Foreign trade in commerce refers to the exchange of goods, services, and capital across international borders. It plays a fundamental role in the global economy by linking nations, fostering specialization, and enabling access to resources and technologies. Through imports, exports, and entrepôt trade, foreign trade in commerce facilitates economic growth, innovation, and cultural exchange. It also introduces businesses and governments to unique challenges, such as navigating international regulations and addressing trade barriers.
What is Foreign Trade in Commerce
Foreign trade in commerce is the process of buying, selling, and exchanging goods and services across countries. Unlike domestic trade, foreign trade operates under international laws, involves currency exchange, and often requires compliance with trade agreements and tariffs. It is an integral part of globalization, connecting economies and promoting mutual growth.
The Pillars of Foreign Trade in Commerce
Foreign trade is classified into three main categories:
- Import Trade: The acquisition of goods or services from other countries for domestic consumption or further production.
- Export Trade: The sale of domestically produced goods or services to foreign markets.
- Entrepôt Trade: Importing goods with the intention of re-exporting them after minor processing or without significant modifications.
Each type of trade contributes uniquely to a country’s economy. Imports provide access to resources unavailable domestically, exports generate revenue, and entrepôt trade strengthens a nation’s position as a trading hub.
Relevance in Modern Commerce
Foreign trade in commerce forms the backbone of the modern global economy. Countries like China, the U.S., and Germany thrive on international trade, leveraging it to sustain industries, enhance innovation, and maintain their positions as economic powerhouses. Global trade agreements, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), further underline the importance of foreign trade in commerce.
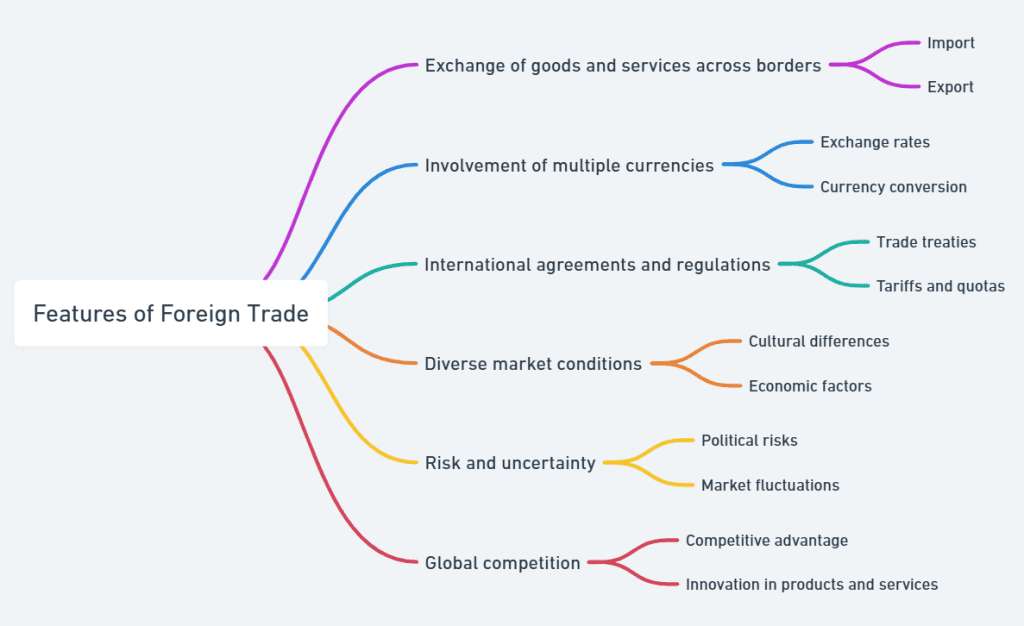
Features of Foreign Trade in Commerce
Foreign trade involves unique characteristics that set it apart from domestic trade. These features highlight its complexity and influence on the global stage.
International Scope
Foreign trade operates beyond national borders, making it inherently international. Businesses that engage in foreign trade gain access to vast markets, allowing them to diversify their customer base. For instance, a small textile manufacturer in India can reach customers in Europe and North America through exports.
Specialization and Comparative Advantage
Nations often focus on industries where they have a comparative advantage, leading to economic specialization. For example, Japan’s emphasis on electronics and Germany’s focus on automotive manufacturing stems from their respective advantages in these sectors. Specialization leads to efficient production, higher-quality goods, and increased global trade volumes.
Complex Documentation
Engaging in foreign trade requires extensive paperwork to ensure transparency and compliance. Common documents include:
- Bill of Lading: Proof of shipment.
- Letter of Credit: Ensures payment security.
- Customs Declaration Forms: Required for clearance of goods at ports.
These documents reduce risks and promote smooth transactions.
Currency Exchange
Foreign trade necessitates dealing with multiple currencies, which introduces complexities like exchange rate volatility. For example, a weaker domestic currency may increase the cost of imports, while boosting export competitiveness.
Government Regulations
Governments influence foreign trade through policies like tariffs, quotas, and subsidies. These regulations aim to protect domestic industries but can sometimes distort market dynamics.
Technological Integration
Modern foreign trade relies heavily on technology, from digital payments to advanced logistics systems. Platforms like Alibaba and Amazon facilitate cross-border e-commerce, making foreign trade more accessible to small businesses.
Benefits of International Trade for a Business
Foreign trade in commerce offers immense benefits, enabling businesses to grow, innovate, and secure a competitive edge.
Access to New Markets
Businesses expand their reach by entering international markets. For instance, Apple’s global presence allows it to cater to millions of customers worldwide. This diversification reduces reliance on domestic demand and provides stability.
Increased Revenue
Exporting goods to foreign markets generates additional revenue streams. Companies like Samsung and Toyota owe a significant portion of their profits to global sales.
Resource Optimization
International trade allows businesses to source raw materials or components from countries where they are abundant or cheaper. For example, India imports crude oil from the Middle East to meet its energy needs.
Cost Efficiency and Economies of Scale
Access to larger markets supports mass production, reducing per unit costs. Businesses achieve economies of scale, which enhance profitability and competitiveness.
Innovation and Knowledge Sharing
Foreign trade fosters technological and cultural exchange. Collaborations with international firms lead to the adoption of advanced practices and innovation. For example, global partnerships in the pharmaceutical industry have accelerated vaccine development.
Job Creation
Export-driven industries create employment opportunities. In India, the IT sector’s focus on international markets has generated millions of jobs.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Expansion | Access to global customers, reducing dependency on local markets. |
| Revenue Growth | Increased sales and profits through exports. |
| Technological Advancements | Adoption of cutting-edge innovations and methodologies. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced costs through mass production and efficient resource utilization. |
| Employment Opportunities | Job creation in export-oriented sectors. |
Common Barriers to International Trade
Despite its advantages, foreign trade in commerce faces several challenges that can hinder its potential.
Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers
Governments impose tariffs to protect domestic industries, increasing costs for importers and exporters. Non-tariff barriers, like quotas or licensing requirements, create additional obstacles.
Cultural and Language Differences
Understanding cultural nuances is essential for success in foreign markets. For example, marketing strategies effective in Western countries may not resonate in Asian cultures. Language barriers also pose communication challenges.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
Different countries have varied regulations concerning imports, exports, and intellectual property. Non-compliance with these laws can lead to penalties, delays, or bans.
Infrastructure Limitations
Inadequate infrastructure in developing nations affects the efficiency of foreign trade. Poor roads, ports, and storage facilities increase costs and delays.
Economic and Political Instability
Political unrest or economic instability in trading countries can disrupt supply chains and pose financial risks. Businesses need contingency plans to mitigate such uncertainties.
Exchange Rate Volatility
Currency fluctuations can lead to unpredictable costs and profits. For example, a sudden depreciation of the Indian Rupee could increase the cost of imports for Indian businesses.
Foreign Trade in Commerce FAQs
Why is foreign trade in commerce critical for economic growth?
Foreign trade boosts economic growth by enabling resource specialization, increasing employment, and fostering innovation. It integrates countries into the global economy, enhancing overall prosperity.
What are the key types of foreign trade in commerce?
Foreign trade includes import trade (buying goods), export trade (selling goods), and entrepôt trade (importing for re-export).
How does exchange rate volatility impact foreign trade in commerce?
Exchange rate fluctuations affect the cost of imports and exports, influencing profit margins and pricing strategies for businesses.
What role does technology play in foreign trade in commerce?
Technology simplifies logistics, enhances communication, and facilitates cross-border e-commerce, making international trade more efficient.
What are the primary challenges faced in foreign trade?
Challenges include tariffs, legal regulations, cultural differences, and infrastructure deficiencies, all of which can hinder trade efficiency.


