The difference between industry and commerce lies in their functions, processes, and the roles they play in the economy. Industry refers to producing goods and services, based on manufacturing, extraction, or construction. Commerce, alternatively, relates to the purchase and sale of goods and services, linking the producers and customers. Both are essential for making any economy run smoothly since each is dependent on the other so products move from being manufactured to getting transported and sold.
What is Industry?
Industry refers to the sector of an economy that is concerned with the production and manufacturing of goods. It involves transforming raw materials into finished products or services. The industry is the backbone of economic development as it contributes significantly to job creation, the GDP of a country, and the overall economy. It includes various sub-sectors, such as manufacturing, mining, construction, and agriculture.
Features of Industry
Industries are important to the economy as they change raw materials into finished products and create employment. Industries deal with large-scale productions and technological advances to respond to market demands.
- Product Generation: Industries will engage in the conversion of raw material to a sellable and usable product.
- Employment Generation: Industries develop thousands of job opportunities for people and employ a significant part of the population.
- Investment Intensive: To establish an industrial plant, the initial investment has to be enormous, especially in machinery, technology, and other infrastructures.
- Technological Innovations: The industry depends on innovations, invariably applying modern technologies to increase operational efficiency in production.
- Large-Scale Operations: Industries operate on a large scale for market demand on product.
What is Commerce?
Commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services. It links producers and consumers to exchange goods. Commerce covers the whole process from manufacturer to consumer, encompassing trade in goods and services, banking, insurance, and transport.
Commerce is an important tool for economic development because it ensures the free flow of goods, services, and capital. It provides a crucial link between local businesses and the world market, enabling consumers to access a diverse range of products. In the absence of commerce, the manufactured goods from the industries would not reach the final consumer.
Features of Commerce
Commerce promotes productive and smooth trading, provides financial support, and helps businesses in managing risk, hence growth and global reach.
- Facilitates Trade: It deals in the transaction of movements of goods in selling, trade, buy, and so forth, to enable accessibility to goods.
- Transport: A well-defined transport system is required for commerce in moving goods from industries to markets.
- Global Reach: Expanding the market base exposure of a company, acquiring it access to domestic and international markets.
- Financial Support: Banking and financial activities are part of commerce, through which the businessman can provide capital for growth.
- Risk Management: This offers business continuity within commerce through insurance and other services for risk management.
Difference Between Industry & Commerce
Whereas industries center around the production of goods and services-such goods and services are manufactured, constructed, and extracted-commerce concerns the distribution, exchange, and support services of all these goods to the consumers within this ecosystem. They both together form the backbone of economic activity whereas, on the one hand, the industries make the products and, on the other hand, commerce makes sure that such products are efficiently taken to the correct markets. Hence, for gaining insights about business operation and economic contribution, this distinction has become increasingly relevant. The distinction between industry and commerce can be exemplified by the following points:
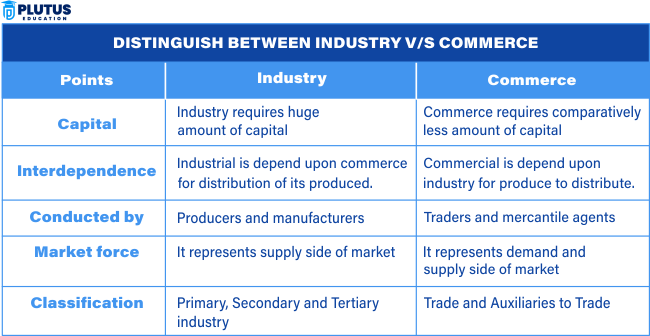
Focus
The Industry is dealing with the goods and services production. It’s an activity like manufacturing, construction, and extraction. It is mainly engaged in creating products for sale or consumption by other sectors of the economy. Industry will, therefore, transform raw materials into finished goods requiring labor, machinery, and raw materials.
Commerce: Commerce is the buying and selling of goods and services. It links producers to consumers and ensures that products are distributed in the market. Commerce includes activities such as trade, transportation, banking, and insurance, and aims to move products from the industry to the end consumer.
Scope
Industry: The scope of industry is limited to the production and manufacturing of goods. It focuses mainly on creating products through processes that require heavy investment in resources and infrastructure. It is said that industry does not really deal with or carry the distribution of these goods, but they actually make them available to commerce, which will do the distribution for them.
Commerce: A broader term, commerce is the entire trade process-from buying, selling, and transporting goods to financing and marketing the products. Commerce ensures that goods reach the consumers and makes the selling of industry products possible, either locally or internationally.
Activities
Industry: The Industry involves activities such as manufacturing, construction, and extraction. These activities are essential to create raw materials or finished products that can be sold in the market. Industry often requires large-scale operations and specialized equipment to transform raw materials into finished goods.
Commerce: Commerce involves a different set of activities. These include trade, transportation, banking, and insurance. Commerce works to move goods from industries to consumers and provides the necessary financial and logistical support to make that happen. It also involves the marketing of products to ensure that they reach the right market and consumers.
Goal
Industry: The main goal of industry is to create products that can be sold or used in other sectors of the economy. Industries focus on the production process and aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase output.
Commerce: The goal of commerce is to distribute these products. It ensures that goods produced by industries are transported, sold, and delivered to consumers. Commerce bridges the gap between production and consumption by managing the flow of goods in the market.
Dependency
Industry: It depends on raw materials, labor, and machinery, as the industry needs these three in constant supply: raw materials to continue production, skilled labor to maneuver machinery, and technological infrastructures to enhance the manufacturing process.
Commerce: Commerce depends on transportation, finance, and marketing. Without effective transportation, goods produced by industry would not reach consumers. Finance and marketing are crucial for ensuring that products are sold, and commerce often relies on banks and insurance to handle risks associated with the movement of goods.
Comparison Table: Industry vs Commerce
| Aspect | Industry | Commerce |
| Focus | Focuses on the production of goods and services using raw materials and labor. | Focuses on the buying, selling, and distribution of goods and services to consumers. |
| Scope | Limited to activities like manufacturing, construction, and processing. | Covers a broader range, including trade and all aids to trade (transport, warehousing, banking, etc.). |
| Activities | Includes manufacturing, mining, construction, and extraction industries. | Includes wholesale/retail trade, transportation, banking, insurance, and advertising. |
| Goal | The primary goal is the creation and transformation of raw materials into finished products. | The goal is the distribution and exchange of products to reach the final consumer. |
| Dependency | Depends on natural resources, raw materials, labor, and machinery. | Depends on transportation, finance, warehousing, and marketing support. |
| Output | Produces tangible goods or services ready for the market. | Ensures goods move efficiently from producers to consumers. |
| Capital Investment | Requires large capital investment in plants, equipment, and machinery. | Requires comparatively lower capital, focused on logistics and service infrastructure. |
| Risk Involved | High risk due to production failures, raw material shortages, or labor issues. | Risk mostly involves market fluctuations, credit issues, and logistical challenges. |
| Economic Role | Backbone of economic development by generating products and employment. | Facilitates economic flow by connecting producers with consumers and ensuring market efficiency. |
| Examples | Textile mills, automobile factories, oil refineries, construction firms. | Retail chains, logistics companies, banks, insurance firms, e-commerce platforms. |
Industry vs Commerce FAQs
1. What is the difference between industry and commerce?
Industry involves the production of goods and services, while commerce deals with their distribution, exchange, and support services.
2. Is commerce a part of industry?
No, commerce and industry are separate components of business. Industry focuses on creation; commerce focuses on movement and facilitation of trade.
3. What are examples of industry and commerce?
Industry: Manufacturing, mining, construction. Commerce: Trade, transport, banking, warehousing, insurance.
4. Why is commerce important to industry?
Commerce helps industries by distributing products, managing supply chains, providing financial support, and reaching consumers.
5. How do industry and commerce work together?
Industry produces goods; commerce ensures they reach the market efficiently. Together, they drive economic growth and consumer satisfaction.


