Risk is an inevitable part of life and business. While ventures may fail, legal troubles arise, or reputations become damaged, foresight helps avoid catastrophe. Risk management identifies potential issues and reduces their impact through proactive planning.
Various risk management strategies target distinct vulnerabilities. Some address financial volatility through mitigation tactics, while others forestall cyber attacks or litigation. Additionally, maintaining a positive public image necessitates dedicated safeguards. Each threat possesses unique characteristics, but they all endanger organizational success if left unattended.
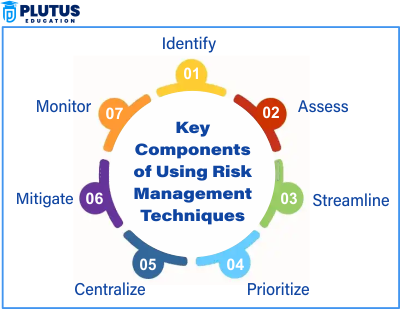
Initially, one canvases all things that could go awry. Called risk identification, this stage involves scrutinizing each mishap’s likelihood and severity. Then, preventative measures are devised through risk assessment. Infrastructure hardening, contingency funds, and security protocols exemplify strategies deployed at this critical planning phase.
What is Risk Management
Risk management is an intricate process requiring nuanced analysis and prudent planning. When exploring new markets or ventures, assiduous consideration of potential difficulties ahead of time helps circumvent issues and calamities. Countless risks lurk in every endeavor, whether regarding finances, personnel, equipment, legalities, or unpredictable forces of nature.
The initial step demands scrupulous identification of all plausible risks. Then, a judicious examination scrutinizes the probability and magnitude of damage for each. Upon compilation of this comprehensive risk assessment, a tactic is formulated to obviate or alleviate as many risks as feasible. Sometimes risk transference through insurance or redistribution lessens the burden.
Risk administration affords manifold benefits. Foreseeing troubles shields the enterprise from immense losses that could threaten solvency. Conformity with regulations builds credibility and trust among clients, employees, and regulatory bodies. Moreover, calculating uncertainties allows measured growth without courting peril. Conversely, neglecting risk oversight invites adverse repercussions, possibly culminating in bankruptcy, legal retribution, or termination of operations. Prudent risk mitigation, therefore, is not an option but a prerequisite for long-term survival and prosperity.
Types of Risk Management
There are various approaches to risk management, and each addresses a distinct challenge. No enterprise can prosper without leveraging multiple techniques. Business itself is intricate. So too are its perils.
Some hazards originate internally. Others from without. Endogenous risks encompass flawed foresight, insufficient personnel, or mechanical breakdowns. Exogenous risks include shifting markets, digital assaults, and novel legislation.
Each peril necessitates a tailored tactic. A single solution cannot possibly remedy all issues. You must comprehend each threat and judiciously opt for the optimal means of containing it. Allow us now to inspect the diverse types independently.
Operational Risk
Operational risks arise from internal deficiencies. Flaws within personnel, infrastructure, or standard processes can breed such risks. An error from an employee epitomizes operational risk in action. So too does a technical malfunction within machinery critical to function.
Many catalysts cultivate this type of risk. Inadequate preparation, insufficient planning, or antiquated systems frequently father such risks. Even seemingly minor mistakes can ripple broadly throughout an organization. Within banking, a solitary misplaced entry endangers countless accounts. In manufacturing, an isolated breakdown endangers total output.
To govern operational risk demands robust frameworks. Employees require consistent retraining. Equipment necessitates scheduled maintenance and updates. Clear protocols for routine tasks must be drafted. When daily activities flow seamlessly, such risks remain low.
Corporations in India have increasingly prioritized operational risk management. Basic tools like procedural checklists and work instructions are leveraged. Sophisticated solutions like risk analytics software are also adopted. The overarching aim is flawless, safe operations liberated from harmfulness.
Financial Risk
Financial risk is an ever-present threat that looms large for any business. Whether from poor cash flow, unfavorable loans, volatile markets or catastrophic losses, the peril of insolvency stalks companies at every turn. Of grave concern is credit risk, the danger of defaulting on debts owed, as well as liquidity risk, the inability to procure urgently needed funds. Foreign exchange fluctuations additionally imperil international operations through unseen currency shifts.
To shield against such hazards demands immense strategic planning, judicious spending and stockpiling reserves for rough waters. Balance sheets must be meticulously monitored and assiduously tended. Financial instruments like hedging contracts and insurance policies can offer a protective buffer from perilous swings.
For Indian enterprises, macroeconomic variables like shifting interest rates, market turbulence or economic downturns regularly endanger bottom lines. It is for this reason scrupulous financial management and strict account auditing prove so fundamentally important. Careful guardians are needed to shepherd companies through risks that ever threaten to destabilize or destroy businesses unprepared to weather financial storms.
Cybersecurity Risk
Cybersecurity endangerment encompasses online safeguarding. In current times, the majority of corporations digitally warehouse information. They employ electronic mail, websites, and programming. However, this introduces many hazards. Hackers can pilfer data. Viruses can cripple frameworks. Deceptive communications can delude staff.
Even insignificant mistakes can induce monumental losses. If client specifics are appropriated, the company can lose credibility. If cybercriminals paralyze the system, the business may halt operations. In India, numerous small enterprises now confront such cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Online deception is proliferating swiftly.
To remain protected, corporations must utilize robust passwords. They must install capable antivirus software. They must coach personnel to identify fraudulent messages. They must update their systems frequently. Employing two-factor authentication can also assist.
Cybersecurity is not solely for large companies. Even schools, shops, and medical practitioners must shelter their intelligence. A strong IT team and regular audits are integral to safety.
Legal Risk
Legal risk is about problems that companies may encounter with the law. If a business fails to abide by regulations, it could potentially face monetary penalties or even litigation. There are many avenues through which this might occur. A company might contravene labor codes, disregard safety protocols, or neglect tax obligations. It may also utilize another entity’s logo or concept without granting permission.
Even a minor legal mistake has the potential to be quite costly. A business could end up embroiled in court proceedings. It may lose both funds and time dealing with the issue. It may further damage its reputation. As such, companies must take legal risk extremely seriously.
To manage this risk, corporations must be knowledgeable regarding rules and legislation. They must hire experienced legal counsel. They must draft clear contracts. They must securely retain records and ensure they are updated. They also should consistently stay abreast of new laws and modifications to existing statutes.
In India presently, numerous startups are focusing on legal risk. They employ legal technology tools. They frequently consult attorneys. They additionally train personnel about regulations and rights. This helps ensure they remain on secure legal footing and are able to persevere.
Reputational Risk
Reputational risk demands vigilance, as losing the public’s favor can doom an enterprise. When customers cease to feel connected to a brand, its revenue dries up. Poor service, scandals, or angry outbursts on forums can initiate such detachment. A single social media post viewed by millions could damage an organization within hours through voyeurism. People wish to support companies that behave with empathy, fairness and integrity. If an entity treats clients or society disrespectfully, it risks losing the loyalty of both.
- To sidestep reputational ruin, firms must prioritize customer satisfaction above all else.
- Complaints should receive immediate redress while marketing stays forthright.
- Employees need training so that courtesy and assistance come naturally.
In contemporary times, reputational demolition spreads faster than ever. Indian companies now monitor networks attentively to respond swiftly to issues. They conduct campaigns and initiatives cleanly and evenhandedly to nurture consumer faith. Supporting ethical causes allows brands to cement trusting relationships and ensure longevity.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate volatility impacts all kinds of enterprises. When rates escalate, loan installments become costlier to repay month after month. But when they descend, financial reserves accumulate slower returns. Profitability and cash flows are susceptible to such swings.
In India, the central bank called the Reserve Bank of India regulates rates to curb price increases. So if rates are lifted, borrowing expenses rise proportionally. Yet when rates devaluate, set deposits award diminished coming earnings. Therefore, businesses must strategize for potential rate changes down the road.
- To mitigate rate risk, firms can sign up for fixed-rate loans.
- They can also devise financial plans factoring in high or low rate scenarios.
- Some use involved instruments like interest rate derivatives to reduce susceptibility to rate shifts.
Banking institutions and finance companies experience rate risks most prominently. However instructional facilities, retailers, and medical centers must monitor rates closely too if they carry heavy debts. Careful forecasting helps dampen rate risks going forward.
Assessing Risks
Risk assessment is the process of thoroughly scrutinizing potential hazards. It enables organizations to discern which threats are more serious and which are less likely to materialize. It also helps determine which risk warrants immediate attention.
To evaluate risks, one first enumerates all possible issues. Then, the probability of each coming to pass is studied. Following that, the magnitude of damage it can inflict is surveyed. Depending on these factors, the risks are prioritized.
Often, companies leverage a tool called a risk matrix. It portrays risks as low, moderate, or high. Pressing risks necessitate swift action. Minor risks can be delayed. Doing so ensures entities use time and money judiciously.
Risk assessment should occur periodically. As the world evolves constantly, new risks may emerge. Old ones may intensify. Regular reviews help the organization remain prepared for any eventuality.
Market Risk
Market risk arises from volatility in pricing. Severe fluctuations in the cost of goods, currencies, or equities could lead to substantial gains or losses for enterprises. This hazard notably affects organizations engaged in large-scale purchasing or sales. It likewise endangers those dealing in shares or transnational commerce.
If equity markets experience a tumultuous downturn, companies see their worth deteriorate precipitously. Similarly, should the rupee undergo an abrupt devaluation, importers must absorb onerous additional expenses. Analogously, an unexpected spike in petroleum costs can render transportation far costlier to conduct. All such possibilities exemplify manifestations of market risk.
To mitigate this risk, corporations meticulously scrutinize marketplace dynamics. They thoughtfully craft prudent investment strategies that avoid overreliance on single assets or territories. Moreover, they may deploy hedging tactics to shelter negotiated agreements from unforeseen market swings.
Indian technology, energy, and export companies conscientiously track this risk. They maintain specialized teams dedicated to making astute short-term decisions based on fluctuating conditions. They also retain flexibility to modify long-term objectives according to evolving market realities.
Relevance to ACCA Syllabus
Risk management has been one of the primary topics in the ACCA Strategic Business Leader (SBL) and Advanced Financial Management (AFM) exams for a long time and has been considered as a pivotal subject for accountancy students. Students must learn, identify, assess, and manage business risks including financial, operational, reputational, and strategic risks. Risk management allows planning of the enterprise’s strategy. The so-called risk management philosophy provides the essentials of corporate governance, strategic decision-making, and enterprise performance.
Types of Risk Management ACCA Questions
Q1. Which of the following is an example of operational risk?
A) A drop in share prices
B) A machine failure causing production delay
C) An increase in interest rates
D) A lawsuit filed by a competitor
Ans: B) A machine failure causing production delay
Q2. Which type of risk arises due to negative public opinion or media coverage?
A) Financial risk
B) Strategic risk
C) Legal risk
D) Reputational risk
Ans: D) Reputational risk
Q3. What is the first step in risk management according to the ACCA framework?
A) Monitor performance
B) Assess the impact
C) Identify risks
D) Transfer the risk
Ans: C) Identify risks
Q4. Interest rate risk is most likely to affect which of the following?
A) Payroll process
B) Loan repayment costs
C) Customer satisfaction
D) Environmental compliance
Ans: B) Loan repayment costs
Relevance to US CMA Syllabus
Risk management, which is a part of the Strategic Financial Management in the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) syllabus, is the main topic of this discussion. The examinee must know how different kinds of risks (such as market, credit, and operational risks) can have a great influence on the financial performance of a business and the methods of risk treatments such as hedging and insurance that can be applied to keep the risks under control.
Types of Risk Management US CMA Questions
Q1. Which of the following risks is directly associated with poor internal processes or human errors?
A) Market risk
B) Credit risk
C) Operational risk
D) Regulatory risk
Ans: C) Operational risk
Q2. Which method is commonly used to reduce foreign exchange risk in multinational companies?
A) Diversification
B) Hedging
C) Leasing
D) Inflation adjustment
Ans: B) Hedging
Q3. Cybersecurity risk would fall under which broader category of risk management?
A) Technological risk
B) Environmental risk
C) Financial risk
D) Strategic risk
Ans: A) Technological risk
Q4. A company reviewing its ability to meet short-term obligations is managing which risk?
A) Credit risk
B) Liquidity risk
C) Operational risk
D) Market risk
Ans: B) Liquidity risk
Relevance to US CPA Syllabus
Risk management is a part of the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) syllabus under areas such as Audit and Attestation (AUD) and Business Environment and Concepts (BEC). It is important to take into account the different types of risk because this is a major factor when it comes to audit planning, internal control evaluation, and compliance with laws and regulations.
Types of Risk Management US CPA Questions
Q1. Which of the following is NOT considered part of enterprise risk management (ERM)?
A) Risk identification
B) Tax calculation
C) Risk assessment
D) Risk response planning
Ans: B) Tax calculation
Q2. Which risk refers to potential losses due to lawsuits or non-compliance with laws?
A) Reputational risk
B) Strategic risk
C) Legal risk
D) Financial risk
Ans: C) Legal risk
Q3. During an audit, a CPA notices weak internal controls. What risk is most likely increased?
A) Market risk
B) Detection risk
C) Operational risk
D) Inherent risk
Ans: C) Operational risk
Q4. A company affected by sudden changes in stock prices is facing which risk?
A) Operational risk
B) Market risk
C) Liquidity risk
D) Credit risk
Ans: B) Market risk
Relevance to CFA Syllabus
The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) program features risk management in the Portfolio Management and Ethical & Professional Standards sections. During the CFA program, the students learn different types of economic and non-financial analyses and how they interfere with investment decisions, portfolio performance, and customer obligations.
Types of Risk Management CFA Questions
Q1. Which of the following best describes market risk?
A) Loss due to employee fraud
B) Risk of default on a bond
C) Loss due to price volatility in financial markets
D) Loss from failing to file legal documents
Ans: C) Loss due to price volatility in financial markets
Q2. Which risk involves the possibility of a borrower failing to repay a loan?
A) Operational risk
B) Market risk
C) Credit risk
D) Strategic risk
Ans: C) Credit risk
Q3. In portfolio management, diversifying investments helps to manage which type of risk?
A) Systematic risk
B) Legal risk
C) Unsystematic risk
D) Strategic risk
Ans: C) Unsystematic risk
Q4. Interest rate fluctuations primarily create which type of risk in fixed-income securities?
A) Operational risk
B) Liquidity risk
C) Credit risk
D) Interest rate risk
Ans: D) Interest rate risk


