Insurance serves as a financial shield, protecting individuals and businesses from potential losses arising from unforeseen events. It is an agreement where the insured pays a premium, and in exchange, the insurer compensates for specific risks. To address various needs, insurance is categorized into different types, enabling individuals and organizations to secure their lives, health, property, and liabilities. This detailed article explores the classification of insurance, diving deep into its types, features, and benefits.
What is Insurance?
Insurance is a contractual arrangement between an individual or organization (policyholder) and an insurance company (insurer). It ensures financial protection against risks like death, accidents, theft, natural disasters, or medical emergencies. The insured pays a pre-determined premium, and in return, the insurer provides coverage as outlined in the policy.
The classification of insurance is essential as it helps categorize policies based on their purpose, benefits, and coverage. Insurance is broadly divided into Life Insurance and General Insurance, each catering to specific needs.
Features of Insurance
Insurance offers several unique features that set it apart as a risk-management tool. These features make insurance a reliable and structured method of financial protection.
- Risk Transfer: The primary purpose of insurance is to transfer risk from the insured to the insurer.
- Pooling of Risks: Insurers pool premiums from policyholders to distribute compensation among those affected by losses.
- Legal Contract: Insurance is governed by a legally binding agreement specifying the terms of coverage.
- Indemnity: General insurance operates on the principle of indemnity, compensating for actual losses incurred.
- Insurable Interest: The insured must have a financial or personal stake in the subject of insurance.
- Premium Payment: The insured pays a premium calculated based on the level of risk and coverage.
- Utmost Good Faith: Both parties must disclose all material facts honestly to ensure fair transactions.
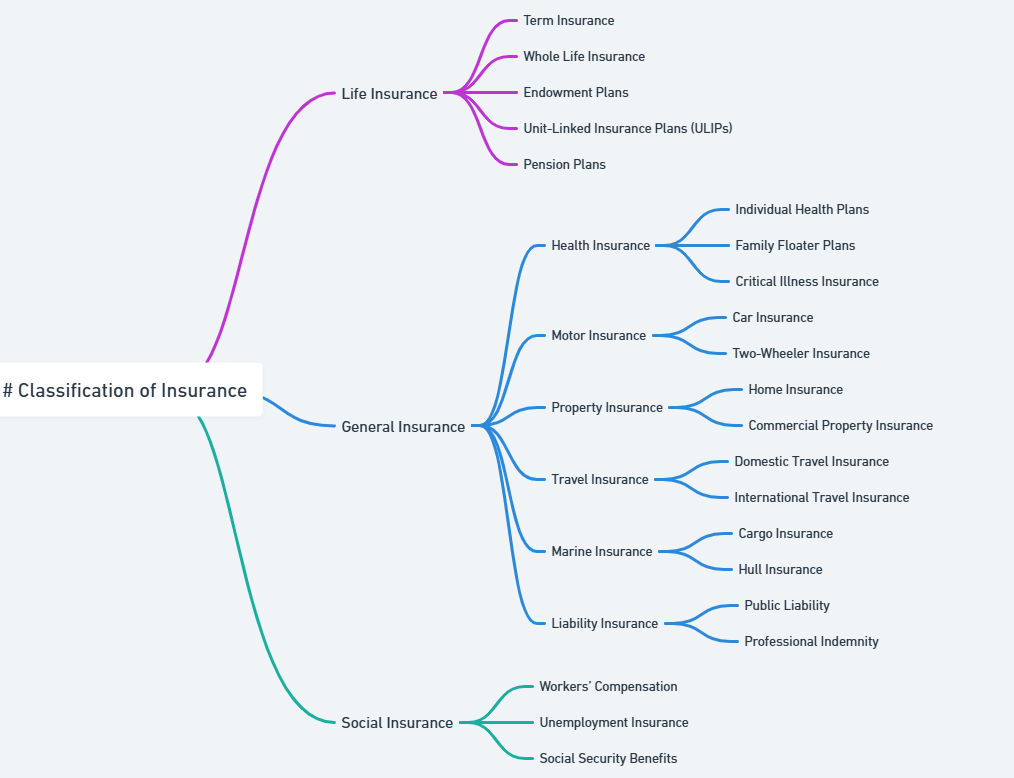
Classification of Insurance
Insurance is broadly classified into Life Insurance and General Insurance, each catering to different types of risks and needs. These categories are further subdivided into specialized types to address specific situations and requirements.
General Insurance
General insurance protects against non-life risks. It is essential for securing assets, safeguarding health, and managing liabilities. Unlike life insurance, which is long-term, general insurance policies are usually short-term contracts renewable annually.
Types of General Insurance
General insurance includes a wide range of policies, each catering to specific risks.
Fire Insurance
Fire insurance protects against damages caused by fire and related perils such as explosions, lightning, or earthquakes. It covers buildings, factories, warehouses, and stock-in-trade. For example, if a factory is damaged by a fire, fire insurance compensates for the repair or replacement costs, helping the business resume operations.
Key Features:
- Coverage includes accidental fires, electrical faults, and natural calamities.
- The policyholder must declare the value of the property insured.
- Compensation is based on the principle of indemnity.
Marine Insurance
Marine insurance ensures the safety of goods and vessels during transportation over water. It is essential for international and domestic trade, where goods face risks like sinking, piracy, or collisions.
Types of Marine Insurance:
- Hull Insurance: Covers damage to the ship or vessel.
- Cargo Insurance: Protects goods being transported.
- Freight Insurance: Secures freight charges if goods are lost or damaged.
Marine insurance facilitates global commerce by minimizing trade risks.
Motor Insurance
Motor insurance is mandatory for vehicles and protects against losses due to accidents, theft, or third-party liabilities. It is divided into:
- Third-Party Liability Insurance: Covers damages caused to a third party.
- Comprehensive Insurance: Includes third-party liability and own vehicle damages.
Motor insurance ensures that vehicle owners are financially protected against legal claims and repair costs.
Health Insurance
Health insurance provides financial coverage for medical expenses, ensuring access to quality healthcare. It includes hospitalization, surgery, and treatment costs.
Benefits:
- Coverage for pre- and post-hospitalization expenses.
- Cashless treatment options at network hospitals.
- Financial relief during critical illnesses.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance covers legal liabilities arising from accidental harm or damage caused to third parties. It is particularly useful for businesses and professionals.
Examples of Liability Insurance:
- Professional Indemnity Insurance: Protects professionals like doctors and lawyers from legal claims due to errors or negligence.
- Public Liability Insurance: Covers businesses against claims for injuries or damages suffered by third parties on their premises.
Travel Insurance
Travel insurance offers protection against risks encountered during travel. It covers trip cancellations, lost baggage, flight delays, and medical emergencies.
| Type of General Insurance | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Fire Insurance | Damages caused by fire and explosions. |
| Marine Insurance | Goods, ships, and freight during transit. |
| Motor Insurance | Vehicle damages and third-party liabilities. |
| Health Insurance | Medical expenses and treatments. |
| Liability Insurance | Legal claims and third-party damages. |
| Travel Insurance | Travel-related risks. |
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to the insured’s family in case of their untimely demise. It also offers savings and investment benefits, making it a versatile financial tool.
Types of Life Insurance
Whole life insurance provides coverage throughout the insured’s lifetime. Upon the insured’s death, the beneficiaries receive the sum assured, ensuring their financial security.
Term Insurance
Term insurance offers life coverage for a specific period. In case of the policyholder’s death during the term, the nominee receives the sum assured. It is an affordable option for securing family financial stability.
Features:
- High coverage at low premiums.
- No maturity benefits if the policyholder survives the term.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage, ensuring financial security for the policyholder’s family. It includes a death benefit and may also have a savings component.
Endowment Plans
Endowment plans combine life insurance with savings. They provide a lump sum payout on maturity or in case of the policyholder’s death during the term.
Advantages:
- Helps in achieving financial goals like education or marriage.
- Offers maturity benefits.
Unit-Linked Insurance Plans (ULIPs)
ULIPs combine life insurance with investment. A portion of the premium is used for life coverage, while the rest is invested in market-linked instruments like stocks or bonds.
Child Plans
Child plans are designed to secure a child’s future by providing financial resources for education or other milestones.
Pension Plans
Pension plans offer regular income post-retirement, ensuring financial independence for the policyholder.
| Type of Life Insurance | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Term Insurance | Financial security during the policy term. |
| Whole Life Insurance | Lifelong coverage with death benefits. |
| Endowment Plans | Savings with life cover. |
| ULIPs | Investment and insurance benefits. |
| Child Plans | Securing a child’s future. |
| Pension Plans | Post-retirement income security. |
Life Insurance vs. General Insurance
While both life insurance and general insurance serve to mitigate risks, they differ in purpose and structure. Life insurance primarily addresses the financial uncertainties of life, providing long-term coverage and serving as a tool for wealth creation. In contrast, general insurance focuses on protecting assets and liabilities, typically offering short-term, renewable coverage.
| Aspect | Life Insurance | General Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides life coverage. | Covers assets, health, or liabilities. |
| Duration | Long-term (often lifetime). | Short-term, renewable annually. |
| Premiums | Higher due to lifelong benefits. | Comparatively lower for short durations. |
| Benefits | Death or maturity payout. | Compensation for damages or losses. |
Classification of Insurance FAQs
What is the importance of insurance classification?
It categorizes policies based on specific needs, helping individuals and businesses choose suitable coverage.
How does general insurance differ from life insurance?
General insurance covers non-life risks like health, property, and vehicles, while life insurance focuses on securing the insured’s life.
Can a single policyholder buy both life and general insurance?
Yes, many policyholders combine both types to cover different risks comprehensively.
What are the benefits of fire insurance?
Fire insurance compensates for damages caused by accidental fires, explosions, and natural disasters.
Why is health insurance crucial?
Health insurance provides financial relief during medical emergencies, ensuring access to quality healthcare.


