The concept of public relations is the strategic art of managing communication between any organization and its myriad stakeholders. It is built to promote trust, transparency, and a good reputation, which promotes long-term relationships where both parties benefit the organization and the audiences. It is different from direct marketing and advertising because public relations aims to achieve earned trust through authentic and credible communication. As such, regardless of whether it is a big multinational or small local venture, effective PR shapes the way an entity is viewed by its public, whether customers, investors, employees, media, or society.
What Is Public Relations (PR)?
Public relations often is defined as the deliberate and planned effort toward establishing and maintaining a favorable relationship between an organization and its public. “Publics” refers to the groups of people with whom an organization interacts, including employees, customers, investors, community members, representatives of the media, and governmental bodies.
Public relations emerged as a distinct professional discipline in the early 20th century and has evolved in a rapidly changing environment, integrating traditional media, digital platforms, and interpersonal communication. It’s not just crisis management; rather, it is working on brand reputation enhancement, key message dissemination, and harmony between organizational objectives and expectations of society.
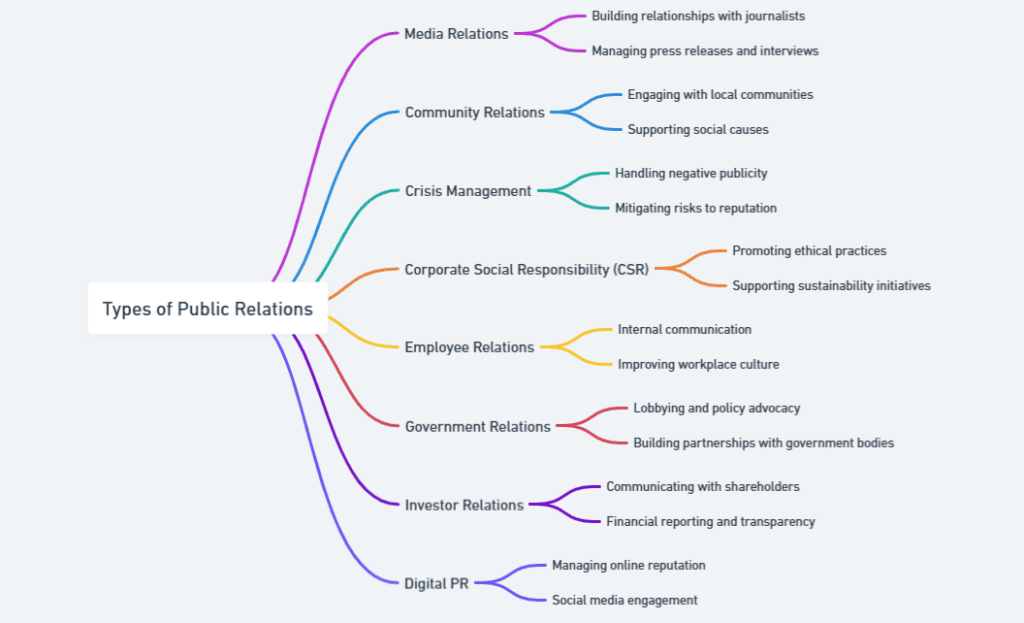
Types of Public Relations
Public Relations/Public Affairs is a broad discipline incorporating many specialized functions designed to serve the needs of various stakeholders and organizational goals. All these contribute to a coordinating strategy that can synchronize with an organization’s broader communication goals.
Media Relations
Media relations is a cornerstone of PR that involves managing an organization’s interactions with journalists, reporters, and media outlets.
- Key Activities: Distributing press releases, arranging interviews, organizing press conferences, and responding to media inquiries.
- Objective: Generate positive news coverage, manage narratives, and ensure accurate representation in the media.
- Example: A tech company announcing a product launch through exclusive media coverage in technology blogs and mainstream newspapers.
Community Relations
This type of PR focuses on building long-term relationships with the communities in which an organization operates. Its goal is to show corporate social responsibility and work positively for society.
- Key Activities: Sponsoring local events, participating in community development programs, and engaging with non-profit organizations.
- Objective: Build goodwill and strengthen the company’s presence within local communities.
- Example: A retail chain funds scholarships for underprivileged students in areas where its stores are located.
Crisis Communication
Crisis communication involves handling unexpected events or controversies that could harm an organization’s reputation.
- Key Activities: Preparing contingency plans, addressing rumors or misinformation, and issuing timely crisis updates.
- Objective: Minimize reputational damage and reassure stakeholders.
- Example: A food manufacturer issuing a public apology and recalling products following reports of contamination.
Employee Relations
Employee relations is an important aspect of PR that refers to organizational internal communication. It keeps employees informed, engaged, and in step with the mission and value of the organization.
- Key Activities: Conducting town halls, publishing newsletters, and organizing team-building initiatives.
- Objective: Build morale and foster a strong organizational culture.
- Example: A company launching an internal campaign to celebrate employee achievements and promote workplace diversity.
Financial Relations
Financial relations target investors, shareholders, and financial analysts. This type of PR is crucial for maintaining trust and transparency regarding a company’s financial health.
- Key Activities: Publishing annual reports, conducting investor meetings, and issuing financial press releases.
- Objective: Build investor confidence and encourage long-term investment.
- Example: A startup sharing its quarterly growth metrics and projections to attract venture capital funding.
Government Relations
Also known as lobbying, government relations involve interacting with regulatory bodies and policymakers to influence decisions that align with organizational objectives.
- Key Activities: Policy advocacy, submitting regulatory proposals, and engaging in public policy discussions.
- Objective: Shape favorable policies and maintain compliance with regulations.
- Example: An energy company lobbying for incentives to adopt renewable energy projects.
Primary Role of Public Relations
The primary role of public relations is to build, maintain, and protect an organization’s reputation while ensuring transparent and effective communication with its stakeholders. PR serves as the glue that connects an organization to its audience, fostering trust, loyalty, and mutual respect.
Core Functions of Public Relations
- Reputation Management: A strong reputation is an intangible asset that directly influences an organization’s success. PR helps manage perceptions by consistently communicating values, achievements, and commitments.
- Stakeholder Engagement: PR facilitates meaningful dialogue between an organization and its audiences, ensuring that concerns are addressed and trust is nurtured.
- Crisis Mitigation: PR professionals play a pivotal role in managing crises by communicating swiftly and effectively to mitigate damage.
- Brand Positioning: PR ensures that the organization’s brand identity aligns with its values and resonates with its target audience.
Why Public Relations Matters
In today’s interconnected world, public perception can make or break an organization. PR addresses immediate concerns and lays the groundwork for long-term success by aligning communication strategies with organizational goals.
Public Relations vs. Marketing
Public relations and marketing often overlap, but they serve distinct purposes and utilize different approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for effectively integrating PR into a broader communication strategy.
| Aspect | Public Relations | Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Build trust and manage reputation | Drive sales and consumer action |
| Audience | Stakeholders (internal and external) | Target consumers and buyers |
| Strategy | Long-term relationship building | Short-term revenue generation |
Integrated Strategies
Successful organizations often blend PR and marketing to achieve their objectives. For example, a PR campaign might highlight a company’s philanthropic initiatives, while a marketing campaign leverages this goodwill to boost product sales.
Public Relations vs. Advertising
Public relations and advertising are complementary tools in the communication toolbox. While advertising focuses on paid media placements, PR relies on earned media and organic coverage.
| Aspect | Public Relations | Advertising |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Typically cost-effective; relies on earned media | Paid placements, often expensive |
| Credibility | Builds trust through third-party endorsements | Perceived as promotional |
| Focus | Reputation and relationship management | Immediate brand awareness |
Real-World Example
A non-profit organization may use PR to secure a news article about its work in disaster relief, while simultaneously running advertisements to solicit donations.
Public Relations vs. Communications
Public relations is a subset of communications, which is a broader discipline encompassing various forms of interaction.
| Aspect | Public Relations | Communications |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on reputation and stakeholder relations | Includes PR, internal communication, and advertising |
| Methods | Press releases, crisis management, and campaigns | Emails, memos, advertisements, and more |
Working in Public Relations
Public relations is a dynamic and rewarding career path that requires creativity, strategic thinking, and strong interpersonal skills.
Skills Required
- Writing Proficiency: Exceptional ability to craft compelling narratives.
- Media Expertise: In-depth understanding of media landscapes and news cycles.
- Problem-Solving: Ability to manage crises and adapt to evolving challenges.
- Relationship-Building: Establishing trust with stakeholders and the media.
Career Opportunities
- PR Specialist: Manages communication strategies and campaigns.
- Crisis Manager: Handles reputation risks and crisis communication.
- Corporate Communications Director: Oversees all PR and internal communication efforts.
Concept of Public Relations FAQs
What is the primary focus of public relations?
The primary focus is to build and sustain a positive reputation for an organization while fostering trust through effective communication.
How does PR differ from marketing?
PR focuses on reputation and stakeholder engagement, while marketing aims to drive sales and promote products.
What are the core functions of PR?
Core functions include reputation management, stakeholder engagement, and crisis communication.
Why is PR essential for businesses?
PR builds credibility, fosters relationships, and ensures long-term trust, which is vital for sustainable success.
How does PR contribute to crisis management?
PR addresses crises swiftly and transparently to minimize reputational damage and rebuild trust with stakeholders.



