One commonly confused term is the difference between a stock market and a stock exchange: mostly because the terms are rather commonly used interchangeably. They are two entirely different facets of trading that represent integral parts of the financial ecosystem. A stock market is a very broad term referring to the whole system where all financial instruments such as shares, bonds, and derivatives can be bought or sold. Stocks, however, have a specific entity or platform within the stock market, in which these transactions take place with regulated conditions. A distinction between the two is critical for investors, traders, and other financial enthusiasts.
What is Stock Market?
Stock market can be defined as the overall system whereby financial instruments such as shares, Debentures, and derivatives are bought, sold, and traded. It provides a marketplace for companies and investors to relate to each other in order to increase capital movement and wealth creation.
Key Features of the Stock Market
- Broad Scope: The stock market encompasses all trading activities in financial instruments, whether they happen on an organized stock exchange or through over-the-counter platforms.
- Two segments: The primary market, is the stage where companies issue fresh equity shares to the public by raising capital through Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). Secondary Market, in this segment, existing shares are sold between investors.
- Global Network: The stock market operates on global and regional platforms because it links together all investors worldwide.
- Diverse Instruments: Besides stocks, the market allows for trading mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), bonds, and derivatives.
Functions of the Stock Market
- Capital Raising: Companies can raise capital by using the stock market, and issuing shares to the public.
- Liquidity: The shares can be bought or sold quickly, thus giving a liquid marketplace for the financial assets.
- Price Discovery: The stock market determines the fair price of shares as possible by the stocks and demand forces.
- Wealth creation: It provides an avenue through which the wealth of individuals and institutions can be expanded through investments.
What is Stock Exchange?
The stock exchange is the controlled marketplace for trading shares, Debentures, and derivatives. It’s a central place for buying and selling financial instruments with complete transparency and fairness in the transaction process.
Key Features of a Stock Exchange
- Defined Platform: The stock exchanges can either be physical, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), or electronic, such as NASDAQ.
- Standardization and Regulation: All the securities listed are traded under standardized rules to ensure order and accountability.
- Authorized Membership: Only licensed brokers and dealers can trade on a stock exchange directly.
- Transparency and Pricing: Exchanges provide real-time pricing information and ensure all trades are executed transparently.
Functions of a Stock Exchange
- Facilitating Trade: It offers a systematic outlet for buyers and sellers to trade securities.
- Price Discovery: This displays the prevailing market price of securities via real-time data.
- Investor Protection: It enacts laws that safeguard from fraudulent and unfair practices.
- Economic Growth: Proper resource distribution can be facilitated by the linking of investors to companies.
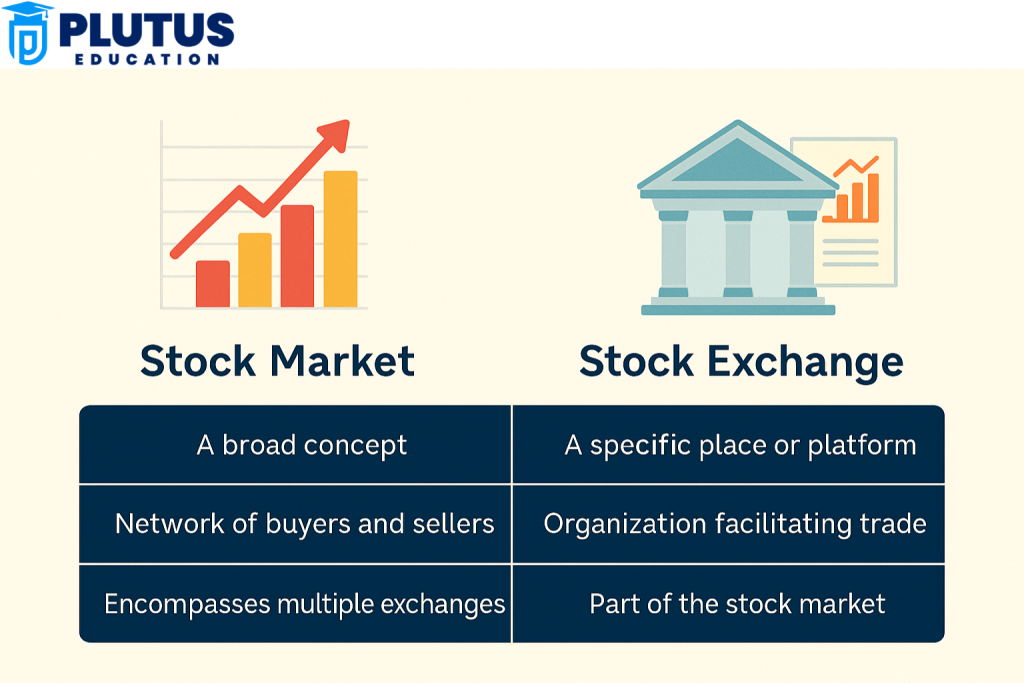
Difference Between Stock Market & Stock Exchange
The difference between stock market and stock exchange lies in their scope, functionality, and purpose. Here are the key differences in detail:
Scope & Definition
- Stock Market: All dealings, whether on the stock exchange or over the counter, fall under the term. It is a very general term covering primary and secondary markets and all participants within it: investors, brokers, etc.
- Stock Exchange: A stock exchange is a part of the stock market, which particularly lists and trades securities; in other words, it is a regulated body providing a safe environment for safe transactions.
Functionality & Operations
- Stock Market: A stock market is a framework that frames an entire ecosystem of financial trading. It connects the investors with companies and facilitates direct investments and secondary trading through such a framework. Markets also incorporate mechanisms such as over-the-counter trading, which refers to the trade of securities directly between parties without a central platform.
- Stock Exchange: The stock exchange offers a single platform for trading listed securities under a control mechanism. It functions based on strict rules in all aspects of the system to guarantee transparency, efficiency, and fairness in transactions. Stock exchanges are not the stock market since they can only trade standardized securities that have been listed.
Participants
- Stock Market: The stock market includes a wide range of participants, such as individual investors, institutional investors, brokers, companies, and regulatory bodies. It provides opportunities for direct investments in IPOs through the primary market and facilitates secondary trading for liquidity.
- Stock Exchange: It limits direct participation to authorized brokers and dealers. Individual investors must operate through these intermediaries to access the exchange. This controlled access ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Regulatory Framework
- Stock Market: It is a truism that as a whole, the stock market operates under broad financial regulation, although it includes unregulated or less regulated components, such as OTC trading. Diversity can make the stock market more accessible but risky and inefficient.
- Stock Exchange: Even the stock exchanges happen to be regulated entities with severe compliance with financial laws. All these trades in this platform are well supervised to maintain legal and ethical standards.
Purpose
- Stock Market: The stock market’s primary goal is to facilitate capital flow between companies and investors, supporting economic growth and wealth creation. It includes multiple avenues for trading, making it versatile and comprehensive.
- Stock Exchange: Stock exchanges, however, focus on providing a reliable and regulated environment for trading. Their primary purpose is to ensure transparency, efficiency, and fairness in transactions.
| Point of Difference | Stock Market | Stock Exchange |
| Meaning | A stock market is a broad term for the place where people buy and sell shares. | A stock exchange is a specific platform where buying and selling actually happens. |
| Scope | It includes all stock exchanges and other trading activities. | It is part of the stock market — like NSE or BSE in India. |
| Function | Allows investors to trade in shares, bonds, mutual funds, etc. | Provides the system to list companies and match buyers and sellers of stocks. |
| Example | Indian stock market includes NSE, BSE, and all share trading platforms. | NSE (National Stock Exchange), BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) are stock exchanges. |
| Control | Controlled by overall market forces and SEBI regulations. | Controlled by their own rules and SEBI guidelines. |
| Traded Items | Shares, mutual funds, bonds, derivatives, commodities, etc. | Mainly company shares and listed securities. |
| Type | Broader system where many exchanges operate. | One of the units that make up the stock market. |
Stock Market vs Stock Exchange FAQs
How is a stock market different from a stock exchange?
A stock market represents an entire process of buying and selling financial instruments; on the other hand, a stock exchange represents a particular venue where listed securities are traded.
Are securities allowed to be traded outside of a stock exchange?
Yes, securities can also be traded in over-the-counter (OTC) markets, which is an all-inclusive part of the stock market.
What is a stock exchange?
Examples: National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
Contribution of the stock market towards economic growth?
The stock market offers a route to capital formation, increases liquidity, and helps wealth creation; therefore, the general growth of the economy is impacted.
What is the difference between the primary and secondary markets in the stock exchange?
Issuance of new shares is dealt with by the primary market, while the secondary market deals with the trading of existing shares among investors.


