National income refers to the total value in money of all goods and services produced within a country for a given time, often during one year. Calculations of national income help track the performance of the country’s economy. It therefore helps policymakers decide fiscal policies, taxation, and other areas of economic planning in any country.
What is National Income?
National income refers to all the income earned by a nation’s residents from the production of its goods and services within some specified period. It basically measures the economic health condition of a country and aids in determining the standard of living and economic welfare of that country’s citizens. The net income generated by all the factor inputs of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship, whether from sources within the domestic economy or foreign economies, forms the gross national income.
As its name suggests, national income is an important indicator among economists because it enables researchers to evaluate the general outcome of economic activities and helps make policy. National income comprises several varieties such as wages, interest, rents, and profits. The primary purposes of computing national income are to calculate the general economic output of a region that can be used while benchmarking the economic performance across nations and studying changes across time in a country.
Normally, one can express the national income in monetary terms to make comparisons between two or more different time periods or countries. With national income data, economists formulate policies on such issues as inflation, unemployment, and inequality in incomes. National income figures that are accurate ensure proper budgeting and spending by the governments concerned and allow them to levy taxes properly, among other factors.
How Can We Calculate National Income?
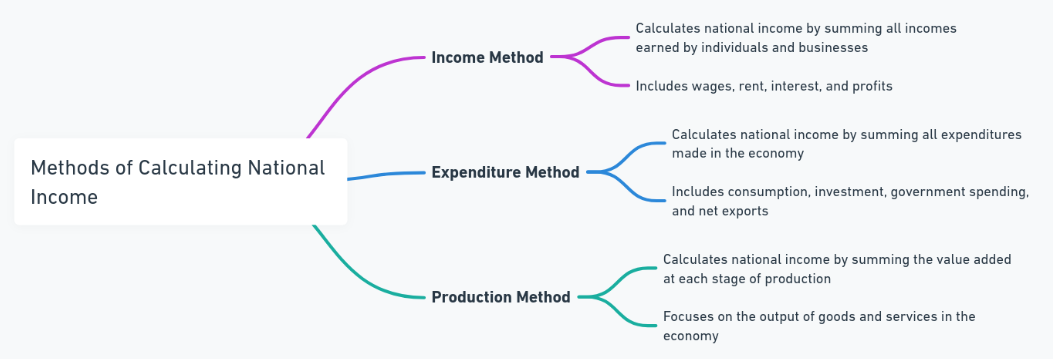
Various methods can compute national income depending on the angle of view of the economy. The three most common methods to compute national income are Product Method, also known as Value Added Method, Income Method, and Expenditure Method. Each method calculates national income from a different angle, but should all yield the same result if correctly done.
We calculate national income by considering the total output of goods and services, income generated by factors of production, and the total expenditure of the economy. Economists use these methods to determine the total economic activity and its distribution within the economy. In practice, it calculates national income by considering data from different sectors of the economy such as agriculture, industry, and services.
Methods for Calculating National Income
The methods are interlinked and learning the subtleties of each helps one get the right estimate of the national income. This involves methods such as the Product Method and Income Method. While an Expenditure Method looks to the consumer and investment expenditures for their answer.
Product Method or Value-Added Method
The Product Method also known as the Value-Added Method happens to be one of the most frequently applied methods of calculating national income. The method primarily computes the aggregate value added at all the stages of producing goods and services during their entire economic process.
The basic idea of the Product Method is that it calculates the value added by each producer in the production chain. The double counting of the intermediate goods is avoided by subtracting the cost of the intermediate goods from the total value of goods and services produced. By measuring the value added at each stage of production, the Product Method provides an accurate picture of economic output.
Calculation Using the Product Method
To calculate national income using the Product Method, you follow these steps:
- Calculate Gross Value of Output: The first step is the computation of the gross value of output. This is the total sum of all the goods and services produced by the firms and industries within the country.
- Subtract Value of Intermediate Goods: Intermediate goods are the products that are used in the process of production of other goods and services. Having them already included in the gross value, we only subtract for the intermediate goods so as not to have double counted them.
- Sum of Value Added by All Sectors: Subtracting the intermediate goods leaves the result of the sum value added to the economy. What is obtained now is the total of all sectors within the economy, including agriculture and manufacturing as well as services.
For example, if a car manufacturer purchases steel, rubber, and other parts to assemble a car, the value added by the manufacturer is the difference between the final price of the car and the cost of the materials used. By adding up these values from all industries, we can determine the total national income.
Income Method
The Income Approach to measuring national income takes an income approach in that national income is considered the aggregation of all incomes generated by different factors of production within any country. The incomes summed include wages, rent, interest, and profits.
This concept simply states that the entire earnings for the economy are exactly equivalent to the total amount produced in the economy. By utilizing this method, Income Measurement calculates the distribution of income among various factors and sectors of production and an economy.
Calculation Using the Income Method
To calculate national income using the Income Method, follow these steps:
- Identify All Sources of Income: The first stage involves calculating all sources of income generated in the economy, including wages earned through labor, rent earned by land, interest earned by capital, and profits earned through entrepreneurship.
- Add Incomes: Add up all income generated by individuals, businesses, and government entities from all factors of production.
- Adjustment for Indirect Taxes and Subsidies: Taking into account indirect taxes such as VAT and subsidies helps to avoid miscalculations. While indirect taxes add to the income obtained, subsidies subtract from the income. Hence, we have to adjust those in the final computation.
Expenditure Method
The Expenditure Method calculates national income based on the total expenditure made on the final goods and services produced in an economy. It takes into account the total spending in the economy, which includes consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports, which is the difference between exports and imports.
The Expenditure Method assumes that producers would spend all income generated on consumption, investment, and government expenditure. Therefore, by taking total spending, we reach the national income.
Calculation Using the Expenditure Method
To calculate national income using the Expenditure Method, follow these steps:
- Total Consumption Expenditure: The households incur the total expenditure on consumption goods and services. Examples of these are food, clothing, and entertainment.
- Calculate Investment Expenditure: This is an expenditure that comprises investment expenditure on capital goods by firms and changes in inventories.
- Add Government Expenditure: The third is government spending on goods and services like defense, education, and health.
- Accounting for Net Exports: Finally, calculate net exports by subtracting the total value of imports from the total value of exports.
By adding up these four components, we arrive at the total national income using the Expenditure Method.
Methods of Calculating National Income FAQs
What is the Product Method for calculating national income?
The Product Method (or Value-Added Method) calculates national income by summing the value added at each stage of production in the economy. It avoids double-counting by only considering the final value of goods and services produced.
How does the Income Method differ from the Product Method?
The Income Method calculates national income by summing the incomes earned by the factors of production (wages, rent, interest, and profit), while the Product Method focuses on the total value added in the production process.
What is the Expenditure Method of calculating national income?
The Expenditure Method calculates national income based on the total spending in the economy, including consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net exports. It focuses on the flow of expenditure within an economy.
What are the advantages of using the Product Method?
The Product Method offers an accurate representation of the total output of an economy and prevents double counting by subtracting the cost of intermediate goods. It is particularly useful for economies with a well-defined production structure.
What are the main challenges with the Income Method?
The Income Method can be challenging due to the difficulty of tracking informal sector income and non-market transactions. Additionally, accurate data on income distribution might be hard to collect in developing economies.


