Modern business accounting principles assure accuracy, transparency, and compliance—all of which rely on a well-maintained general ledger. The general ledger is more than a data storage; this crucial financial instrument assists decision-making, supporting the auditing function and internal controls. From surveying company assets and liabilities to monitoring income and expenses, the general ledger provides a panoramic view of the company’s financial health. Its functionality is something that business owners, accountants, and commerce students must know about.
What Is a General Ledger?
A general ledger (GL) is the principal book of account where all transactions affecting the business’s finances are posted with the intention of classification and reporting. The accounts fall into five categories: assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Each account is responsible for tracking a specific type of transaction, such as rent paid, salaries, sales revenue, or amounts owed on loans.
The general ledger is the foundation of every financial accounting system, serving as a complete record of all monetary transactions within a business. It categorizes and consolidates all the data needed to prepare vital financial statements like the balance sheet and income statement. The general ledger follows the principles of double-entry accounting, meaning every transaction affects at least two accounts—one is debited, and the other is credited. This ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains balanced. Accurate reporting and auditing of a business’s financial state would be nearly impossible without a general ledger.
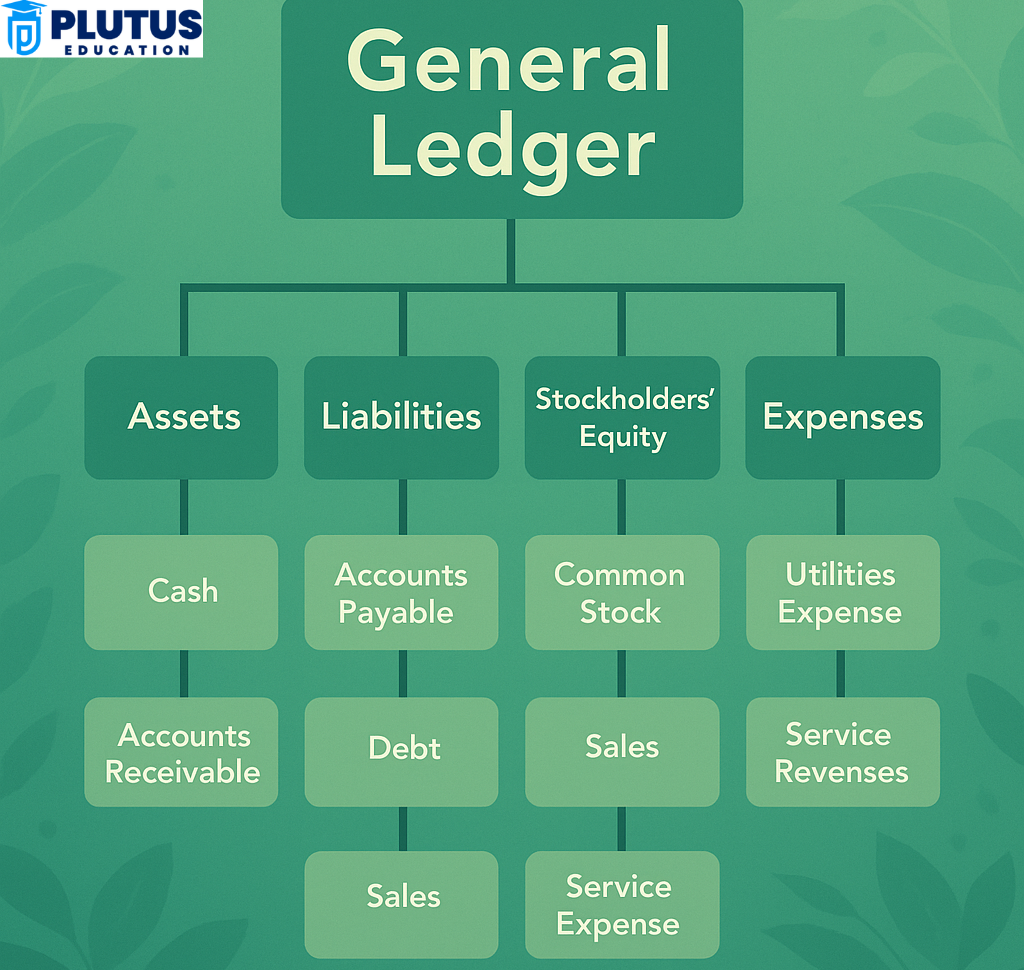
Accounts and Classifications
Positions of account types are the ledger with multiple other types of accounts for categorizing business activities. Common accounts include cash accounts, accounts payable, revenue from sales, utility expenses, and shareholder equity. These account types vary from the reporting requirements. For example, asset accounts indicate what the company owns, and liabilities indicate what it owes. Separate from clarity and accuracy, reporting occurs during audits and for financial analysis.
Debits and Credits
All transactions are recorded in the general ledger using the debit-credit mechanism of double-entry accounting. Thus, a debit in one account must be offset by a credit in another, maintaining the balance. This reduced the margin of error and fraud since any imbalance indicates immediately that something has gone wrong. It serves as the foundation for financial integrity and audit readiness.
Journal Entries and Posting
Every transaction is documented in journals and is transferred into the ledger. An entry in the journal consists of the date and reference of the transaction, the debit amount, and the credit amount. With an entry in the ledger, the business organizes a well-categorizable view of all its financial data so that tracking and reconciliation can comfortably happen across departments.
Trial Balance Take-in
The updated ledger is converted into a trial balance for the company’s use. The trial balance ensures that total debits equal total credits, a preliminary check before a financial statement can be prepared. Such procedures help accountants find and rectify mistakes at the earliest possible stage. It also lays the groundwork for a smooth financial reporting process that will be accurate at the end of the month or year.
Source of Financial Statements
The general ledger feeds data into key financial reports like income, balance, and cash flow statements. These statements are critical for stakeholders in assessing financial health and performance. With accurate ledger entries, businesses can produce such statements quickly and confidently, which gives them trust with investors and efficiency in operations.
How a General Ledger Works?
The general ledger is where all a company’s financial records are kept. It consists of collecting and summarizing the transactions recorded in the journals under specific accounts to bring all the information into a particular area of accounting.
Day-to-day business transactions are recorded in this ledger, enabling the month-end and year-end closing of accounts. Such an organization aids in tracing every dollar earned or spent with that related operating activity.
- Recording Transactions in Journals
Every transaction starts with a journal entry containing essential information such as date, description, amount, and affected accounts. These entries will be updated and posted to the correct ledger accounts. For example, a $1,000 inventory purchase on credit is recorded as:
- Debit: Inventory (Asset) $1,000
- Credit: Accounts Payable (Liability) $1,000
With such dual entries, clarity and accountability shine throughout financial transactions.
- Posting to Ledger Accounts
Once transactions are recorded, they are posted into the relevant accounts of the general ledger. Each account will indicate a running balance, giving an up-to-date impression of activity within the company from the beginner’s view. The object of posting is to categorize the financial data; thus, compiling reports and finding inconsistencies will be more comfortable. These detailed records become crucial during audits or financial reviews.
- Trial Balance and Balancing
After posting all transactions to the accounts, a trial balance is drawn. Meaning total debits are equal to total credits and thus disclose the actual balance of the books. In the case of a difference, the accountants can go back to the ledger entries and identify and correct the errors. Therefore, a trial balance is necessary for an accurate production of financial statements.
- Audit and Compliance Readiness
Because the general ledger is the document that contains every financial event, it is also the most critical legal document during audit instances. Auditors usually trace some random samples of transactions back to the original journal entry and ledger balances. The perfectly maintained general ledgers made the audit smoother and showed the company’s compliance with the standards and regulations in accounting.
- Use in Budgeting and Forecasting
The current historical data from the general ledger is the baseline for projects leading into the future. Today, most businesses analyze past revenue and expenditure trends to create realistic budgets. Good forecasting on reliable ledger data translates into good financial planning and resource allocation, critical to maintaining profitability and growth.
How General Ledger Supports Double-Entry Accounting?
The true working heart of double-entry accounting is the general ledger. Every transaction generally affects at least two ledger accounts in this system of accounting; hence, no loss, and everyone’s mutual free-for-all. If organizations did not operate this way, their books could become imbalanced, thus making the hunt for errors, if not fraudulent activity, much harder. The GL supports this by keeping identical debit and credit records.
Debits versus Credits Explained
In accounting language, debits increase asset and expense accounts while reducing liabilities and equity. Credits do the opposite. Every transaction must include one debit and one credit to maintain the balance. This example creates balance in that the financial records remain accurate and reliable.
Maintains the Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Equity, which is the basis of all financial statements. Every entry in a general ledger is a must for it to uphold this formula. This balancing system places the business in an ideal position to detect errors as they happen so that a clean record can remain for audits.
Application in Ledger Structure
The general ledger sorts any transaction into a relevant account. This classification allows accountants to prepare a detailed revenue, assets, and liabilities report. These detailed sections are essential for analyzing profitability, identifying waste, and keeping track of spending patterns over time.
Automation and Software Integration
Most modern accounting systems post journal entries to the general ledger automatically using ERP or financial software, thus reducing the chances of human error and the time taken.
The automated ledger gives real-time visibility of financials to facilitate the decision-making process with data-driven trackability, flexibility, and fluidity in organizational progress.
Loss Detection and Correction
Error detection becomes an internal mechanism of keeping one’s accounts, instead of doing a manual count simultaneously. This built-in validation protects businesses against undetected financial misstatements and fraud.
What Does a General Ledger Tell You?
Beyond just numbers, it tells a business’s overall financial story. It narrates how a company earns, spends, borrows, and grows. When the company has managed to do this well, it offers rich financial health, profitability, and future perspectives. It covers everything from daily decisions to long-term strategy; the general ledger is the foundation of financial literacy and transparency in every organization.
Understanding Financial Position
General ledger tracking provides knowledge of asset, liability, and owner equity values, primarily used to construct a balance sheet. Indicates where a company is in terms of financial footing: strong financing position or over-leveraged. Organizations utilize that data to analyze liquidity, solvency, and return on equity—the three most important indicators from which stakeholder arguments spring.
Measure Profitability
Income statements originate from GL revenue and expenditure accounts. This would indicate whether a company is making profits or losses. It enables better criterion budgeting and optimization of resources, which will emerge from identifying the most profitable activities driving the most significant costs.
Cash Tracking
Businesses can review cash transactions by reviewing their cash inflows and outflows. This is not classified as a cash flow statement, but gives everything necessary to prepare one. Companies can anticipate liquidity shortages and plan short-term funding needs by understanding cash flow.
Trends and Deviations Recognition
An example of using this general ledger in a business organization is comparing monthly, quarterly, or yearly amounts to determine financial trends. It also reflects anomalies, such as unexpected spikes in expenses that may lead to investigations and timely corrective actions.
Stakeholder Communication
Investors, auditors, tax authorities, and managers rely on general ledger data to assess performance and compliance. It increases credibility and trust in the business. A well-maintained GL demonstrates fiscal responsibility and prepares the business for funding rounds, mergers, or regulatory inspections.
What is General Ledger FAQs
What is a general ledger in accounting?
A general ledger is the central accounting record that summarizes a business’s financial transactions, categorized under accounts like assets, liabilities, income, and expenses.
How does a general ledger function in business accounting?
Consolidating journal entries into categorized accounts using double-entry accounting. This is what balances the ledger in business and, therefore, guarantees the accuracy of financial statements.
What is the difference between a general ledger and a journal?
A journal is where transactions are first recorded in chronological order. These entries are then posted to the general ledger, which categorizes them by account type.
Why is a general ledger important in financial reporting?
It forms the basis for preparing balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements concerning accuracy, transparency, and compliance with the rules and regulations.
What role does the general ledger play in double-entry accounting?
It assumes a double-entry system where every transaction affects two accounts, ensuring efficiency in keeping the books accurate and error detection.


