Cost and budgeting are management tools in cost and financial management that are both standard costing and budgetary control. While both approaches are directed toward the premise of economic effectiveness and cost management, they are differentiated with respect to scope, application, and objective. While standard costing specifies predetermined costs for materials, labor, and overheads to help businesses measure and control production costs, budgetary control sets or defines financial plans and has functional efficiency parameters so that all departments work under financial targets. Standard costing and budgetary control differ enough to assist organizations in making sound financial decisions and controlling their variances while aligning their objectives and strategies for future growth. Efficiency results in not only managing wastages but also optimizing resource utilization and maintaining consistency with finances by using both methods.
What is Standard Costing and What Does it Do?
Standard costing is the method by which a production unit sets predetermined costs for raw materials, labor, and overhead. Collectively, these are known as standards. Organizations will compare their standards to actual expenses incurred throughout the operations. The difference between the actual and the standard cost connotes a variance. Managers use this kind of information to find out inefficiencies and correct them in real time.
Standard costing plays a significant part in controlling costs and evaluating performance. Not only does it give a constant price for a product, but it also detects fluctuations in the costs at early stages and helps control the production budget. This is particularly beneficial to manufacturing companies because their production cycles mostly involve the exact prices.
What is Budgetary Control, and Why Does It Matter?
Simply put, budgetary control means preparing comprehensive budgets by departments and checking actual performance against these targets. Budgetary control tracks both spending and income as well as investment to make sure that financial activities are going in the intended direction. Managers exercise budgetary control to use resources appropriately and to discover times when the budget is exceeded and in what areas adjustments need to be made for greater financial health.
Unlike standard costing, which can be limited to production costs, budgetary control applies to the whole organisation, from sales to marketing and HR to administration. All these departments can thus work towards the same financial objectives and enhance the overall strategic alignment. This has been employed by private, public, and non-profit sectors, making it a sound tool for financial planning.
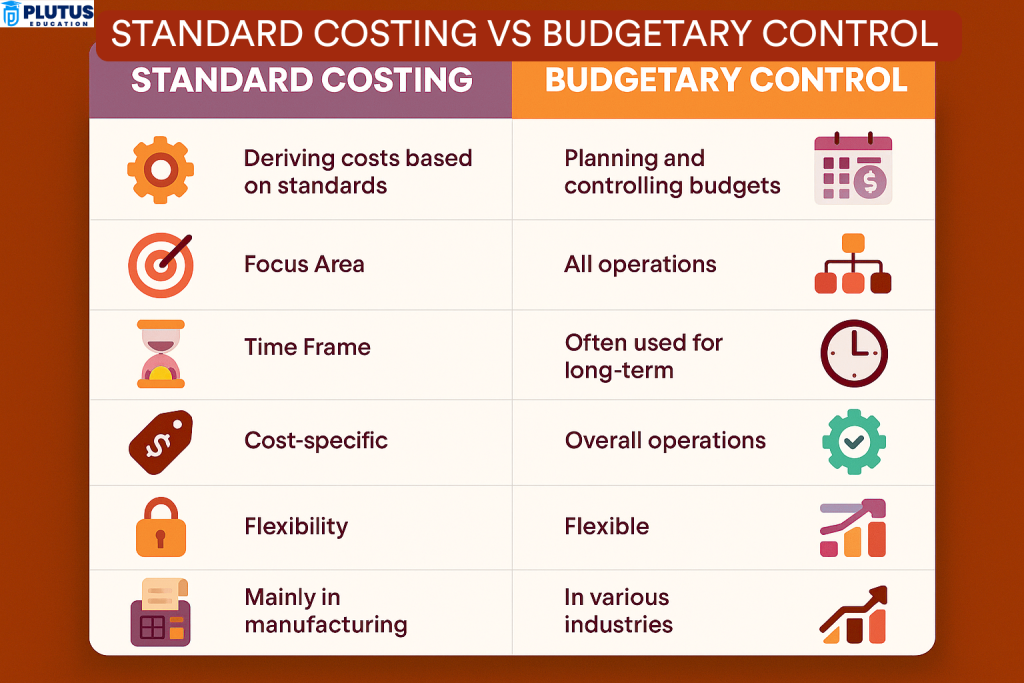
Key Differences Between Standard Costing and Budgetary Control
Though both techniques involve setting financial expectations and analyzing variances, their scope and usage differ significantly. Standard costing deals specifically with production costs, while budgetary control manages the overall economic plan of an organization.
| Aspect | Standard Costing | Budgetary Control |
| Definition | A cost control method that uses predetermined costs for materials, labor, and overhead to measure performance. | A financial control method that involves planning budgets and comparing actual results to control organizational spending. |
| Purpose | To establish standard cost benchmarks and detect cost deviations in production. | To manage financial operations by planning, monitoring, and adjusting departmental and project-level budgets. |
| Scope | Limited to production and manufacturing-related costs. | Organisation-wide; includes all functions—sales, admin, HR, marketing, etc. |
| Application | Mainly used in manufacturing industries. | Applicable to all sectors and business types, including service and non-profit. |
| Focus | Operational cost efficiency through cost standardization and variance control. | Strategic financial planning and control across multiple departments. |
| Time Frame | Continuous and real-time during the production process. | Usually planned annually with monthly or quarterly performance reviews. |
| Cost Elements Covered | Covers only direct and indirect production costs such as material, labour, and overhead. | Covers all financial elements, including income, expenses, investments, and revenues. |
| Variance Analysis | Focuses on the difference between standard and actual production costs. | Focuses on the difference between budgeted and actual financial results. |
| Decision-Making Use | Supports short-term operational decisions like process improvements and cost cuts. | Guides long-term strategic financial decisions and resource allocation. |
| Responsibility Centered | Cost responsibility is usually focused on production managers or operational heads. | Involves all department heads and managers who are accountable for their budgets. |
| Update Frequency | Standards are revised periodically based on cost trends or market conditions. | Budgets are reviewed annually or as needed based on financial performance. |
| Primary Outcome | Maintains cost consistency and improves operational productivity. | Ensures financial discipline and goal-oriented performance across the organisation. |
| Data Dependence | Based on technical estimates and production history. | Based on past financial performance, market forecasts, and strategic goals. |
| Integration with Systems | Commonly integrated with ERP and production costing software. | Integrated into financial planning systems, accounting platforms, and dashboards. |
| Examples of Use | Used to monitor material wastage in a factory or labor efficiency in an assembly unit. | Used to ensure a marketing department stays within its annual expense limit. |
| Control Mechanism | Controls variances in input usage and cost per unit in production. | Controls departmental spending and ensures organisational financial alignment. |
Businesses often use both tools simultaneously. While standard costing helps control production costs at the micro level, budgetary control provides the big-picture financial roadmap.
Benefits of Using Standard Costing and Budgetary Control Together
When organizations use standard costing and budgetary control together, they gain a comprehensive control system that works at both operational and strategic levels. Standard costing keeps production efficient and lean. At the same time, budgetary control ensures the organization sticks to its financial goals.
Using both tools results in
- Better variance analysis—comparing production variances and budget deviations.
- Improved cost visibility—identifying high-cost areas early.
- Aligned goals—linking daily operations with annual financial targets.
- Enhanced decision-making—using accurate data to guide policy.
Combining both methods creates a structured financial discipline across the organization and boosts profitability.
Applications and Relevance in Modern Business
Standard costing works well in product-driven environments such as factories, textile industries, or electronics assembly lines. It helps these organizations reduce waste, increase labor efficiency, and control inventory costs. On the other hand, budgetary control supports financial management across industries such as banking, retail, healthcare, and education.
- Today, businesses use budgetary control in ERP systems, financial software, and cloud platforms to track real-time expenses. Similarly, standard costing systems are integrated with manufacturing software to ensure constant monitoring of resource usage and cost per unit.
- Organizations benefit from standard costing by ensuring accurate pricing and cost benchmarking. Budgetary control improves fiscal responsibility and strategic financial planning.
Standard Costing and Budgetary Control Real-World Example
Consider a company that manufactures mobile phones. It uses standard costing to determine that producing one device should cost SGD 100. However, the actual cost per unit turns out to be SGD 110. The variance is analyzed, and it’s found that raw material prices increased. Managers negotiate better deals with suppliers to bring costs down again. Simultaneously, the company has an annual budget of SGD 5 million. Each department is assigned a portion. Through budgetary control, the company tracks whether each team is staying within their assigned financial boundaries. If marketing exceeds its budget, funds may be reallocated from underutilized departments like HR. This example highlights how both techniques are vital for day-to-day operations and long-term success.
Standard Costing vs Budgetary Control FAQs
What is the primary purpose of standard costing?
The primary purpose of standard costing is to control production costs by comparing actual expenses with preset cost standards and identifying inefficiencies.
How does budgetary control support strategic goals?
Budgetary control ensures departments stay within financial limits, which supports overall organisational goals through effective planning and monitoring.
Can standard costing be used outside of manufacturing?
Standard costing is best suited for manufacturing but can be adapted in service sectors where repeatable, cost-based processes exist.
What are the benefits of using both standard costing and budgetary control?
Using both tools provides real-time cost monitoring and long-term financial planning, improving cost efficiency and strategic alignment.
How do variances in standard costing differ from those in budgetary control?
Standard costing variances focus on cost components (like material or labour), while budgetary control variances assess total financial performance against planned targets.


