Understanding how savings differ from investments is very important for anyone aiming to achieve a firm foundation for their future. Savings mean putting away some dollars into safe, low-risk accounts for emergent cases and short-term objectives. Investments mean putting money into stocks, bonds, or real estate to gain wealth over time. It is this combination of when and how to save or invest that will lead one to achieve financial safety along with long-term prosperity.
What Is Saving?
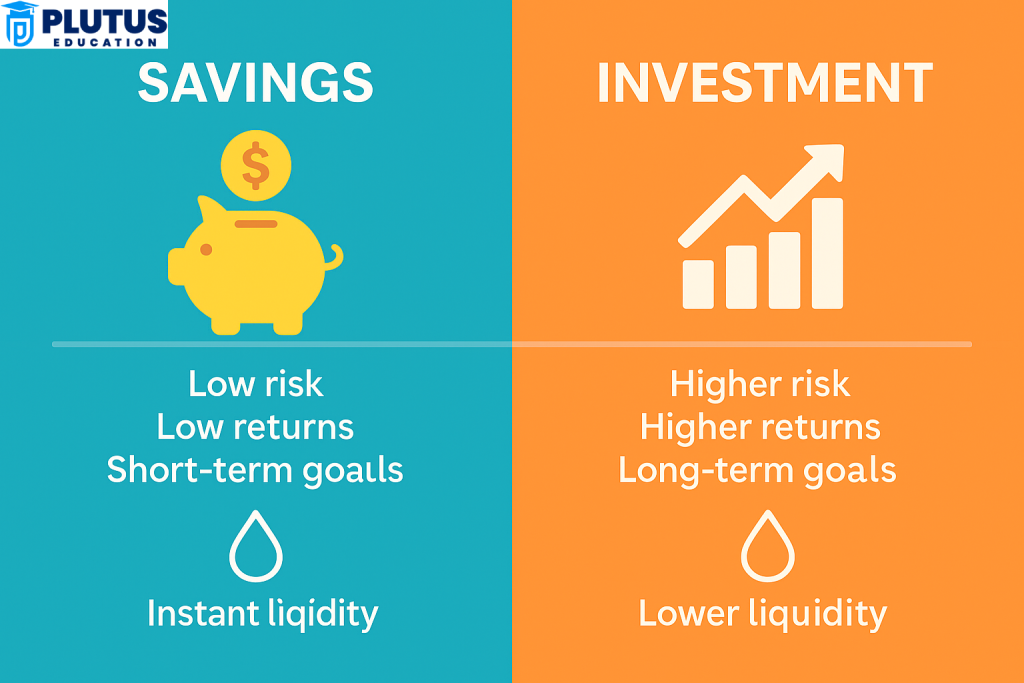
Savings refer to the act of setting aside some of your income in a safe place, such as a savings account, for future use. People save for emergencies, short-term needs, or planned expenses. The main objective is to preserve the money and not to grow it. It is the beginning of any financial plan and provides one with the assurance of safety.
A savings account is the safest of the investment options, with easy liquidity. This means that one can actually access money anytime one needs it. The returns from saving are low because interest rates are low, but saving ensures security and accessibility. The real beauty of this is that it guarantees that you can access funds without borrowing or relying on credit in emergencies.
Saving becomes the financial safety net that cushions you from sudden shocks. Individuals with a regular saving habit feel more in control of their finances and less anxious about the future. It also creates the foundation for eventual investment.
Types and Benefits of Savings
Savings can be stored in:
- Regular savings accounts
- Fixed deposits
- Money market accounts
These options carry very low risk. The benefits include
- Easy access to cash
- Principal safety
- Small, steady interest earnings
- Reduced financial stress
Saving is best for goals like building an emergency fund, buying a gadget, or planning a trip. However, it is not ideal for growing wealth due to low returns.
What Is Investment?
Furthermore, the most appropriate horizon for investments is the distant one. The far-off approaches are to be adopted to satisfy one’s long-term financial objectives. Long-term goals may comprise retirement planning, funding one’s education, or purchasing a home. Savings typically offer creditworthiness, whereas investments are aimed at growth. The lesser-known threat of market-linked investments comes from their up-and-down movement for very short periods. However, in almost all observations, they have conveniently beaten and surpassed all forms of traditional savings in the long run.
Those who invest wisely see their money grow faster, helping them beat inflation and reach financial independence sooner. Investment also brings the opportunity to generate passive income through dividends or rental income.
Types and Benefits of Investment Options
Investments may comprise any of the following:
- Stocks and equity mutual funds
- Bonds and fixed-income
- Real estate
- Gold or commodities
Some Pros of investing:
- High potential returns
- Protection from inflation
- Diversification of assets
- Capital appreciation in the long run
But investments can be risky. The market might be volatile; economic changes or poor timing might see gains turn into losses. Therefore, one should invest in someone who understands risk and is in it for the long haul.
Key Differences Between Savings and Investment
Knowing the difference between savings and investment is essential for an optimal combination of financial planning. Savings and investments have different purposes and operate on different principles, reflecting the difference between savings and investment. One preserves money; the other grows it. Both, however, are equally important. An individual without savings has no financial stability, whereas one without investments has wealth that does not produce enough for the future.
| Aspect | Savings | Investment |
| Definition | Money set aside in low-risk, easily accessible accounts for future needs. | Allocation of money into assets to earn returns and grow wealth over time. |
| Objective | Preserve capital and maintain liquidity for emergencies or short-term goals. | Grow wealth over the long term through appreciation or income generation. |
| Risk Level | Very low or no risk. | Medium to high risk, depending on asset type. |
| Return Potential | Low returns (typically 2–4% annually). | High returns (can range from 8% to 15% or more annually). |
| Time Horizon | Short-term (0–2 years). | Long-term (3 years and above). |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid money is available instantly or within 1–2 days. | Less liquid—may take days, months, or years to convert into cash. |
| Instruments Used | Savings accounts, fixed deposits (FDs), recurring deposits (RDs), etc. | Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, gold, ETFs, etc. |
| Inflation Protection | Poor – savings often don’t beat inflation. | Strong – many investments outperform inflation over time. |
| Principal Security | High – money is safe and rarely loses value. | Low to medium – risk of losing principal in market downturns. |
| Accessibility | Immediate – funds are easily withdrawn without penalty. | Restricted – some investments may have lock-in periods or exit loads. |
| Income Generation | Limited – via low interest earnings. | Moderate to high – through dividends, capital gains, or rental income. |
| Management Complexity | Very simple – no need for financial knowledge. | Complex – requires market understanding and periodic monitoring. |
| Ideal For | Emergency fund, travel, short-term expenses, basic financial safety. | Retirement planning, wealth building, education fund, long-term goals. |
| Tax Implications | Interest is usually taxable, but at lower rates. | Gains may be taxed as per capital gains or dividend income rules. |
| Example Scenario | Saving ₹10,000 monthly for a medical emergency fund. | Investing ₹10,000 monthly in mutual funds for retirement over 10 years. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible—deposit or withdraw anytime. | Less flexible—early withdrawal might reduce returns or involve charges. |
Pros and Cons of Savings and Investment
The path to achieving financial security lies in choosing fearlessly where and how to invest your money. Saving and investing are two of the most commonly cited tools, but they serve two different purposes. While saving mainly focuses on safety and liquidity, investing is about adding wealth over time. Weighing the pros and cons of saving versus investing helps individuals find the right balance while being able to make informed financial decisions in accordance with their goals and consideration of factors such as risk tolerance.
Pros of Saving
Saving is a somewhat cautious method of financial management directed toward security, liquidity, and financial discipline. This technique is likely to be adopted for any financial undertaking, even in preliminary stages, as savings constitute the groundwork for emergencies and short-term targets.
- Gives liquidity: This fund might be accessed almost instantaneously without penalties if the funds saved were in bank accounts or liquid funds in case of unexpected expenses or even emergencies.
- Principal protection: Savings are usually reserved in bank accounts and fixed deposits, which do not allow your money to go through wild market fluctuations. Thus, the principal amount undergoing saving shall be kept in safety.
- Emergency provisions: Savings can cushion bitterly during unforeseen events, illness, losing a job, or urgent travelling. Having an emergency fund naturally takes away some financial stress during testing times.
- Fosters a culture of financial discipline: Creating a habit where one saves a certain percentage of one’s income builds strong financial discipline. This discipline is the backbone of sound financial planning and sets the stage for investments down the road.
Cons to Saving
Saving is essential, but it has its drawbacks that limit long-term financial growth in high-inflation periods or in phases geared toward building wealth.
- Low returns: Interest rates offered by a savings account or fixed deposit are very low and so low that over the long haul, they are unable to build wealth or even beat inflation materially.
- Inflation erodes purchasing power: Inflation averaging at 5%–6% for several economies commonly tends to lessen the real value of money in savings, implying that money you put away retains lesser purchasing power later.
- Doesn’t help in building long-term wealth: Savings will not earn a considerable return. Just savings can procrastinate wealth formation and hinder long-term financial objectives such as retirement living or ownership of a home.
- Opportunities lost by not investing: Every moment spent keeping money in a low-yielding instrument is a potential moment of gains lost, which could have been realized in an upside way by investing in high-return investments like mutual funds, stocks, or real estate.
Pros of Investing
Investing means putting your money in assets such as stocks, mutual funds, or property targeted at generating returns and the creation of long-term wealth. Investing entails risk; however, it also signifies growth and protection against inflation.
- Higher returns than savings: Investments usually offer returns that are considered higher than savings in the long term. Equity and mutual fund assets can return anywhere from 10-15% a year over a period, which significantly augments one’s wealth.
- Better protection from inflation: Investments will, unlike savings, usually give inflating returns. Investing in growth assets today protects the future real value of your money.
- Asset Diversification: Investing offers the ability to spread your money across different instruments like stocks, bonds, real estate, and gold, which helps manage risk and improve overall portfolio stability.
- Helps achieve long-term financial goals: Investing is essential for meeting long-term objectives such as buying a house, funding higher education, or retiring comfortably. The compounding effect works in your favour when investing early and consistently.
Cons of Investing
With benefits come a certain degree of risk and drawbacks. Thus, it is worth knowing about the disPros before investing any considerable amount and going for an aggressive strategy.
- Risk of capital loss: Investments can lose value due to market volatility, poor economic conditions, or underperforming assets, and thus, the invested capital in a high-risk venture can even be wiped out.
- Requires knowledge of the market: Investing successfully requires a good understanding of markets, instruments, and timing. Depending on the level of research or guidance, investors could make bad investment decisions that would affect their returns or multiply their risk.
- Longer time commitment: Most investments take time before they yield meaningful returns. For example, equity investments may take hold with a 3-5 year horizon or longer to bounce back from the downswing and to grow.
- Less liquidity: Once money is invested, it doesn’t mean one can always lay hands on it in short order. The timing of selling of shares, real estate property, or long-term bonds may take reasonable time and thus be unsuitable for short-term financing.
When to Save and When to Invest?
Knowing when to save or when to invest certain funds is essential for financial success. Both paths play important roles in different life stages and depend heavily on the set financial goals, time frame, and risk tolerance.
Save When?
Savings should be prioritized when you’re building an emergency fund, planning for short-term goals (within a year), or need liquidity. If you’re trying to avoid debt or cover essential expenses, saving is the safer and more accessible option.
Invest When?
Investment makes sense when your basic financial foundation is secure — your emergency fund is full, and you have surplus money. If your goals are longer-term (3+ years), such as retirement, buying property, or wealth creation, investing will help your money grow faster than saving.
Start by saving 20–30% of your monthly income, allocating it toward an emergency fund and short-term goals. Once that foundation is secure, shift excess funds into investments. As your knowledge and income grow, increase the share of investments in your portfolio to fight inflation and create wealth.
Why Balancing Savings and Investments is the Best Strategy?
Relying only on savings can keep you financially stuck. Investing without a savings cushion can lead to financial stress. That’s why balancing both is critical. A healthy financial plan includes:
- 20% savings: For short-term needs and emergencies.
- 30–40% investments: For long-term goals and wealth growth.
- 40–50% expenses: For living needs.
This balance ensures you are financially prepared for today and tomorrow. Keep revisiting your plan as your income, expenses, and life goals evolve.
Difference Between Savings and Investment FAQs
Can I save and invest at the same time?
Yes. Start by saving for short-term needs, then begin investing for long-term goals. Balancing both builds financial stability and growth.
What is safer: savings or investment?
Savings are safer because they have low risk. Investments carry higher risk but offer higher returns over time.
Do savings protect against inflation?
No. Savings offer low returns and may lose value over time due to inflation. Investments are better at beating inflation.
What is the right time horizon for investments?
Investments work best for goals 3–10 years away. For shorter periods, savings are more appropriate.
Should I prioritize saving or investing first?
Start with saving to build an emergency fund. Once that’s done, focus on investing to grow your wealth.