Starting a business in India can be exciting, but one of the first and most important decisions you’ll need to make is choosing the right type of business structure. The two most popular forms for small businesses are sole proprietorship and partnership. Each comes with its features, benefits, legal formalities, and limitations. Understanding the difference between sole proprietorship and partnership can help you select the right path based on your business goals, investment capacity, and the number of people involved. A sole proprietorship is a business that is owned and managed by a single person. It is simple to start, requires minimal compliance, and the owner has full control over all decisions and profits. On the other hand, a partnership firm is owned by two or more individuals who share responsibilities, investments, and profits according to an agreed partnership deed. While a partnership allows for shared risk and decision-making, it also requires more planning, legal documentation, and mutual trust. Choosing between the two depends on many factors, such as the nature of your business, scale of operations, capital availability, and your willingness to share control. This article will clearly explain the major differences to help you decide what’s best for your business journey.
What is Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a business structure owned and operated by one individual. This structure is one of the simplest and most common forms of business ownership, requiring minimal formalities to set up. The owner has full control over business decisions, enjoys all profits, and is responsible for all liabilities. Due to its simplicity, a sole proprietorship is ideal for small businesses, freelancers, and independent contractors looking for autonomy in operations.
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Independence: The owner usually has complete authority over business decisions, allowing for swift and flexible management.
- Starting Costs are Low: Startup costs are marginal because registration and regulatory constraints bare much.
- First Income: The profits will go to the entrepreneurs only without needing to divide them, making the motivation and reward even greater.
- There is Privacy: There is no need to disclose finances and operations to the public, preserving privacy.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Unlimited Liability: This means that any owner could be personally responsible for any debt incurred, posing a high threat to personal assets should business failure occur.
- Limited Access to Capital: Raising funds is a major challenge since external investors may not be excited about donating money to a single-owner business.
- Limited Continuity: At approximately times of retirement, incapacitation or death of the owner, the business is typically dissolved.
- Workload and Responsibility: Single owners take on the entire workload of making decisions, resulting in prolonged working hours and high levels of stress.
A sole proprietorship provides a streamlined approach to business ownership, offering simplicity and control but with limitations in liability and continuity.
What is Partnership?
A partnership is an enterprise where two or more individuals have joint ownership and control of a business. Partnerships merge the resources, skills, and capital of various partners to improve the ability of the business to expand and thrive. Partnerships are established through an agreement that describes the roles of partners, profit margins, and management responsibilities. Partnerships exist in the form of general partnerships and limited partnerships, depending on the degree of participation and liability.
Advantages of Partnership
- Resource Pooling: Alliances facilitate the pooling of financial resources, talent, and experience, considerably raising the chances of successful business operations.
- Shared Responsibility: Work and administration responsibilities are shared, lessening the individual burden on the partner.
- Expanded Access to Capital: Partnerships can usually raise capital and attract investors more effectively than sole proprietorships.
- Flexibility: Partnerships are flexible in the role aspect, as partners can concentrate in areas where they are proficient, which improves efficiency.
Disadvantages of Partnership
- Shared Liability: This usually means that partners are personally liable for their respective business debts in general partnerships, which raises financial risks.
- Conflict Potential: Differing perspectives between partners on the decision-making process, as well as profit sharing, may lead to internal conflicts, which can negatively affect the operations of the business.
- Profit Sharing: Partners would also have to share profits, which means that individual shares of profit can be less than that in a sole proprietorship.
- Complex Dissolution: Dissolving a partnership can be legally complex, requiring formal agreements and settlements.
A partnership provides an opportunity to combine skills and resources, making it suitable for businesses that require a collaborative approach to achieve growth.
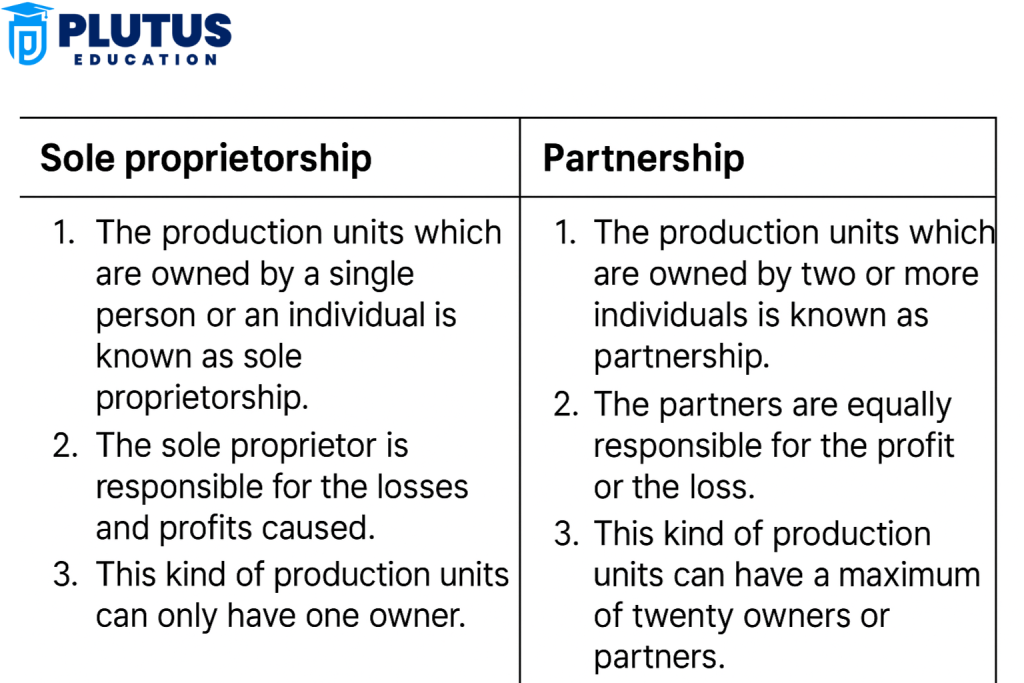
Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Partnership
The distinctions made by these foundations between sole proprietorship and partnership constitute unique features that affect liability, management, and sharing of profits. While a sole proprietorship provides full control and profit entitlement, a partnership distributes these elements among multiple owners.
| Basis of Difference | Sole Proprietorship | Partnership |
| Ownership | Owned by a single individual | Owned by two or more individuals |
| Formation | Easy to form, minimal legal formalities | Requires a partnership agreement or deed |
| Legal Status | Not a separate legal entity from the owner | Not a separate legal entity from partners |
| Capital Contribution | Capital is contributed by the sole owner | Capital is contributed by all partners |
| Decision Making | Quick decisions by the sole owner | Joint decision-making, often needs consultation |
| Profit Sharing | Entire profit belongs to the owner | Profits are shared as per the agreed ratio |
| Risk and Liability | Unlimited liability for the owner | Unlimited liability shared by all partners |
| Continuity | Ends with owner’s death or incapacity | May continue as per agreement even if a partner exits |
| Compliance | Less regulatory compliance | Requires registration and partnership compliance |
| Suitable For | Small-scale businesses, individual operations | Medium-scale businesses with shared responsibilities |
Difference Between Sole Proprietorship and Partnership FAQs
1. What is the main difference between sole proprietorship and partnership?
The main difference is in ownership. One person owns a sole proprietorship, while a partnership involves two or more people sharing ownership, responsibilities, and profits.
2. Which is easier to start: sole proprietorship or partnership?
A sole proprietorship is much easier and quicker to start. It requires minimal documentation and no formal registration, while a partnership needs a partnership deed and may require registration.
3. Is liability different in sole proprietorship and partnership?
Yes. In both structures, liability is unlimited, but in a partnership, all partners share the liability jointly and severally. In a sole proprietorship, only the single owner bears the full risk.
4. Who controls the business in each type of firm?
In a sole proprietorship, the single owner has full control over all decisions. In a partnership, decisions are made jointly or as per the terms mentioned in the partnership deed.
5. Can a sole proprietorship be converted into a partnership firm?
Yes. A sole proprietorship can be converted into a partnership by adding partners and drafting a legal partnership agreement. This helps expand the business and share responsibilities.
6. Which business form is better for small-scale operations?
A sole proprietorship is ideal for small-scale or home-based businesses due to its simple structure, fewer regulations, and low startup cost.