Commercial or mercantile laws are laws that govern trade and business activities. This law consists of statutes about contracts for business, sales of goods or property, defining categories of partnership, rules of setting up companies, and other related topics. The foundation that becomes the bottom line of that law states that every economic activity must take place in a legally, ethically, and statistically prescribed manner. Such an enactment advocates for less fraud, settling the parties’ differences, and establishing confidence and trust among partners through legal recourse and protection. Understanding mercantile law has become essential in a global economy like ours, where trade is no longer geographically confined. It must set standard rules for all international trade to follow easily. Startup founders, corporate legal advisors, or any other stakeholder in the business ecosystem should have sufficient knowledge about the scope and elements of mercantile law to allow for well-informed decision-making and compliance.
What is Mercantile Law?
Mercantile law concerns the rules governing individuals trading with one another and businesses. It ensures trade practices that are transparent, fair, and accountable. Forming a contract, trading goods, or dissolving a company are all aspects of mercantile law within which these events are framed.
Meaning of Mercantile Law in Simple Terms
Mercantile law defines different aspects of trade and commerce. It applies to business contracts, selling goods and services, and dealing with partnerships. This law governs trade by permitting legal limitations within which parties should operate in the performance of their obligations in transactions. Any activity related to mercantile principles is worth mentioning, from the mere signing of a business deal to a transaction involving promissory notes.
Purpose and Importance in Business
Equally, the law has been enacted to protect the interests of all individuals within a trading environment by ensuring fairness in all trading activities. It provides the ethical conduct that companies adopt as a guide for consumers to safeguard their rights and mechanisms for settling disputes. It further gives businesses a framework to grow and boosts investors’ confidence by reducing legal uncertainties in commercial dealings.
Areas Governed by Mercantile Law
Mercantile laws govern contracts, sales, partnerships, negotiable instruments, and corporate governance. Moreover, legal mechanisms related to international trade are included under this term, ensuring that all cross-border transactions are consistent and safe.
Business Law Versus Mercantile Law
Business law is the broader concept that covers all the laws dealing with business, for example, tax and labour laws, whereas mercantile law deals only with commercial transaction laws. Under business law, it is essential to study mercantile law, a critical subset that deals with the core of trade and contractual dealings.
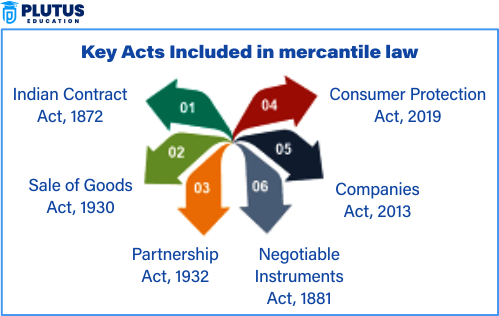
Sources of Mercantile Law
The mercantile law framework is built on statutory provisions, judicial decisions, conflicting trade customs, and international conventions. These sources give rigidity and flexibility in enforcement according to the changes in business practices that are being developed.
Statutory Law and Legislation
Statute law is the primary source of mercantile law. It comprises all acts and statutes made by the legislative organs. The most relevant laws governing business transactions in India are the
Indian Contract Act of 1872, the Sale of Goods Act of 1930, and the Companies Act of 2013. They are structured, codified documents that standardize trade practices. Common Law and
- Judicial Decisions Statutes that interpret statutory provisions are generally determined by court decisions, especially at higher judicial ranks. This creates essential precedents in law that lend consistency to the application of rules.
- In terms of changing society and business practices, the common law evolves, thus making the law adaptable.
- Generally Accepted Customs and Trade Usages. These customs refer to long business practices that are accepted and followed; referees can rely upon these, as there is no written law or precedent.
- Recognised trade usages offer pragmatic solutions to disputes and are hence integral for industries with certain practices, such as textiles or shipping.
- International Treaties and Conventions: Trade rules are harmonized between nations through these treaties and conventions.
- The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) significantly reduces business legal risks, thus instilling confidence in international market operations.
Scope of Mercantile Law
This is of extensive scope and breadth, covering various sectors and types of transactions. From simple business agreements to the most complex international contract undertakings, all are under mercantile law and are aligned with legal backup.
Contract Law and Its Foundation in Commerce
Contract law forms the foundation of mercantile law, as it deals with agreements made between two or more parties in a relationship. It ensures that mutual consent forms all contracts with a legal purpose and consideration. Thus, this area is significant for all businesses, from freelancers to corporations.
Sale of Goods and Consumer Protection
This field deals with trading, wherein goods are exchanged for money. It stipulates the rights of buyers and sellers, warranties, terms of sale, and modes of remedies against breaches. It protects consumers from deceit, defective products, and unfair practices.
Partnership Legislation and Business Collaborations
Partnership law governs the relationship between two or more people running a business. It defines profit-sharing, responsibilities, liabilities, and dispute-resolution mechanisms. A conflict avoidance principle is laid down in a well-drafted partnership agreement based on legal principles.
Company Law and Corporate Governance
The law related to companies controls all phases of the lifecycle of companies, operations, and finally, dissolution. That legislation ensures companies are following standard corporate norms, prescribed rights and obligations towards shareholders, and transparency and accountability in operations. It is indeed the central law for corporate governance.
Negotiable instruments
Negotiable instruments, such as checks, promissory notes, and bills of exchange, are valuable in commercial terms. The laws of commerce specify the making, endorsement, and payment obligations associated with negotiable instrument transactions to enhance their credibility.
Elements of Mercantile Law
Legal foundations of business. Elements provide that all forms of trade are conducted efficiently, safely, and fairly.
Maximum Legal Setting and Standardisation
Mercantile law creates a statutory setting that shall permeate all commercial activity. It determines how firms make contracts, deliver goods, and settle disputes. All of them will work together to minimise risk and establish legal liability.
Standardised Commercial Procedures
Standardisation provides certainty for smooth business conduct by regulating all business activities from contract negotiation to payment. The procedure eliminates uncertainties and encourages the parties to act according to common usage so that contracts can be aided in their performance.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
All these official methods of settling disputes, litigation, arbitration, and mediation have been instituted in mercantile law as methods of settling conflicts sooner and more equitably, so business operations may continue unaffected.
Regulatory Compliance Coupled With Ethics
Particular compliance includes government criteria concerning tax provisions, labour laws, and environmental legislation. Mercantile law is key in enforcing these business requirements for ethical conduct and transparency.
Facilitating Both Domestic And International Trade
This is also open to businesses investing internationally by making exceptions from unfair trade laws and motivating such investment. It diminishes the legal uncertainties governing international trade, thus making it sustainable.
Mercantile Law FAQS
What is the scope of Mercantile Law?
Mercantile law applies to all commercial transactions and sectors, such as contracts, sales, partnerships, and company operations. It allows businesses to ensure that they operate legally and ethically.
What are the sources of Mercantile Law?
The sources include statutory law, judicial decisions, trade customs, and international treaties. They provide a measure of legal enforcement while allowing flexibility for changing business environments.
Why is Mercantile Law important for businesses?
It facilitates fair trading, protects Stakeholders, assures compliance, and diminishes the threat of disputes. For legal clarity and operational security assurance, businesses need mercantile law to walk with them.
What does Mercantile Law cover?
It covers contracts, sales of goods, company law, partnership regulations, and domestic and international negotiable instruments.
How does Mercantile Law assist International Trade?
By aligning itself with treaties and conventions, it helps standardise rules on opposite sides, reducing legal friction and ensuring an uninterrupted flow of global transactions.


