Indeed, in a world completely uncertain, financial cover becomes more of a necessity than an option. Insurance is one of the few practical tools through which one can guard oneself against the horrors of loss due to accidents, sickness, and even disruption of business activity. An insurance contract is an enforceable contractual agreement between an individual (or entity) and the provider for payment at regular intervals called premiums if the insured shall suffer financial loss as per the stipulations in the policy. Thus, such agreements offer security to individuals and businesses to shift risks and ensure stability in untimely occurrences. The gist is that it may be any life, health, vehicle, or property insurance; the right policy is the key to long-term financial planning.
What is Insurance Policy?
Insurance is a system that provides financial coverage or reimbursement of loss due to a contingency risk. Insurance releases the individual’s economic burden of such risks. In short, the insured pays the premium; in return, the insurance company takes responsibility for certain types of loss. This contract thus acts as a risk-sharing mechanism so that people bounce back quickly after unfortunate incidents. Insurance does not eliminate risk, but it reduces the financial shock.
Why Insurance is Necessary in Modern Life?
From involuntary human-induced factors to natural disasters and aspects of society that together regularly upset an individual’s financial security, things can give way at the blink of an eye. Nevertheless, a person who has insurance should never lack money in the face of emergencies. Procuring a house or running a business will also become less risky as there will be a safety net. It is paramount that insurance coverage is expanded with ever-increasing healthcare costs, interferences, unpredictable meteorological and climatic changes, and expanded legal liabilities influencing almost every aspect of financial operations today.
How Insurance Builds Financial Discipline?
Regularly paying premiums will make a habit of consistent financial planning. Long-term thinkers make retirement plans and reduce unnecessary spending to buy policies. Investments like life insurance have investment or savings options alongside coverage to help build wealth while remaining insured.
How Insurance Works?
By understanding the mode of insurance operation, buyers can choose better plans and use their policies better. Five main processes comprise understanding the insurance concept: risk assessment, policy issuance, premium payment, settlement of claims, and renewal. Each ensures the transaction is transparent, fair, and compliant with the law.
Step 1: Risk Assessment: The Ground for Fair Premiums
Insurers assess the likelihood of offering coverage before insuring a person or thing. That usually includes age, health, location, profession, previous claims history, and lifestyle. The next stage of this process is called underwriting. It determines the amount of premium, further limits against coverage, and conditions for holding the policy. For instance, a smoker may pay higher premiums for life insurance compared with a non-smoker due to increased risk.
Step 2: The Formality of Policy Issuance
Once an assessment of risk is carried out and after the parties agree to its terms, the contract must be issued, and the policy document must be issued to the interested party in this event, namely, the proposer. This document mainly contains details about the scope of coverage, the duration, exclusions, benefits, and rules for claim proceedings. Being legally binding, it must be understood in its entirety; misunderstanding of any of these terms is liable to lead to claims being repudiated or disputes arising.
Step 3: Premium Payment: The Cost of Protection
Premiums refer to the periodic payments by a policyholder to keep an insurance policy in force. These payments can be monthly, quarterly, or annual. Specific policies may require full premium payment at once and a waiver for the default option. A policyholder facing premium defaults could lapse or terminate his cover and ruin himself financially.
Step 4: Claim Process and Settlements
Whenever a loss from an insured peril occurs, an insured must file a claim with all the necessary documentation: bills, FIR reports, death certificates, etc. The claim is then carefully examined and verified by the insurer. Once all is well with proving the claim and complying with the policy terms, the claim gets fully approved and settled. Cashless settlements for claims are usually available under health insurance and vehicle insurance for empanelled hospitals or garages.
Step 5: Renewal and Continuation of Policy
Most insurance is written for a limited period, so renewal must continue. Renewal entails reviewing premiums or altering policy particulars. Late payment of the premium may lead to penalisation or cancellation. Renewal reminders and auto-pay prove advantageous in avoiding lapses in coverage.
Parts of an Insurance Policy in Your Contract
An insurance contract will include clauses that define the coverage’s rights, obligations, and boundaries. Knowledge of all the components will assist policyholders in making their choices, managing the policy, and claiming benefits.
Rights of Policyholders and Insurers
A policyholder is any person or establishment that has a policy and pays premiums due on that policy. The insurer provides the benefits covered by the insurance policy. By the indemnity provisions of the insurance law, metropolitan underwriters can enforce all policy provisions in good faith against the policyholder.
Premium and Payment Terms
The premium is determined based on the nature of risk assumed, the value insured, the duration of exposure, and any other relevant policy characteristics.
Each line of business, including life insurance, health insurance, and vehicle insurance, has a different premium pattern according to the sector. Some policies offer no claim or loyalty bonus discount for healthy behaviours, encouraging regular payment with decreasing costs.
Coverage What Will Be Covered, What Is Omitted
Coverage outlines the specific risks for which compensation is payable, such as death in an insurance policy, surgical procedures covered in a health insurance policy, and an accident under a motor insurance policy. Through careful reading, policies should ascertain what kinds of events fall under coverage. Ideal protection is where coverage appropriately matches one’s lifestyle and risks faced.
Exemptions—What’s Not Covered
Every policy has some exclusions laying down the few conditions under which the insurer will not pay. Most health policies, for example, do not cover pre-existing conditions; another might be suicide within a year for life insurance or an accident under the influence of alcohol in motor insurance. Knowing these things should discourage that kind of surprise when timeliness does not allow making an actual claim.
Riders and Add-Ons
Riders are optional add-ons that expand or modify your coverage. Here are some examples:
- Critical Illness Rider: Coverage of events like cancer, heart attack, and stroke.
- Accidental Death Benefit: Pays an additional benefit in case of accidental death.
- Waiver of Premium: Waives future premiums in case of disability.
These features will enhance the value of the base plan, giving overall more complete protection.
Major Types of Insurance Policies and Their Uses
Many policies are well-positioned in the insurance world to provide for individuals, families, or businesses as required. Policies included in this list refer to the most commonly issued and covered.
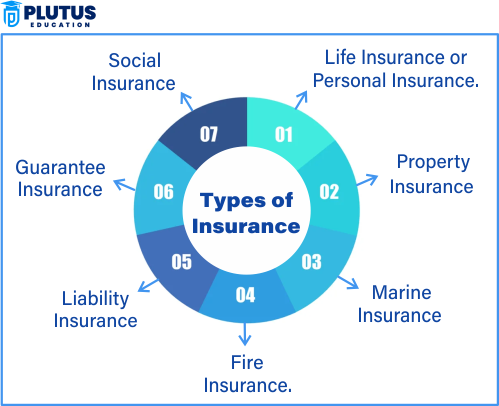
Life Insurance
Life insurance covers the financial risks involved with dying. It is essential to ensure that the dependent has coverage or potential assurance of finances in the future.
- Term Life: Low cost for a high sum insured and a fixed period cover.
- Whole Life: The plan often includes coverage until death and savings.
- Endowment/ULIP: Combines benefits for insurance with investment.
Health Insurance Cover
This is directed towards medical expenses related to doctor visits, surgeries, and hospitalisation.
- Individual Plans: Coverage for one person.
- Family Floater Plans: Coverage for the entire family.
- Critical Illness Plans: Lump-sum payment upon diagnosis of critical diseases.
Health insurance lessens the burden during emergencies and also encourages preventive health care.
Property Insurance
It protects tangible properties like homes, offices, and warehouses.
- Home Insurance: Protects against fire, theft, and natural calamities.
- Commercial Property Insurance: For businesses to cover machinery, buildings, and stocks.
It is compulsory for any person who owns high-value properties or operates a business.
Motor Insurance
It protects your vehicle from loss or damage and liability to others.
- Mandatory by law: Third-Party Liability.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Covers losses on own damages and compensates third-party damages.
- No depreciation add-on: Full reimbursement irrespective of depreciation cuts.
Car insurance ensures that all is fulfilled in terms of compliance and provides total peace of mind while traveling in any part of the country.
Travel Insurance and Liability Insurance
Travel insurance includes cancellation of trips, provides medical protection while abroad, and covers loss. Liability insurance covers the exposure to legal liability due to a third party’s negligence, harm, and mistakes, which are especially important to key professionals like doctors and architects. These are the best fit for traveling worldwide or business professionals likely to have very high legal exposure.
Gains of Insurance
Insurance is not just money but also peace of mind, better planning, and safety for one’s financial legacy.
Safeguarding Against Financial Uncertainty in Emergencies
Insurance ensures that emergencies, these being medical, legal, and operational, do not drive the savings into oblivion. While turning uncertainty into stability, insurance cushions the financial blow when an accident occurs to the party or affects them.
Promotes Accumulation of Wealth over the Long-Term
Specific policies will build assets and create opportunities for improved financial growth. Life insurance policies, like ULIPs and endowment plans, promise returns on investment. Thus, combined with tax benefits, these policies become great instruments in long-term financial planning.
Financial Benefits and Protection Under Law
Premiums paid for life and health insurance would be eligible under Sections 80C and 80D under the Income Tax Act in India. Therefore, taxable income is lowered by providing critical protection besides liability insurance, which offers legal defense and coverage of personal and business assets in lawsuits.
Enhances Economic Stability
Generally deals with enhancing national economic growth by absorbing income volatility. The insured individual or business recovers faster, typically maintains consumption, and avoids dependency on public finances after disasters or losses.
What is Insurance Policy FAQs
Q1. What is an insurance policy?
An insurance policy is a legal agreement between an insurer and a policyholder, offering financial protection against specified risks in exchange for premium payments.
Q2. What are the main components of a policy?
Key components include premium, coverage, exclusions, policyholder, insurer, claim procedure, and policy term.
Q3. How does insurance provide financial protection?
Insurance transfers risk to the insurer. In a covered event, the insurer compensates the policyholder, preventing financial hardship.
Q4. What types of insurance should everyone have?
At a minimum, individuals should have life, health, and vehicle insurance. Businesses should add property and liability insurance as well.
Q5. What are policy riders, and should I buy them?
Riders are optional benefits that customize and expand your coverage. Buy them based on your lifestyle, profession, and risk exposure.


