Retailers are those people who play a significant role in trade and business. They are the last link in connecting products of the manufacturer to the very last consumer. A retailer is an individual or business which sells commodities or services directly to the ultimate customer, who generally uses such items for his/her personal use, rather than selling them again. Retailers deal in smaller amounts and have products available conveniently at the place and time. Retailing is not just the art of selling products; it encompasses holding, promoting, and presenting the goods in an attractive manner. A retailer becomes a face of the market to a consumer. He understands consumer requirements and recommends an appropriate product. He latches on to the buyer comments and passes them on to wholesalers and manufacturers. Create a demand; help producers understand what buyers want; and keep the economy moving.
What is a Retailer?
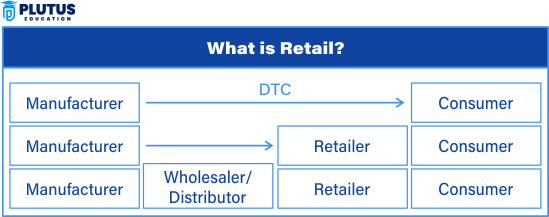
A retailer is a business or individual who buys goods from wholesalers or producers and sells them directly to consumers in small quantities. The goods are meant for personal use and not for resale. Retailers operate at the end of the distribution chain. They provide convenience, availability, and customer service to help buyers make decisions.
Retailers deal in a wide variety of products like groceries, clothes, electronics, and medicines. They usually have a physical store or an online platform. Some retailers sell only one type of product (like a shoe store), while others sell many types (like a supermarket).
In the Indian context, retailing includes both organized and unorganized sectors. Organized retailers include shopping malls, brand stores, and online platforms. Unorganized retail includes local kirana shops, street vendors, and weekly markets.
Retailers bridge the gap between demand and supply. They help manufacturers reach buyers and help customers find products easily. Their main focus is to provide good service, maintain variety, and create a pleasant shopping experience.
Features of a Retailer
Retailers have special features that make them different from wholesalers, distributors, and producers. These features help in identifying the structure and function of retail businesses.
- Sells in Small Quantities
Retailers sell goods in small units that customers use personally. They break bulk from wholesalers and pack goods in small, usable formats. This makes it easy for customers to buy only what they need. - Deals with Final Consumers
Retailers serve the end-user. They sell directly to people and not to businesses. This direct interaction helps them understand customer needs and build relationships. - Offers Wide Variety
Retail stores often keep multiple brands and types of the same product. This variety helps buyers compare and choose as per their taste, need, and budget. - Provides Personal Service
Retailers offer suggestions, give product demos, and help in post-sale support. Good service helps them retain regular customers and build trust. - Located Near Customers
Retailers set up shops in markets, near residential areas, or online to stay close to buyers. Easy access increases footfall and sales. - Carries Promotional Activities
Retailers display products, give discounts, and run offers. These promotions increase sales and create product awareness. - Maintains Inventory
Retailers keep ready stock of goods for immediate sale. They manage storage and ensure timely availability to meet daily demand.
These features explain how retailers operate and why they are crucial in any economy.
Types of Retailers
Retailers are of different kinds, depending on how they sell, what they sell, and how they operate. The types of retailers help classify retail businesses for better understanding and planning.
1. Based on Ownership and Size
- Independent Retailers
These are small shops run by one person or a family. Kirana stores, local general stores, and corner shops fall in this category. They operate with low cost and personal relations. - Chain Stores
These are multiple outlets owned by a company. Examples are Bata, Reliance Trends, and Vishal Mega Mart. All stores follow the same format, pricing, and display style. - Franchise Stores
These work under the name of a big brand but are owned by local operators. Brands like McDonald’s, KFC, and FirstCry run through franchise models. They get business support from the parent brand. - Departmental Stores
These are big stores that sell various product categories under one roof. Examples include Lifestyle, Shoppers Stop, and Big Bazaar. They provide a wide shopping experience.
2. Based on Product Sold
- Specialty Stores
These stores sell only one category like electronics, books, or footwear. They focus on deep variety and expert advice in one field. - General Merchandise Stores
These sell various everyday products in one place. Examples are grocery stores, supermarkets, and discount shops.
3. Based on Selling Platform
- Online Retailers
These sell through websites and apps. Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra are leading online retailers. They offer home delivery and a wide product range. - Vending Machines and Kiosks
These are automatic machines placed at public spots. They sell water bottles, snacks, or tickets without human help.
All these types show how retailing adapts to market needs and customer convenience.
Functions and Role of a Retailer
Retailers do more than just sell products. They play many roles that support the supply chain, enhance customer experience, and improve business outcomes.
- Connects Producers and Consumers
Retailers bring goods from manufacturers or wholesalers and deliver them to customers. They make sure products reach users quickly and conveniently. - Creates Demand and Awareness
Retailers display goods attractively and share product information. They help buyers know about new items, features, and offers, which increases demand. - Provides Customer Service
Retailers guide shoppers, answer questions, handle returns, and give after-sales support. Their service builds customer loyalty and repeat business. - Carries Inventory and Stock
Retailers maintain products in-store or in the warehouse. This ready stock reduces the time between need and purchase. - Gathers Market Feedback
Retailers interact daily with customers and listen to their likes, complaints, and suggestions. They pass this feedback to producers for improvement. - Offers Credit Facility
Small retailers often allow trusted customers to buy on credit. This builds long-term relationships, especially in rural and small-town India.
Retailers form the most visible face of the market. Their actions directly affect product sales and brand reputation.
Difference Between Retailers and Wholesalers
Retailers and wholesalers both deal with goods, but their role, customer type, and working method differ clearly.
| Point | Retailer | Wholesaler |
| Deals With | Final Consumers | Retailers or Other Businesses |
| Quantity of Sale | Small, as per customer need | Large, in bulk quantities |
| Location | Near residential or market areas | Often in wholesale markets or commercial hubs |
| Customer Interaction | High, personal service to buyers | Low, business-focused transactions |
| Credit Facility | Often given to loyal customers | Common among trusted retailers |
| Product Range | Wider for daily use and variety | Limited, focused on selected items in bulk |
Understanding this difference helps in choosing career paths, planning trade, and managing supply chains effectively.
Importance of Retailers in the Economy
Retailers play a big role in both national economies and local markets. They support economic growth, generate employment, and provide easy access to goods. Retailing is very important, therefore, retailers are important.
- Retailers help manufacturers reach the last-mile customer in every village, town, and city. Without retailers, producers cannot distribute or promote goods easily.
- Retail businesses create jobs in sales, delivery, inventory, billing, and store operations. Many young people and part-time workers get employment through retail.
- Retailers support rural and urban economies by keeping essential goods available at the right time and price. They handle seasonal demand and daily supply.
- They promote entrepreneurship. Many individuals run their own retail shops with small investments and become self-reliant.
- Modern retail formats bring global products to Indian homes. They boost e-commerce, supply chain innovation, and retail technology.
This importance shows why the government supports retail through policy and training programs.
What is a Retailer FAQs
Q1: What is simply a retailer?
Conclusively, a retailer is an individual or a shop that sells goods directly to people in smaller quantities for daily or personal consumption.
Q2. What’s the different standpoint between wholesaler and retailer?
Retailers sell to final users in little quantities, while wholesalers sell to other businesses and shops but in bulk quantities.
Q3- Examples of Retailers.
Local kirana stores, supermarkets, retail clothing stores, mobile stores, pharmacies, and various online platforms like Amazon, are examples of retailers.
Q4-What skills are important in retailing?
Communication, inventory handling, billing, product knowledge, and customer service skills are necessary for retail both in general and during sample performance.
Q5. What are online retailers?
Online retailers sell products using websites and apps. They deliver orders to customers and offer payment, return, and tracking services.


