Under business accounting, minor expenses of petty imports like postage, refreshments, or local travel can easily untidily clamber on top of the other petty things in the cash book. At this point, a petty cash book becomes essential. It is used as a subsidiary ledger to record all small-value transactions accurately. This way, the petty cash books help clear cash inflows for the petty expenses: they will help keep the tiny financial distances orderly, correctly recorded, and accounted for. This system will best suit organizations with an added focus on transparency and discipline concerning operational expenses.
What is a Petty Cash Book?
An auxiliary accounting record is maintained to record the small, frequent cash payments. These may be expenses incurred for courier charges, office supplies, bus fares, refreshments, etc. Instead of mainly burdening the main cash book, these smaller entries are recorded by a designated petty cashier in the petty cash book.
Purpose of the Petty Cash Book
This book intends to separate small payments organized and disjointed from the main cash flow. This, in turn, allows for a smooth flow of financial records that are easy to audit and reconcile.
Role of the Petty Cashier
A petty cashier is responsible for casting out cash and writing entries for every petty expenditure. This title means petty outflows cannot rule over internal controls.
Amount Allocation Method
A petty cashier receives a set amount under the Imprest System for a given period. This will, in turn, govern attaining expenses and furnish a replenishment cycle proportional to actual use.
Maintenance of Small Expenditures
Each transaction should have proper documentation through vouchers or receipts. These would then be passed on for audit and, upon the main cashier’s or accounts department’s approval, for reimbursement.
Audit & Transparency
With the help of supporting vouchers and a precise categorization of all transactions, the petty cash book renders clarity and an easy way for the audit.
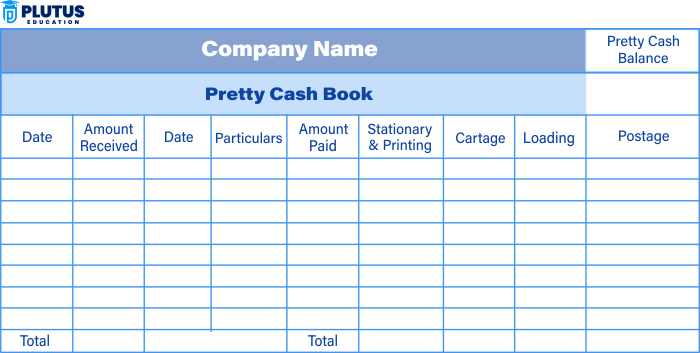
Types of Petty Cash Book
The two common types of petty cash books are the Columnar Petty Cash Book and Imprest Petty Cash Book. Each serves a different accounting needs but aims to manage minor financial transactions efficiently.
Columnar Petty Cash Book
It has various columns that categorize expenses under headings such as postage, stationery, travel, etc., giving an analytical view of the spending pattern.
Advantages of Columnar Format
Providing a specific column for each head of expenditure helps analyze the cash expenditure flow and identify possible cost control areas.
Practical Usage
This method is mostly applicable in medium—to large-scale organizations where petty expenses occur daily. It also enhances visibility for departmental budgeting.
Columnar Format Example
| Date | Particulars | Postage (₹) | Travel (₹) | Stationery (₹) | Misc. (₹) | Total (₹) |
| 01-Apr-25 | Courier Charges | 40 | 40 | |||
| 02-Apr-25 | Bus Fare | 55 | 55 | |||
| 03-Apr-25 | Pens & Notebooks | 225 | 225 |
Imprest Petty Cash Book
It is more of a rigid method where an advanced sum is fixed and replenished on time, thus ensuring that the amount does not exceed the authorized limit.
How the Imprest System Works?
The petty cashier is given a fixed amount, say, ₹2,000. When any expense occurs, it gets recorded, and then the cash is replenished at the end of the cycle, keeping the same amount afloat.
Imprest Format Example
| Date | Particulars | Voucher No. | Cash In (₹) | Cash Out (₹) | Balance (₹) |
| 01-Apr-25 | Opening Balance | – | 2,000 | 2,000 | |
| 02-Apr-25 | Bus Fare | 101 | 55 | 1,945 | |
| 03-Apr-25 | Courier Service | 102 | 40 | 1,905 |
Key Features of a Petty Cash Book
A properly maintained petty cash book is an efficient and disciplined way of preserving cash flow. Once we understand its primary characteristics, we realize its accounting significance.
- Categorization of Transactions: Expenses are classified under clear heads like conveyance, postage, refreshments, and stationery. This systematic division aids in better budgeting and control.
- Single Authority for Transactions: A single authority for petty cash keeps the business administration clear of errors in small expense tracking.
- Imprest System Control: Replenishing based on actual uses ensures cash is used within limits and accounted for periodically.
- Accuracy and Accountability: A voucher or bill supports every transaction, allowing every amount to be withdrawn, spendable, and verifiable.
- Reduced Main Cash Book Entries: Minimize the entries for petty expenses from the main cashbook to keep it uncluttered and to enhance clarity in the primary financial statements.
- Audit Trail Creation: Establishes a solid audit trail for all petty cash transactions to ensure compliance and reduce any misappropriation risk.
Benefits of Maintaining a Petty Cash Book
A petty cash system can yield various operational and financial advantages for companies of all walks of life, enhancing internal control and the management of petty expenses.
- Time-Saving: Recording minor payments separately serves to ease the work for the finance team and keep the central ledger cleaner.
- Delegated Responsibility: A petty cashier takes ownership of petty expenses, improving control and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Cost Control: Managing categorized transactions allows management to investigate spending patterns further and decide on cost reduction.
- Efficient Reconciliation: Each entry backed by receipt documentation promotes an easy, precise reconciliation.
- Audit and Review Support: The availability of proper documentation further provides transparency in support of the internal and external audits.
Example of Petty Cash Book in Action
For example, a common occurrence happens in most retail stores. The petty cashier will have been given ₹2,000 at the start of the month. The petty cashier will be recording various expenditures such as ₹105 for postage, ₹55 for auto fare, ₹85 for refreshments, and ₹195 for taxi fare, supported by vouchers. At the end of the month, the petty cashier submits the record for reimbursement. The finance team checks the receipts, repays the petty cashier, and tidies the accounting books and options, ready for any audit.
Petty Cash Book FAQs
1. Why is maintaining a petty cash book important?
It helps record and manage small, frequent expenses without overloading the main cash book, ensuring clarity and accountability.
2. How does the Imprest system work in petty cash?
Under this system, a fixed amount is provided at the start of a period. The cashier records all expenses, and the fund is replenished for the amount spent.
3. What are the types of petty cash books used in businesses?
The two main types are the Columnar Petty Cash Book and the Imprest Petty Cash Book, each suited to different organizational needs.
4. What are typical expenses recorded in a petty cash book?
Common entries include local travel fares, stationery, postal services, refreshments, and minor office supplies.
5. Where can I get a sample petty cash book format?
You can create one using Excel or download templates from accounting software platforms or educational websites.


