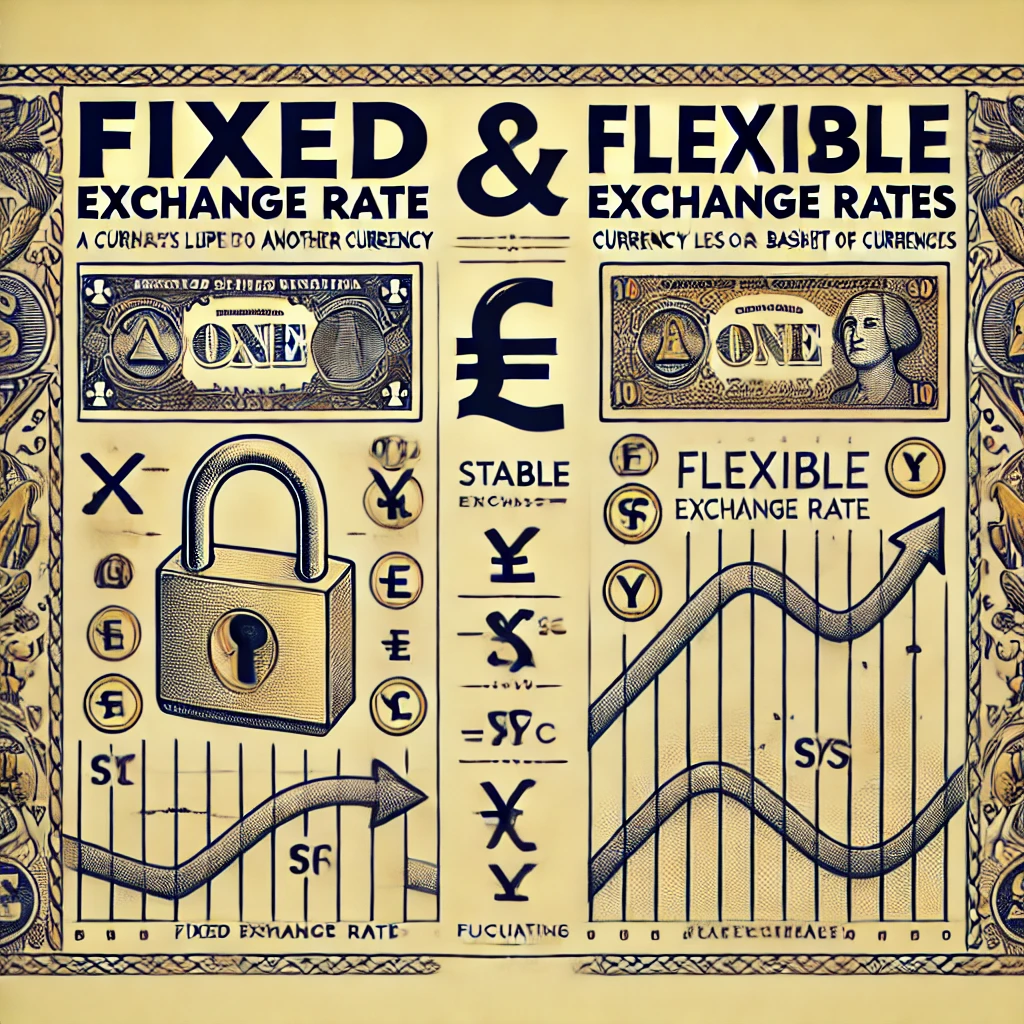
The terms fixed and flexible exchange rate are basic to understanding how nations manage the currency values relative to others. A fixed exchange rate is also referred to as a pegged exchange rate where the currency value of a country is pegged or tied to some other major currency, such as the US Dollar, or a basket of currencies. A flexible exchange rate, on the other hand, is determined by market forces, wherein there is no direct governmental or central bank intervention.
These systems affect trade, investment, and economic stability. Below is a full discussion of their differences, implementations, advantages, and disadvantages.
Difference Between Fixed and Flexible Exchange Rate
The basic difference between a fixed and a flexible exchange system lies in the method of the maintenance of currency value. Under a fixed system, authorities fix the value. When it comes to systems where exchange rates are flexible, the market forces control the currency value based on supply and demand dynamics.
| Feature | Fixed Exchange Rate | Flexible Exchange Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Determination | Greater; focus on domestic economic goals. | Determined by foreign exchange market forces. |
| Stability | Stable; minimal fluctuations. | Volatile; subject to market dynamics. |
| Adjustment Mechanism | Government intervention through reserves. | Adjusts naturally through market mechanisms. |
| Impact on Trade and Investment | Encourages long-term trade and investment by reducing risks. | Exposes traders to exchange rate risks. |
| Speculative Activity | Lesser due to controlled rates. | Higher due to currency volatility. |
| Monetary Policy Autonomy | Limited; central bank focuses on exchange rate stability. | Greater; focuses on domestic economic goals. |
| Examples | Hong Kong Dollar, Saudi Riyal. | USD, Euro, Japanese Yen. |
What is Fixed Exchange Rate?
A fixed exchange rate system involves setting a stable exchange rate by pegging the currency to another stable currency or a basket of currencies. This ensures predictability and is particularly beneficial for countries reliant on trade with the pegged currency’s nation.
Implementation of Fixed Exchange Rates
- Reserve Maintenance: The central bank holds substantial foreign reserves to buy/sell currency to maintain the fixed rate.
- Monetary Policy: Policies align with the fixed exchange rate goals, often sacrificing inflation control.
- Exchange Controls: Government restrictions prevent drastic currency fluctuations by controlling foreign exchange access.
Advantages of Fixed Exchange Rates
- Stability: Promotes confidence among traders and investors.
- Inflation Control: Acts as a check on inflation by tying to a stable foreign currency.
- Facilitates Trade: Reduces exchange rate uncertainty, boosting trade.
Disadvantages of Fixed Exchange Rates
- Reserve Dependency: Requires large foreign reserves.
- Loss of Monetary Policy Control: Limits autonomy to address domestic economic conditions.
- Risk of Speculative Attacks: Vulnerable if investors doubt the government’s ability to maintain the peg.
What is Flexible Exchange Rate?
In an elastic exchange rate system, the open market determines currency values by supply and demand. Most developed financial systems use this system to let economic factors decide exchanges in movements.
Implementation of Flexible Exchange Rates
- Market Determination: The value of currencies depends on trade balances, interest rates, and economic health.
- Role of Central Bank: The intervention is minimal and usually made only when extreme volatility is being reached.
- Capital Freedom: The flow of foreign exchange has no restriction so a liberal economic environment is provided.
Advantages of Flexible Exchange Rates
- Economic Autonomy: Allows independent monetary policy for domestic goals.
- Market Efficiency: Reflects real economic conditions.
- Shock Absorption: Adjusts to economic shocks without draining reserves.
Disadvantages of Flexible Exchange Rates
- Volatility: Creates uncertainty, potentially deterring trade and investment.
- Speculation: Prone to speculative currency trading.
- Inflation Risk: Can lead to higher inflation due to unchecked currency depreciation.
Fixed and Flexible Exchange Rate FAQs
What is the primary difference between fixed and flexible exchange rates?
Fixed rates are set by government policies, while flexible rates fluctuate according to market forces.
Why do some countries prefer fixed exchange rates?
They provide stability and predictability, crucial for economies heavily reliant on trade.
What are the main advantages of flexible exchange rates?
They offer monetary policy freedom and better reflect economic conditions.
Can a country switch between these systems?
Yes, based on economic priorities and challenges, nations can transition from one system to another.
Which system is better for developing nations?
It depends on the nation’s trade dynamics and economic goals. Fixed rates might suit economies needing stability, while flexible rates work better for those seeking growth autonomy.